Summary
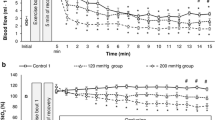
The present study was undertaken to compare the effects of maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise on maximum oxygen uptake and blood flow in the lower extremity. Mean maximum oxygen uptake in maximal treadmill exercise was higher than that in bicycle exercise (p<0.001). Mean values and standard errors of blood flow measured immediately after maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise in the thigh were 39.1±4.0 and 44.2±2.8 ml/100 ml·min, the difference not being significant. However, a significant difference in blood flow in the calf measured immediately after both types of exercise was observed (p< 0.001). Blood flow in the thigh immediately after bicycle exercise was significantly higher than that in the calf (p<0.001), whereas the difference between thigh and calf in treadmill exercise was small and statistically not significant. Leg blood flow, the average value of blood flow of the thigh and calf added together, was used as an index of blood flow in the lower extremity. It was found that the leg blood flow was significantly higher on the treadmill than with bicycle exercise (p<0.05). From these results, it is suggested that the lower maximum oxygen uptake observed during bicycle exercise as compared with treadmill exercise seems to be due to a lower blood flow in the lower limb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonde-Petersen, F., Henriksson, J., Lundin, B.: Blood flow in thigh muscle during bicycle exercise at varying work rates. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 34, 191–197 (1975)
Chase, G. A., Grave, C., Rowell, L. B.: Independence of change in functional and performance capacities attending prolonged bed rest. Aerospace Med. 37, 1232–1238 (1966)
Clausen, J. P., Lassen, N. A.: Muscle blood flow during exercise in normal man studied by the 133 xenon clearance method. Cardiosvasc. Res. 25, 245–254 (1971)
Cobb, L. A., Smith, P. H., Lwai, S., Short, F. A.: External iliac vein flow; its response to exercise and relation to lactate production. J. Appl. Physiol. 26, 606–610 (1969)
Elsner, R. W., Carlson, L. D.: Postexercise hyperemia in trained and untrained subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 17, 436–440 (1962)
Faulkner, J. A., Roberts, D. E., Elke, R. L., Conway, J.: Cardiovascular responses to submaximum and maximum effort cycling and running. J. Appl. Physiol. 30, 457–461 (1971)
Grimby, G., HÄgendal, E., Saltin, B.: Local xenon 133 clearance from the quadriceps muscle during exercise in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 22, 305–310 (1967)
Hermansen, L., Saltin, B.: Oxygen uptake during maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 26, 31–37 (1969)
Hermansen, L., Ekblom, B., Saltin, B.: Cardiac output during submaximal and maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 29, 82–86 (1970)
Humphreys, P. W., Lind, A. R.: The blood flow through active and inactive muscles of the forearm during sustained handgrip contractions. J. Physiol. 166, 120–135 (1963)
Kamon, E., Pandolf, K. B.: Maximal aerobic power during laddermill climbing, uphill running and cycling. J. Appl. Physiol. 32, 467–473 (1972)
Matsui, H., Kitamura, K., Miyamura, M.: Comparison of calf blood flow measured by the two strain-gauge plethysmography. J. Physiol. Soc. Jap. 40, 137–139 (1978)
Miyamura, M., Honda, Y.: Oxygen intake and cardiac output during maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 32, 185–188 (1972)
Miyamura, M., Kitamura, K., Yamada, A., Matsui, H.: Cardiorespiratory responses to maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise in trained and untrained subjects. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 18, 25–32 (1978)
Nilsson, B., Ingver, D. H.: Intramuscular pressure and contractill strength related to muscle blood flow in man. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest., Suppl. 93, 31–38 (1967)
Pirnay, F., Marechal, R., Radermecher, R., Petit J. M.: Muscle blood flow during submaximum and maximum exercise on a bicycle ergometer. J. Appl. Physiol. 32, 210–212 (1972)
Reybrouck, T., Heigenhauser, G. F., Faulkner, J. A.: Limitation to maximum oxygen uptake in arm, leg and combined arm-leg ergometry. J. Appl. Physiol. 38, 774–779 (1975)
Taylor, H. L., Buskirk, E., Henschel, A.: Maximal oxygen intake as on objective measure of cardiorespiratory performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 8, 73–80 (1955)
Whitney, R. J.: The measurement of volume change in human limbs. J. Physiol. 121, 1–27 (1953)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsui, H., Kitamura, K. & Miyamura, M. Oxygen uptake and blood flow of the lower limb in maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 40, 57–62 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00420989
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00420989