Abstract
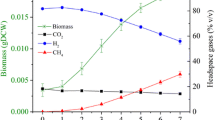
Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum was grown on a mineral salts medium in a fermenter gassed with H2 and CO2, which were the sole carbon and energy sources. Under the conditions used the bacterium grew exponentially. The dependence of the growth rate (μ) on the concentration of H2 and CO2 in the incoming gas and the dependence of the growth yield (\(Y_{CH_4 }\)) on the growth rate were determined at pH 7 (the pH optimum) and 65° C (the temperature optimum).
The curves relating growth rate to the H2 and CO2 concentration were hyperbolic. From reciprocal plots apparent K s values for H2 and CO2 and μmax were obtained: app. \(K_{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}} }\) = 20%; app. \(K_{{\text{CO}}_{\text{2}} }\) = 11%; μ = 0.69 h-1; t δ (max)=1 h.
\(Y_{CH_4 }\) was 1.6 g mol-1 and almost independent of the growth rate, when the rate of methane formation was not limited by the supply of either H2 or CO2. The yield increased to near 3 g mol-1 when H2 or CO2 were limiting. These findings indicate that methane formation and growth are less tightly coupled at high concentrations of H2 or CO2 in the medium than at low concentrations. The physiological significance of these findings is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balch, W. E., Fox, G. E., Magrum, L. J., Woese, C. R., Wolfe, R.: Methanogens: Reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol. Rev. 43, 260–296 (1979)
Balch, W. E., Wolfe, R. S.: New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressurized atmosphere. Appl. Environ Microbiol. 32, 781–791 (1976)
Coultate, T. P., Sundaram, T. K.: Energetics of Bacillus stearothermophilus growth: Molar growth yield and temperature effects on growth efficiency. J. Bacteriol. 121, 55–64 (1975)
Diekert, G. B., Graf, E. G., Thauer, R. K.: Nickel requirement for carbon monoxide dehydrogenase formation in Clostridum pasteurianum. Arch. Microbiol. 122, 117–120 (1979)
Diekert, G., Klee, B., Thauer, R. K.: Nickel, a component of factor F430 from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch. Microbiol. 124, 103–106 (1980)
Downs, A. J., Jones, C. W.: Energy conservation in Bacillus megaterium. Arch. Microbiol. 105, 159–167 (1975)
Fuchs, G., Moll, J., Scherer, P., Thauer, R.: Activity, acceptor specificity and function of hydrogenase in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. In: Hydrogenases: Their catalytic activity, structure and function (H. G. Schlegel, ed.), pp. 83–92. Göttingen: Goltze 1979
Fuchs, G., Stupperich, E.: Evidence for an incomplete reductive carboxylic acid cycle in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch. Microbiol. 118, 121–125 (1978)
Fuchs, G., Stupperich, E., Thauer, R. K.: Acetate assimilation and the synthesis of alanine, aspartate, and glutamate in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch. Microbiol. 117, 61–66 (1978)
Fuchs, G., Thauer, R. K., Ziegler, H., Stichler, W.: Carbon isotope fractionation by Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch. Microbiol. 120, 135–139 (1979)
Hippe, H., Caspari, D., Fiebig, K., Gottschalk, G.: Utilization of trimethylamine on other N-methyl compounds for growth and methane formation by Methanosarcina barkeri. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 494–498 (1979)
Hungate, R. E.: Hydrogen as an intermediate in the rumen fermentation. Arch. Microbiol. 58, 158–164 (1967)
Kuenen, J. G.: Growth yields and “maintenance energy requirement” in Thiobacillus species under energy limitation. Arch. Microbiol. 122, 183–188 (1979)
Mah, R. A., Ward, D. M., Baresi, L., Glass, T. L.: Biogenesis of methane. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 31, 309–341 (1977)
Mainzer, S. E., Hempfling, W. P.: Effects of growth temperature on yield and maintenance during glucose limited continuous culture of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 126, 251–256 (1976)
McInerney, M. J., Bryant, M. P., Pfennig, N.: Anaerobic bacterium that degrades fatty acids in syntrophic association with methanogens. Arch. Microbiol. 122, 129–135 (1979)
Pirt, S. J.: Principles of microbe and cell cultivation. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications 1975
Pirt, S. J.: The maintenance energy of bacteria in growing cultures. Proc. Roy. Soc. London B 163, 224–231 (1965)
Roberton, A. M., Wolfe, R. S.: Adenosine triphosphate pools in Methanobacterium. J. Bacteriol. 102, 43–51 (1970)
Schönheit, P., Moll, J., Thauer, R. K.: Nickel, cobalt and molypdenum requirement for growth of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch. Microbiol. 123, 105–107 (1979)
Stadtman, T. C.: Methane fermentation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 121–142 (1967)
Stephen, H., Stephen, T.: Solubilities of inorganic and organic compounds. Vol. 1. Oxford, London, New York, Paris: Pergamon Press 1963
Stouthamer, A. H., Bettenhaussen, C.: Utilization of energy for growth and maintenance in continuous and batch cultures of microorganisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 301, 53–70 (1973)
Stouthamer, A. H., Bettenhaussen, C. W.: Determination of the efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation in continuous cultures of Aerobacter aerogenes. Arch. Microbiol. 102, 187–192 (1975)
Taylor, G. T., Pirt, S. J.: Nutrition and factors limiting the growth of methanogenic bacterium (Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum). Arch. Microbiol. 113, 17–22 (1977)
Tempest, D. W.: The biochemical significance of microbial growth yields: a reassessment. Trends Biochem. Sciences 3, 180–184 (1978)
Tewes, F. J., Thauer, R. K.: Regulation of ATP-synthesis in Glucose fermenting bacteria involved in interspecies hydrogen transfer. In: Syntrophism and other microbial interactions. Stuttgart: Fischer 1979
Thauer, R. K., Fuchs, G.: Methanogene Bakterien. Naturwissenschaften 66, 89–94 (1979)
Thauer, R. K., Jungermann, K., Decker, K.: Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol. Rev. 41, 100–180 (1977)
Uden, N. van: Kinetics of nutrient-limited growth. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 23, 473–486 (1969)
Weimer, P. J., Zeikus, J. G.: One carbon metabolism in methanogenic bacteria: Cellular characterization and growth of Methanosarcina barkeri. Arch. Microbiol. 119, 175–182 (1978)
Wolfe, R. S.: Microbial biochemistry of methane: a study in contrasts. Part I: Methanogenesis. In: Microbial Biochemistry, Vol. 21 (J. R. Quayle, ed.), pp. 268–300. Baltimore: University Park Press 1979
Wolin, E. A., Wolfe, R. S., Wolin, M. J.: Viologen dye inhibition of methane fermentation by Methanobacilus omelianskii. J. Bacteriol. 87, 993–998 (1964)
Zehnder, A. J. B.: Ecology of methane formation: In: Water pollution microbiology, Vol. 2 (R. Mitchell, ed.), pp. 349–376. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 1978
Zehnder, A., Wuhrmann, K.: Physiology of a Methanobacterium strain AZ. Arch. Microbiol. 111, 199–205 (1977)
Zeikus, J. G.: The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bact. Rev. 41, 514–541 (1977)
Zeikus, J. G., Wolfe, R. S.: Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum sp. n., an anerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J. Bacteriol. 109, 707–712 (1972)
Zeikus, J. G., Fuchs, G., Kenealy, W., Thauer, R. K.: Oxidoreductases involved in cell carbon synthesis of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J. Bacteriol. 132, 604–613 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
K s: H2 and CO2 concentration supporting 0.5 μmax; μmax: specific growth rate at “infinite” substrate concentration; Y s:growth yield (g dry weight/mol substrate); t δ: doubling time
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schönheit, P., Moll, J. & Thauer, R.K. Growth parameters (K s, μmax, Y s) of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum . Arch. Microbiol. 127, 59–65 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00414356
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00414356