Summary
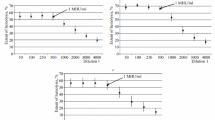
The complement system can be activated by many factors, including immune complexes, leading to the generation of biologically active split products like C5a anaphylatoxin. This study presents a technique which may be used for measuring C5a activity in human serum. The tetanus-anti-tetanus immune complex and aggregated human IgG were used as model activators of the complement cascade. The C5a activity was measured by C5a-induced chemiluminescence of granulocytes; furthermore, a radioimmunoassay was used to detect the C5a peptide. There was a strongly positive correlation between the two assay systems. The described method should be useful as an alternative means of detecting complement activation in the serum of patients with inflammatory diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chenoweth DE, Hugli TE (1980) Binding and degradation of C5a by human neutrophils. J Immunol 124:1517
Fernandez HN, Henson TM, Otani A, Hugli TE (1978) Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under simulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol 120:109–115
Fischer H, Ernst M, Maly F-E, Kato T, Wokalek H, Heberer M, Maas D, Peskar B, Rietschel ET, Staudinger HJ (1982) Chemiluminescence assays in the diagnosis of immune and hematological diseases. In: Serio M, Pazzagli M (eds) Luminescent assays: perspectives in endocrinology and clinical chemistry. Raven Press, New York, pp 229–241
Goodman MG, Chenoweth DE, Weigle WO (1982) Induction of interleukin 1 secretion and enhancement of humoral immunity by binding of human C5a to macrophage surface C5a receptors. J Exp Med 1156:912–917
Hammerschmidt DE, Bowers TK, Lammi-Keefe CJ, Jacob HJ, Craddock PR (1980) Granulocyte aggregometry, a sensitive technique for the detection of C5a in complement activation. Blood 55:898–902
Hugli TE (1981) The structural basis for anaphylatoxin and chemotactic functions of C3a, C4a, and C5a. CRC Crit Rev Immunol 1:321–366
Hugli TE, Chenoweth DE (1980) Biologically active peptides of complement: Techniques and significance of C3a and C5a measurements. In: Immunoassays: Clinical laboratory techniques for the 1980s. Alan Liss, New York, pp 443–460
Maly F-E, Kapp A (1982) A rapid and sensitive bioassay for C5a based on C5a-induced chemiluminescence of normal human granulocytes. Immunobiol 162, 390
Maly F-E, Kapp A, Rother U (1983) C5a-induced chemiluminescence of human granulocytes and its amplification by a serum factor. Immunobiology 164:90–97
Ritzmann SE, Daniels JC (1982) Immune complexes: Characteristics, clinical correlations and interpretive approaches in the clinical laboratory. Clin Chem 28:1259–1271
Wagner JL, Hugli TE (1984) Radioimmunoassay for anaphylatoxins: A sensitive method for determining complement activation products in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 136:75–88
Weigle WO, Morgan EL, Goodman MG, Chenoweth DE, Hugli TE (1982) Modulation of the immune response by anaphylatoxin in the microenvironment of the interacting cells. Fed Proc 41:3099–3103
WHO Technical Report Series (1977) no 606, pp 1–85
Ziccardi RJ, Cooper NR (1980) Development of an immunochemical test to assess C1 inactivator function in human serum and its use for the diagnosis of hereditary angio-oedema. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 15:465–471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapp, A., Maly, F.E. & Schöpf, E. Detection of complement activation in human serum using C5S-Induced chemiluminescence of human granulocytes. Arch Dermatol Res 278, 41–43 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412494
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412494