Summary
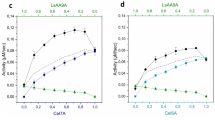
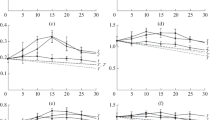
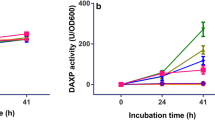
The cellulase complex of Trichoderma koningii has been separated into four apparently pure components namely cellobiase, a C1-like component and two new components, one a CM-cellulase, the other named component C2. All four are necessary for efficient solubilisation of native cellulose. 2. The two new components together constitute the composite CM-cellulase-short-fibre forming activity described by Halliwell and Riaz (1970). 3. Alone only components C2 and C1 have any action on the substrate, the former being somewhat more effective than the C1 component which shows weak solubilising power. 4. Component C2 degrades cellulose weakly to short-fibres but synergises extensively with the CM-cellulase in promoting this process. In contrast the CM-cellula se fails to react significantly with component C1. 6. The interaction of all four components in contributing to the degradation of native cellulose is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björndal, H., Eriksson, K.E.: Extracellular enzyme system utilized by the rot fungus Stereum sanguinolentum for the breakdown of cellulose. Arch. Biochem. 124, 149–153 (1968).
Enger, M. D., Sleeper, B. P.: Multiple cellulase system from Streptomyces antibioticus. J. Bact. 89, 23–27 (1965).
Eriksson, K.-E., Pettersson, B.: Extracellular enzyme system utilized by the rot fungus Stereum sanguinolentum for the breakdown of cellulose. Arch. Biochem. 124, 142–148 (1968).
Halliwell, G.: The action of cellulolytic enzymes from Myrothecium verrucaria. Biochem J. 79, 185–192 (1961).
—: The breakdown of cellulose and its derivatives by enzymes from Myrothecium verrucaria. Biochem. J. 85, 67–72 (1962).
—: Hydrolysis of fibrous cotton and reprecipitated cellulose by cellulolytic enzymes from soil microorganisms. Biochem. J. 95, 270–281 (1965).
—: Solubilisation of native and derived forms of cellulose by cell-free microbial enzymes. Biochem. J. 100, 315–320 (1966).
Halliwell, G.: In: Seminar on Thermophiles, Microbiology Group, Society of Chemical Industry, London, September 1969 (Verbal communication, to be published elsewhere).
—, Riaz, M.: The formation of short-fibres from native cellulose by components of Trichoderma koningii cellulase. Biochem. J. 116, 35–42 (1970).
Mandels, K., Reese, E. T.: Fungal cellulases and the microbial decomposition of cellulosic fabric. Dev. Ind. Microbiol. 5, 5–20 (1964).
Norkrans, B.: Cellulose and cellulolysis. Advanc. appl. Microbiol. 9, 91–130 (1967).
Pettersson, G.: Separation of cellulases on Sephadex G-100. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 77, 665–667 (1963).
—: Isolation of a cellulase from Penicillium notatum. Arch. Biochem. 123, 307–311 (1968).
—, Cowling, E. B., Porath, J.: Isolation of a low molecular weight cellulase from Polyporus versicolor. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 67, 1–8 (1963).
—, Porath, J.: Multiplicity of the cellulolytic enzymes of Polyporus versicolor. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 67, 9–15 (1963).
Prins-van der Meulen, P. Y. F., Van der Marel, T., Ritter, F. J.: Starch-gel electrophoresis of cellulase from Myrothecium verrucaria. T.N.O. Nieuws. 23, 275–282 (1968).
Reese, E. T. (Editor): Advances in enzymic hydrolysis of cellulose and related materials. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1963.
Selby, K.: Mechanism of biodegradation of cellulose. In: Biodeterioration of materials (Ed.: A. H. Walters and J. L. Elphick), pp. 62–78. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Co. 1968.
—, Maitland, C. C.: The cellulase of Trichoderma viride. Biochem. J. 104, 716–724 (1967).
Smith, B. F., Davison, S., Smith, F.: Determination of cellulose in textile fibres. Text. Res. J. 32, 29–38 (1962).
Wood, T. M.: Cellulolytic enzyme system of Trichoderma koningii. Biochem. J. 109, 217–227 (1968).
Yamane, K., Suzuki, H., Nisizawa, K.: Purification and properties of extracellular and cell-bound cellulase components of Pseudomonas fluorescens var. cellulosa. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 67, 19–35 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halliwell, G., Riaz, M. Interactions between components of the cellulase complex of Trichoderma koningii on native substrates. Archiv. Mikrobiol. 78, 295–309 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412270
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00412270