Abstract
The major types of cytochromes present in Chloroflexus aurantiacus strain J-10-f1 were determined by analysis of cell-free preparations and membranes from cells grown phototrophically and chemotrophically. Reduced minus oxidized difference spectroscopy as well as quantitative analysis of the pyridine ferrohemochromogens in alkaline solution were used to determine the classes of cytochromes present.
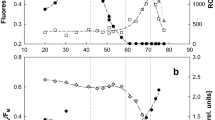
Evidence for membrane-bound cytochromes of the b and c-type was found in cell-free preparations of phototrophically grown cells. Difference spectra revealed absorption maxima at 553 nm, 523 nm, and 418 nm and a shoulder at 562 nm. Protoheme and heme c were identified as alkaline pyridine ferrohemochromogens with absorption maxima at 556 and 550 nm respectively. The ratio of heme c to protoheme in the cell-free preparation was about 10 to 1 with 0.65 μmol of heme c and 0.067 μmol of protoheme per gram of total cell protein. Dithionite plus carbon monoxide minus dithionite reduced difference spectra of membranes revealed a peak at 414 nm and troughs at 552, 523, and 423 nm consistent with a CO-binding cytochrome c.
Similar analyses of chemotrophically grown cells revealed evidence for the presence of membrane-bound cytochromes of the c, b, and a classes with absorption maxima at 552–557 and 593–596 nm. Protoheme, heme c and heme a were detected as pyridine ferrohemochromogens with maxima at 556, 550, and 588 nm respectively. The ratio of heme c to protoheme was about 3 to 1 with 0.44 μmol of heme c and 0.16 μmol of protoheme per gram of total cell protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baines BS, Williams HD, Hubbard JAM, Poole RK (1984) Partial purification and characterization of a soluble haemoprotein, having spectral properties similar to cytochrome a 1, from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 171:309–314
Bartsch RG (1971) Cytochromes: Bacterial. In: San Pietro A (ed) Methods in enzymology, vol XXIII, part A. Academic Press, New York London, pp 344–363
Bartsch RG (1978) Cytochromes. In: Clayton RK, Sistrom WR (eds) The photosynthetic bacteria. Plenum, New York London, pp 249–279
Bowyer JR, Crofts AR (1980) The photosynthetic electron transfer chain of Chromatium vinosum chromatophores: Flash-induced cytochrome b reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta 591:298–311
Bruce BD, Fuller RC, Blankenship RE (1982) Primary photochemistry in the facultatively aerobic green photosynthetic bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6532–6536
Castenholz RW, Pierson BK (1981) Isolation of members of the family Chloroflexaceae. In: Starr MP, Stolz H, Trüper HG, Balows A, Schlegel HG (eds) The prokaryotes: a handbook on habitats, isolation, and identification of bacteria, vol I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 290–298
Gaul DF, Knaff DB (1983) The presence of cytochrome c 1 in the purple sulfur bacterium Chromatium vinosum. FEBS Lett 162:69–74
Gennis RB, Casey RP, Azzi A, Ludwig B (1982) Purification and characterization of the cytochrome c oxidase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides Eur J Biochem 125:189–195
Hüdig H, Drews G (1983) Characterization of a new membrane-bound cytochrome c of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. FEBS Lett 152:251–255
Kienzl PF, Peschek GA (1982) Oxidation of c-type cytochromes by the membrane-bound cytochrome oxidase (cytochrome aa 3) of blue-green algae. Plant Physiol 69:580–584
King MT, Drews G (1975) The respiratory electron transport system of heterotrophically grown Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Arch Microbiol 102:219–231
Knaff DB, Buchanan BB (1975) Cytochrome b and photosynthetic sulfur bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 376:549–560
Knaff DB, Kraichoke S (1983) Oxidation-reduction and EPR properties of a cytochrome complex from Chromatium vinosum. Photochem Photobiol 37:243–246
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Matsushita K, Shinagawa E, Adachi O, Ameyama M (1982) o-Type cytochrome oxidase in the membrane of aerobically grown Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett 139:255–258
Pierson BK, Castenholz RW (1974a) A phototrophic gliding filamentous bacterium of hot springs, Chloroflexus aurantiacus, gen. and sp. nov. Arch Microbiol 100:5–24
Pierson BK, Castenholz RW (1974b) Studies of pigments and growth in Chloroflexus aurantiacus, a phototrophic filamentous bacterium. Arch Microbiol 100:283–305
Pierson BK, Keith LM, Leovy JG (1984) Isolation of pigmentation mutants of the green filamentous photosynthetic bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus. J Bacteriol 159:222–227
Pierson BK, Thornber JP, Seftor REB (1983) Partial purification, subunit structure and thermal stability of the photochemical reaction center of the thermophilic green bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus. Biochim Biophys Acta 723:322–326
Poole RK, Van Wielink JE, Baines BS, Reijnders WNM, Salmon I, Oltmann LF (1983) The membrane bound cytochromes of an aerobically grown, extremely thermophilic bacterium, PS3: characterization by spectral deconvolution coupled with potentiometric analysis. J Gen Microbiol 129:2163–2173
Sasaki T, Motokawa Y, Kikuchi G (1970) Occurrence of both a-type and o-type cytochromes as the functional terminal oxidases in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochim Biophys Acta 197:284–291
Sistrom WR, Clayton RK (1964) Studies on a mutant of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides unable to grow photosynthetically. Biochim Biophys Acta 88:61–73
Sperry JF, Wilkins TD (1976) Cytochrome spectrum of an obligate anaerobe, Eubacterium lentum. J Bacteriol 125:905–909
Steinmetz MA, Fischer U (1982) Cytochromes, rubredoxin, and sulfur metabolism of the non-thiosulfate-utilizing green sulfur bacterium Pelodictyon luteolum. Arch Microbiol 132:204–210
Steinmetz MA, Trüper HG, Fischer U (1983) Cytochrome c-555 and iron-sulfur-proteins of the non-thiosulfate-utilizing green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium vibrioforme. Arch Microbiol 135:186–190
Takamiya K (1983) Properties of the cytochrome c oxidase activity of cytochrome b 561 from photoanaerobically grown Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Plant Cell Physiol 24:1457–1462
Takamiya K, Hanada H (1980) Cytochrome b 560 in chromatophores from Chromatium vinosum. Plant Cell Physiol 21:979–988
Takamiya K, Hanada H (1983) Isolation and purification of cytochrome b 561 from a photosynthetic bacterium, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Plant Cell Physiol 24:1449–1455
Takamiya K, Doi M, Okimatsu H (1982) Isolation and purification of a ubiquinone-cytochrome b-c 1 complex from a photosynthetic bacterium, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Plant Cell Physiol 23:987–997
Vermeglio A, Carrier JM (1984) Photoinhibition by flash and continuous light of oxygen uptake by intact photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 764:233–238
Yu, CA, Mei Q-C, Yu L (1984) Isolation and characterization of cytochrome c 1 from photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 118:964–969
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierson, B.K. Cytochromes in Chloroflexus aurantiacus grown with and without oxygen. Arch. Microbiol. 143, 260–265 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00411247
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00411247