Abstract
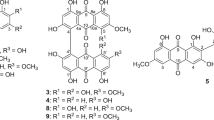
The occurrence of emodin, erythroglaucin, physcion, physcion-9-anthrone, questin, catenarin, and catenarin-8-methyl ether in different species of the Aspergillus glaucus group (genus Eurotium) was investigated. So far catenarin-8-methyl ether (1, 4, 6-trihydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methylanthraquinone) has not been described as a natural product; it was therefore given the name rubrocristin. The chemical and physical properties of rubrocristin are reported. In addition a new violet pigment (C16H12O5) was isolated and characterized by its MS-, IR- and UV-spectra.
The antimicrobial properties of all substances were examined in the agar diffusion assay. Gram-positive bacteria were the most sensitive organisms and catenarin was the most active naturally occurring substance. Synthetically obtained 1, 4, 6, 8-tetrahydroxy-anthraquinone was slightly more active than catenarin, whereas rubrocristin showed no antibacterial activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MIC:
-
Minimal inhibitory concentration
- TLC:
-
Thin layer chromatography
- PTLC:
-
Preparative thin layer chromatography
References
Anke, H., Kolthoum, I., Laatsch, H.: Metabolic products of microorganisms. 192. The anthraquinones of the Aspergillus glaucus group. II. Biological activity. Arch. Microbiol. 126, 231–236 (1980)
Anke, H., Zähner, H., König, W. A.: Metabolic products of microorganisms. 170. On the antibiotic activity of cladosporin. Arch. Microbiol. 116, 253–257 (1978)
Anslow, W. K., Raistrick, H.: The molecular constitution of catenarin and erythroglaucin, metabolic products respectively of Helminthosporium catenarium Drechsler and of species in the Aspergillus glaucus series. Biochem. J. 34, 1124–1133 (1940)
Ashley, J. N., Raistrick, H., Richards, T.: The cristalline colouring matters of species in the Aspergillus glaucus series. II. Biochem. J. 33, 1291–1303 (1939)
Berry, D. R.: The environmental control of the physiology of filamentous fungi. In: The filamentous fungi, Vol. I. Industrial mycology (J. E. Smith, D. R. Berry, eds.), pp. 16–32. London: Arnold 1975
Blaser, P.: Taxomonische und physiologische Untersuchungen über die Gattung Eurotium Link ex Fries. Dissertation Nr. 5323, Eidgenössische Hochschule Zürich (1974)
Brockmann, H., Budde, G.: Zur spektroskopischen Identifizierung des Stammkohlenwasserstoffes mehrkerniger Oxychinone. Chem. Ber. 86, 432–443 (1953)
Bu'Lock, J. D.: Secondary metabolism in fungi and its relationship to growth and development. In: The filamentous fungi, Vol. I. Industrial mycology (J. E. Smith, D. R. Berry, eds), pp. 33–58. London: Arnold 1975
Cameron, D. W., Crossley, M. J.: Synthesis of emodin methyl ethers. Aust. J. Chem. 30, 1161–1165 (1977)
Eikhom, T. S., Jonsen, J., Laland, S., Refsvik, T.: On the biosynthesis of gramicidin S. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 76, 465–468 (1963)
Feigl, P.: Tüpfelanalyse, p. 197. Frankfurt: Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft 1960
Gould, B. S., Raistrick, H.: Studies in the biochemistry of microorganisms. XL. The crystalline pigments of species in the Aspergillus glaucus series. Biochem. J. 28, 1640–1656 (1934)
Hsieh, D. P. H.: Biosynthesis of bisfuranoid mycotoxins. Fifth Intern. Fermentation Symposium, Abstracts p. 227, Berlin 1976
Hsieh, D. P. H., Singh, R., Yao, R. C., Bennett, J. W.: Anthraquinones in the biosynthesis of sterigmatocystin by Aspergillus versicolor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 35, 980–982 (1978)
Kurylowicz, W.: Antibiotics, a critical review. Warsaw: Polish Medical Publ. 1976
Piattelli, M., Giudici de Nicola, M.: Anthraquinone pigments from Xanthoria parietina. Photochimistry 7, 1183–1187 (1968)
Raistrick, H.: A region of biosynthesis. Proc. Roy. Soc. London, B 136, 481–508 (1950)
Raistrick, H., Robinson, R., Todd, A. R.: The production of hydroxy-anthraquinones by species of Helminthosporium. Biochem. J. 28, 559–572 (1934)
Raper, K. B., Fennell, D. I.: The genus Aspergillus. Chap. X. Aspergillus glaucus group, pp. 147–196. Baltimore: The Williams and Wilkins Co. 1965
Steglich, W., Lösel, W., Austel, V.: Anthrachinon-Pigmente aus Dermocybe sanguinea (Wulf. ex Fr.) Wünsche und D. semisanguinea (Fr.). Chem. Ber. 102, 4104–4118 (1969)
Strauss, D. G.: Anthracyclines — Modern tumour-inhibiting agents. Folia Microbiol. 23, 152–161 (1978)
Thomson, R. H.: Naturally occurring quinones. Chap. 5: Anthraquinones, pp. 367–535 London, New York: Academic Press 1971
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Metabolic products of microorganisms. 184. H. Anke: On the mode of action of cladosporin. J. Antibiotics 32, 952–958 (1979)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anke, H., Kolthoum, I., Zähner, H. et al. Metabolic products of microorganisms. 185. The anthraquinones of the Aspergillus glaucus group. I. Occurrence, isolation, identification and antimicrobial activity. Arch. Microbiol. 126, 223–230 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409924
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409924