Summary
The hepatotoxic effect of different exposure schemes to carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) was studied in inhalation experiments in rats. The duration of exposures at different concentrations of (CCl4) vapours in air was changed in such a way as to give a constant product of concentration and time (CT). The animals were exposed for 4 successive days a week.
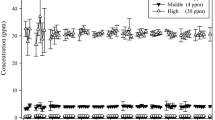
A concentration of 1,625 mg/m3 (250 ppm) (CCl4) for 72 min (CT = 300 ppm × h) caused a higher increase in SGPT activity than the exposure to 325 mg/m3 (50 ppm) for 6h (CT = 300); the effect of 6,500 mg/m3 (1,000 ppm) for 3 min six times at 1-h intervals (CT = 300) had a much smaller effect than the exposure to 6,500 mg/m3 (1,000 ppm) for 18 min (again CT = 300) (1 ppm (CCl4) = 6.5 mg/m3). Similar results were obtained at other concentrations and by increasing the number of exposures up to 18; the effects were also confirmed by other biochemical changes in blood serum and liver and by histological examination of the liver.
The results indicate that the severity of liver lesions is more influenced by the concentration of (CCl4) in the inhaled air (and accordingly in the blood entering the liver) than by the total inhaled (and absorbed) amount of (CCl4). This also explains the differences between the two types of exposure in the concentration of 6,500 mg/m3 (1,000 ppm): blood cannot be saturated with (CCl4) to the same level within 3 min as within 18 min of exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams EM, Spencer HC, Rowe VK, McCollister DD, Irish DD (1952) Vapour toxicity of carbon tetrachloride determined by experiments on laboratory animals. Ind Hyg Occup Med 6:50–66
Almersjö O, Knutson F (1971) Response of some biochemical tests to varying degrees of direct toxic injury of the liver. A comparative study of biochemical and histological changes in the rat after exposure to gaseous carbon tetrachloride for different periods. Acta Chir Scand [Suppl] 416:25–39
Ball WF, Kay K (1956) Serum esterase response in rats exposed to carbon tetrachloride vapor. Arch Ind Health 14:450–457
Block WD, Cornish HH (1958) Effect of carbon tetrachloride inhalation on rat serum enzymes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 97:178–180
Coffin DL, Gardner DE, Sidorenko GI, Pinigin MA (1977) Role of time as a factor in the toxicity of chemical compounds in intermittent and continuous exposures. Part II. Effects of intermittent exposure. J Toxicol Environ Health 3:821–828
Cornish HH, Block WD (1960a) A study of carbon tetrachloride. I. The effect of carbon tetrachloride inhalation on rat serum enzymes. Arch Ind Health 21:549–554
Cornish HH, Block WD (1960b) A study of carbon tetrachloride. II. The effect of carbon tetrachloride inhalation on serum and tissue enzymes. Arch Environ Health 1:96–100
Cornish HH, Dambrauskas T (1961) A study of carbon tetrachloride. III. Tissue enzyme response to carbon tetrachloride inhalation. Ind Med Surg 30:323–326
Dambrauskas T, Cornish HH (1970) Effect of pretreatment of rats with carbon tetrachloride on tolerance development. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1:83–97
Das PK, Chopra P, Nayak NC (1974) Hepatocellular tolerance to carbon tetrachloride induced injury in the rat. A study of its nature and possible mode of evolution. Exp Mol Pathol 21:218–236
Gardner DE, Coffin DL, Pinigin MA, Sidorenko GI (1977) Role of time as a factor in the toxicity of chemical compounds in intermittent and continuous exposures. I. Effects of continuous exposure. J Toxicol Environ Health 3:811–820
ILO (1977) Occupational exposure limits for airborne toxic substances. Occupational Safety and Health Series No 37, ILO, Geneva
Kanics L, Rubinstein D (1968) The effect of chronic carbon tetrachloride inhalation on the secretion of lipid by rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol 17:1959–1967
Kazmina NP (1976) Study of the adaptation processes of the liver to monotonous and intermittent exposures to carbon tetrachloride (in Russian). Gig Tr Prof Zabol 3:39–42
Kontinen A (1967) Simple method for the determination of OCT activity in serum. Clin Chim Acta 18:147–156
Lal H, Puri SK, Fuller GC (1970) Impairment of hepatic drug metabolism by carbon tetrachloride inhalation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 16:35–39
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–268
Packet KJ, Kamphausen U (1975) The carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity as a model of liver damage. First report. Long-time biochemical changes. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 22:84–88
Schwetz BA, Leong BK, Gehring PJ (1974) Embryo- and fetotoxicity of inhaled carbon tetrachloride, 1,1-dichloroethane, and methyl ethyl ketone in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 28:452–464
Seifter SD, Novic B, Muntwyler E (1950) The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch Biochem 25:191–193
Ugazio G, Koch RR, Recknagel RO (1972) Mechanism of protection against carbon tetrachloride by prior carbon tetrachloride administration. Exp Mol Pathol 16:281–285
Ugazio G, Koch RR, Recknagel RO (1973) Reversibility of liver damage in rats rendered resistant to carbon tetrachloride by prior carbon tetrachloride administration: bearing on the lipoperoxidation hypothesis. Exp Mol Pathol 18:281–289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, A., Frantík, E., Holuša, R. et al. Role of time and concentration on carbon tetrachloride toxicity in rats. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 48, 49–60 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405931
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405931