Abstract
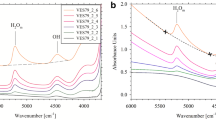
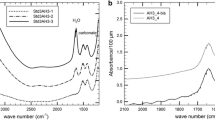
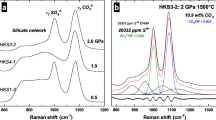
CO2 solubility has a slight negative temperature dependence in olivine melilitite at 30 kb with 9% CO2 dissolved at 1,450 °C, 8.5% at 1,550 °C and 8.3% at 1,650° C. CO2 is dissolved as the carbonate molecule (CO 2−3 ) only. Feldspar melts (albite-anorthite) dissolve much less CO2 at 30 kb (around 2%) with a slight increase with increasing anorthite content. A CO2 absorption peak in infrared spectra of albite-rich glasses diappears in favour of the CO 2−3 peak with increasing anorthite content. It is inferred that CO2 was present as CO 2−3 in albite-rich melts also, but reverts to CO2 during quenching because of bonding differences related to Ca2+ and Na+ in the melts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eggler, D.H.: Role of CO2 in melting processes in the mantle. Ann. Rept. Div. Geophys. Lab., Washington 72, 457–467 (1973)
Eggler, D.H.: Does CO2 cause partial melting in the low-velocity layer of the mantle? Geology 4, 69–72 (1976)
Brey, G., Green, D.H.: The role of CO2 in the genesis of olivine melilitite. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 49, 93–103 (1975)
Brey, G., Green, D.H.: Solubility of CO2 in olivine melilitite at high pressures and role of CO2 in the earth's upper mantle. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 55, 217–230 (1976)
Mysen, B.O., Arculus, R.J., Eggler, D.H.: Solubility of carbon dioxide in melts of andesite, tholeiite, and olivine nephelinite composition to 30 kbar pressure. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 53, 227–239 (1975)
Mysen, B.O., Eggler, D.H., Seitz, M.G., Holloway, J.R.:: Carbon dioxide in silicate melts and crystals. Part I. Solubility measurements. Am. J. Sci. in press (1976)
Newton, R.C., Sharp, W.E.: Stability of forsterite+CO2 and its bearing on the role of CO2 in the mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 26, 239–244 (1975)
Kushiro, T., Satake, H., Akimoto, S.: Carbonate-silicate reactions at high pressures and possible presence of dolomite and magnesite in the upper mantle. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 28, 116–120 (1975)
Irving, A.J., Wyllie, P.J.: Subsolidus and melting relationships for calcite, magnesite and the join CaCO3-MgCO3 to 36 kilobars. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 39, 35–53 (1975)
Wyllie, P.J., Huang, W.-L.: Carbonation and melting reactions in the system CaO-MgO-SiO2-CO2 at mantle pressures with geophysical and petrological applications. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 54, 79–107 (1976)
Boettcher, A.L., Mysen, B.O., Allen, J.C.: Techniques for the control of water fugacity and oxygen fugacity for experimentation in solid-media high-pressure apparatus. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 5898–5901 (1973)
Mysen, B.O., Boettcher, A.L.: Melting of a hydrous mantle: 1. Phase relations of a natural peridotite at high pressures and temperatures with controlled activities of water, carbon dioxide and hydrogen. J. Petrol. 16, 520–548 (1975)
Ching Siang Yeh: Rapid microdetermination of carbon and hydrogen. A new universal combustion tube filling. Microchem. J. 7, 303–310 (1963)
Mysen, B.O., Seitz, M.G.: Trace element partitioning determined by beta track mapping: an experimental study using carbon and samarium as examples. J. Geophys. Res. 80, No. 17, 2627–2635 (1974)
Taylor, J.H., Benedict, W.S., Strong, J.: Infrared spectra of H2O and Co2 at 500° C. J. Chem. Phys. 20, 1884–1898 (1952)
Mansel Davies (ed.): Infrared spectroscopy and molecular structure — an outline of the principles. Amsterdam-London-New York: Elsevier 1963
Hallam, H.E. (ed.): Vibrational spectroscopy of trapped species. Infrared and Raman studies of matrix-isolated molecules, radicals and ions. New York: Wiley 1973
Alpert, N.L., Szymanski, H.A., Keiser, W.E.: IR theory and practice of infrared spectroscopy. New York: Plenum Press sec. ed. 1970
Nyquist, R.A., Kagel, R.O.: Infrared spectra of inorganic compounds. New York and London: Academic Press 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brey, G. CO2 solubility and solubility mechanisms in silicate melts at high pressures. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 57, 215–221 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405226
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405226