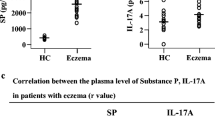
Abstract
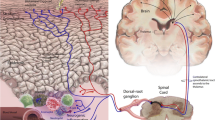
The effects of the neuropeptides substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) on leukocyte infiltration during allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) in mice were studied. Concomitant topical application of SP or CGRP with the allergen oxazolone resulted in enhanced leukocyte recruitment at the sites of challenge. Immunohistochemical studies revealed that the numbers of T-helper (L3T4+) and cytotoxic (Lyt-2) lymphocytes and infiltrating macrophages (BM8+) were increased. In addition, ICAM-1 and MHC class II molecule expression by these cells was enhanced after neuropeptide application. Analysis by confocal laser scanning microscopy revealed an increase in the immunoreactivity for SP and CGRP in nerve fibres during the course of ACD. Flow cytometry studies showed that SP and CGRP did not upregulate expression of the adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 by murine endothelial cell lines in vitro. This suggests that increased infiltration of leukocytes during ACD is not a consequence of direct neuropeptide-promoted upregulation of endothelial adhesion molecules in vivo. In conclusion, our observations provide evidence for a modulatory role of neuropeptides in the pathogenesis of ACD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weigent DA, Blalock JE (1987) Interactions between the neuroendocrine and immune system: common hormones and receptors. Immunol Rev 100: 79–108
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod JJ, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature 304: 129–135
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313: 54–56
Hagermark O, Hokfelt T, Pernow B (1978) Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J Invest Dermatol 71: 233–235
Ebertz JM, Hirshman CA, Kettelkamp NS, Uno H, Hanifin JM (1987) Substance P-induced histamine release in human cutaneous mast cells. J Invest Dermatol 88: 682–685
Wallengren J, Hakanson R (1987) Effects of substance P, neurokinin A and calcitonin gene-related peptide in human skin and their involvement in sensory nerve-mediated responses. Eur J Pharmacol 143: 267–273
Hirata Y, Takagi Y, Takata S, Fukuda Y, Yoshimi H, Fujita T (1988) Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor in cultured vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 151: 1113–1121
Abello J, Kaiserlian D, Cuber JC, Revillard JP, Chayvialle JA (1991) Characterization of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors and adenylate cyclase response in the murine macrophage cell line P388D1. Neuropeptides 19: 43–49
Umeda Y, Arisawa M (1989) Characterization of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor in mouse T lymphocytes. Neuropeptides 14: 237–242
Stephenson JA, Summers RJ (1987) Autoradiographic analysis of receptors on vascular endothelium. Eur J Pharmacol 134: 35–43
Hartung HP, Wolters K, Toyka KV (1986) Substance P: binding properties and studies on cellular responses in guinea pig macrophages. J Immunol 136: 3856–3863
Stanisz AM, Scicchitano R, Dazin P, Bienenstock J, Payan DG (1987) Distribution of substance P receptors on murine spleen and Peyer's patch T and B cells. J Immunol 139: 749–754
Naukkarinen A, Nickoloff BJ, Farber EM (1989) Quantification of cutaneous sensory nerves and their substance P content in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 92: 126–129
Hernanz A, Muelas G, Borbujo J (1989) Plasma neuropeptide pattern in acute idiopathic urticaria. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 90: 198–200
Culson IH, Holden CA (1990) Cutaneous reactions to substance P and histamine in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 122: 343–349
Walker KB, Derwonska MH, Valone FH, Harkonen WS, Frick OL, Scriven KH, Ratnoff WD, Browning JG, Payan DG, Goetzl EJ (1988) Distinct patterns of release of neuroendocrine peptides after nasal challenge of allergic subjects with ryegrass antigen. J Clin Immunol 8: 108–113
Ek L, Theodorsson E (1990) Tachykinins and calcitonin generelated peptide in oxazolone-induced allergic contact dermatitis in mice. J Invest Dermatol 94: 761–763
Girolomoni G, Tigelaar RE (1990) Capsaicin-sensitive primary sensory neurons are potent modulators of murine delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. J Immunol 145: 1105–1112
Gutwald J, Goebeler M, Sorg C (1991) Neuropeptides enhance irritant and allergic contact dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 96: 695–698
Malorny U, Michels E, Sorg C (1986) A monoclonal antibody against an antigen present on mouse macrophages and absent from monocytes. Cell Tissue Res 243: 421–428
Goebeler M, Gutwald J, Roth J, Meinardus-Hager G, Sorg C (1990) Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in murine allergic contact dermatitis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 93: 294–299
Bu'Lock AJ, Vaillant C, Dockray GJ, Bu'Lock JD (1982) A rational approach to the fixation of peptidergic nerve cell bodies in the gut using parabenzoquinone. Histochemistry 74: 49–55
Goebeler M, Meinardus-Hager G, Roth J, Goerdt S, Sorg C (1993) Nickel chloride and cobalt chloride, two common contact sensitizers, directly induce expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) by endothelial cells. J Invest Dermatol 100: 759–765
Seventer GA van, Shimizu Y, Horgan KJ, Shaw S (1990) The LFA-1 ligand ICAM-1 provides an important costimulatory signal for T cell receptor-mediated activation of resting T cells. J Immunol 144: 4579–4586
Mitra RS, Shimizu Y, Nickoloff BJ (1993) Histamine and cis-urocanic acid augment tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated induction of keratinocyte intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression. J Cell Physiol 156: 348–357
Zimmerman BJ, Anderson DC, Granger DN (1992) Neuropeptides promote neutrophil adherence to endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Physiol 263: G678-G682
Sung CP, Arleth AJ, Aiyar N, Bhatnagar PK, Lysko PG, Feuerstein G (1992) CGRP stimulates the adhesion of leukocytes to vascular endothelial cells. Peptides 13: 429–434
Pober JS, Slowik M, DeLuca L, Ritchie AJ (1992) Elevated cAMP inhibits endothelial expression of ELAM-1 and VCAM-1 but not ICAM-1 (abstract). FASEB J 6: A1592
Haegerstrand A, Dalsgaard CJ, Jonzon B, Larsson O, Nilsson J (1990) Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates proliferation of human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 3299–3303
Mitsuhashi M, Ohashi Y, Shichijo S, Christian C, Sudduth-Klinger J, Harrowe G, Payan DG (1992) Multiple intracellular signaling pathways of the neuropeptide substance P receptor. J Neurosci Res 32: 437–443
Lotz M, Vaughan JH, Carson DA (1988) Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science 241: 1218–1221
Ruff MR, Wahl SM, Pert CB (1985) Substance P receptor-mediated chemotaxis of human monocytes. Peptides 6 [Suppl 2]: 107–111
Iwamoto I, Yamazaki H, Nakaoawa N, Kimura A, Tomioka H, Yoshida S (1990) Differential effects of two C-terminal peptides of substance P on human neutrophils. Neuropeptides 16: 103–107
Numao T, Agrawal DK (1992) Neuropeptides modulate human eosinophil chemotaxis. J Immunol 149: 3309–3315
Buckley TL, Brain SD, Rampart M, Williams TJ (1991) Time-dependent synergistic interactions between the vasodilator neuropeptide, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and mediators of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 103: 1515–1519
Davies D, Medeiros MS, Keen J, Turner AJ, Haynes LW (1992) Eosinophil chemotactic peptide sequences in rat alpha-CGRP. Activation of a novel trophic action by neutral endopeptidase 24.11. Ann NY Acad Sci 657: 405–411
Foster CA, Mandak B, Kromer E, Rot A (1992) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is chemotactic for human T lymphocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci 657: 397–404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goebeler, M., Henseleit, U., Roth, J. et al. Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide modulate leukocyte infiltration to mouse skin during allergic contact dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res 286, 341–346 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402226
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00402226