Summary
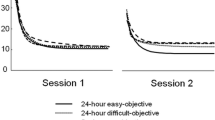
31 healthy male students were given a placebo and two different doses of alcohol (on different occasions and in random order). Choice-reaction-time, tapping-speed, bimanual hand-coordination, critical fusion frequency, standing steadiness, Bourdon's test, blood and urine alcohol content were measured before and 30, 60 and 90 min after drinking. Self-ratings of mood were made. 7 of the subjects were also examined after 2, 3 and 13 hours and altogether 4 doses of alcohol were used for this group. 24 subjects were given an additional dose of alcohol 2 hours after the first one and the tests were repeated 30, 60 and 90 min after the additional dose. The agreement between blood and urine alcohol levels was good and the alcohol curves showed an approximately linear fall-off. For the highest alcohol dose used there was a good agreement between blood alcohol level and test performance. The impairment of performance was most marked after 30–60 min. After 2 hours the impairment was very slight. The performance on Choice reaction time and Coordination was related to blood alcohol level also after a smaller dose. Statistically significant changes were obtained in most tests after the highest dose (0.8 g per kg body weight) and in Choice reaction time and Coordination after the smaller dose (0.4 g per kg body weight). No significant effects were obtained after administration of placebo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonnichsen, R., and G. Lundgren: Comparison of the ADH and the Widmark procedures in forensic chemistry for determinating alcohol. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.) 13, 256 (1957).
Cronholm, B., and L. Molander: Memory disturbances after electroconvulsive therapy. 1. Conditivus 6 hours after electrochock treatment, Acta psychiat. scand. 32, 280 (1957).
Drew, G. C., W. P. Colquhoun, and Hazel A. Long: Effect of small doses alcohol on a skill resembling driving MRC memorandum No. 38, London: H.M.S.O. 1959.
Ekman, G., M. Frankenhaeuser, L. Goldberg, R. Hagdahl, and A.-L. Myrsten: Subjective and objective effects of alcohol as functions of dosage and time. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 6, 399 (1964).
Ideström, C.-M.: The effect of γ-phenyl-propylcarbamate compared with meprobamate and placebo. An experimental psychological study. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 3, 15 (1962).
King, H. E.: Psychomotor aspects of nervous disease. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press 1954.
Milfeldt, M.: Flickerfusion in Neurology. Universitetsförlaget i Århus (1957).
Nash, H.: Alcohol and caffeine. A study of their psychological effects. Springfield, Ill.: Ch. C. Thomas 1962.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ideström, C.M., Cadenius, B. Time relations of the effects of alcohol compared to placebo. Psychopharmacologia 13, 189–200 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401399
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401399