Abstract
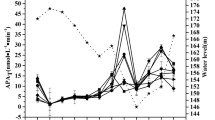
The occurrence and distribution of a special group of bacteria, capable of dissolving insoluble phosphates, were studied in marine environments, especially in sediments. The phosphatase activity was also investigated. Clayey sediments contained more phosphate solubilizing bacteria and phosphatase than sandy sediments. There was a positive correlation between the total phosphate content and the phosphatase activity. The phosphatase activity was recorded in all samples, irrespective of salinity variations. The role of various factors of the sediments in maintaining the phosphate availability in the overlying water is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Alexander, M.: Introduction to soil microbiology, 472 pp. London: John Wiley & Sons. Inc. 1961.
Ayyakkannu, K. and D. Chandramohan: On the occurrence and distribution of phosphobacteria in the marine environment at Porto Novo. Curr. Sci. 39, 398–399 (1970a)
— and D. Chandramohan: Phosphatase activity in marine environments: open sandy beach at Porto Novo. Indian J. exp. Biol. 8, 349–350 (1970b).
Balasubramanyan, K.: Studies on the ecology of the Vellar estuary. 2. Phosphates in bottom sediments. J. zool. Soc. India 13, 166–169 (1961).
Carritt, D. E. and S. Goodgal: Sorption reactions and some ecological implications. Deep Sea Res. 1, 224–243 (1954).
Cashel, M. and E. Freese: Excretion of alkaline phosphatase by Bacillus subtilis. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 16, p. 541 (1964).
Chandrasekaran, S.: Studies on the interrelationship between plants and soil microorganisms in respect to phosphorus solubilization. Ph. D. Thesis, Annamalai University, South India 1966.
Gessner, F.: Untersuchungen über den Phosphathaushalt des Amazonas. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 45, 339–345 (1960).
Halstead, R. L.: Phosphatase activity of soils as influenced by lime and other treatments. Can. J. Soil Sci. 44, 137–144 (1964).
Kramer, M. and S. Erdei: Investigation of the phosphatase activity of soils by means of disodium monophenyl phosphate I. Method. Agrokém. Talajt. 7, 361–366 (1958).
Mazilkin, I. A. and M. G. Kuznetsova: Nuclease and phosphatase activity of soil bacteria. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR (Ser. Biol.) 29, 587–591 (1964) (Chem. Abstr. 61, 16466a, 1964).
Moore, H. B.: Muds of the Clyde sea area. I. Phosphate and nitrogen contents. J. mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 16, 595–607 (1930).
Pomeroy, L. R., E. E. Smith and C. M. Grant: The exchange of phosphate between estuarine water and sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 10, 167–172 (1965).
Ramirez-Martinez, J. R.: Organic phosphorus mineralization and phosphatase activity in soils. Folia microbiol., Delft 13, 161–174 (1968).
Rochford, D. J.: Studies in Australian estuarine hydrology. I. Introductory and comparative features. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 2, 2–116 (1951).
Seshappa, G.: Phosphate content of mud banks along the Malabar coast. Nature, Lond. 171, 526–527 (1953).
Skujins, J.: Enzymes in soil. In: Soil Biochemistry, pp 371–414. Ed. by A. D. McLaren and G. H. Peterson. New York: Marcel Dekker 1967.
Stockfish, K. and W. Benade: Die Charakterisierung der Heilschlamme und verwandter Stoffe — Physikalischen Eigenschaften. Mitt. Labn preuss. geol. Landesanst. 11, 35–83 (1930).
Strickland, J. D. H. and Lucia Solorzano: Determination of monoesterase hydrolysable phosphate and phosphomonoesterase activity in sea water. In: Some contemporary studies in marine sciences, pp 665–674. Ed. by H. Barnes. London: George Allen & Unwin Ltd. 1966.
— and T. R. Parsons: A manual of sea water analysis, 311 pp. Ottawa: Fisheries Research Board of Canada 1968.
Zobell, C. E.: Studies on the bacterial flora of marine sediments. J. sedim. Petrol. 8, 10–18 (1938).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N. K. Panikkar, Panaji
Contribution No. 102, Marine Biological Station, Annamalai University, Porto Novo, Tamil Nadu, South India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayyakkannu, K., Chandramohan, D. Occurrence and distribution of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and phosphatase in marine sediments at Porto Novo. Mar. Biol. 11, 201–205 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401268
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401268