Abstract
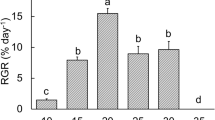
To obtain a direct measurement of the importance of Prochloron sp. to the ascidian Didemnum molle, ascidian colonies from Lizard Island Lagoon, Great Barrier Reef, were grown for 9 d at 0, 10, 40 and 100% sunlight in situ using unidirectional flow chambers. Growth (wet weight) was enhanced up to 40% of full sunlight, at which point growth appears to have been light-saturated. Colonies in 10 and 40% sunlight responded by (1) climbing up the sides of the growth chambers, and (2) flattening out to a more encrusting morphology; also (3) the chlorophyll content of three colonies in zero sunlight decreased by >80%, yet the ascidians remained healthy and did not lose weight. These data show that although the symbiosis may not be obligatory for D. molle, the ascidian's growth is enhanced by Prochloron sp., and the morphology of the ascidian colony is affected by its photobiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Alberte, R. S., L. Cheng and R. A. Lewin: Photosynthetic characteristics of Prochloron sp./ascidian symbioses. I. Light and temperature responses of the algal symbiont of Lissoclinum patella. Mar. Biol. 90, 575–587 (1986)
Bachmann, M. A., A. Maidhof, H. C. Schroder, K. Pfeifer, E. M. Kurz, T. Rose, I. Muller, W. E. G. Müller: Prochloron (Prochlorophyta): biochemical contributions to the chlorophyll and RNA composition. Pl. Cell Physiol., Tokyo 26, 1211–1222 (1985)
Chalker, B. E. and W. C. Dunlap: Primary production and photoadaptation by corals on the Great Barrier Reef. In: Proceedings of the Inaugural Great Barrier Reef Conference, pp 293–298. J. Baker, R. Ed. by M. Carter, P. W. Sammarco and K. Stark. Townsville: James Cook University Press 1983
Fisher, C. R. and R. K. Trench: In vitro carbon fixation by Prochloron sp. isolated from Diplosoma virens. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 159, 636–648 (1980)
Griffiths, D. J. and L. V. Thinh: Transfer of photosynthetically fixed carbon between the prokaryotic green alga Prochloron and its ascidian host. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res 34, 431–440 (1983)
Jeffrey, S. W. and G. F. Humphrey: New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1, and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pfl. 167, 191–194 (1975)
Kott, P.: Algal-bearing didemnid ascidians in the Indo-West Pacific. Mem. Qd Mus. 20, 1–47 (1980)
Kremer, B. P., R. Pardy and R. A. Lewin: Carbon fixation and photosynthates of Prochloron, a green alga symbiotic with an ascidian, Lissoclinum patella. Phycologia 21, 258–263 (1982)
Lewin, R. A.: Prochloron, type genus of the Prochlorophyta. Phycologia 16, p. 217 (1977)
Lewin, R. A.: Prochloron — a status report. Phycologia 23, 203–208 (1984)
Newcomb, C. H. and T. D. Pugh: Blue-green algae associated with ascidians of the Great Barrier Reef. Nature, Lond. 253, 533–534 (1975)
Olson, R. R.: The life history and larval ecology of the colonial ascidian-Prochloron symbiosis Didemnum molle, 269 pp. Ph.D. dissertation Harvard University 1984
Olson, R. R.: Photoadaptations of the Caribbean colonial ascidian-cyanophyte symbiosis Trididemnum solidum. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 170, 62–74 (1986)
Olson, R. R. and J. W. Porter: In situ measurement of photosynthesis and respiration in the ascidian-Prochloron symbiosis Didemnum molle. Proc. 5th int. coral Reef Congr. 5, 257–262 (1985). (Ed by C. Gabrie et al.. Moorea, French Polynesia: Antenne Museum-EPHE)
Pardy, R. L. and R. A. Lewin: Colonial ascidians with prochlorophyte symbionts: evidence for translocation of metabolites from alga to host. Bull. mar. Sci. 31, 817–823 (1981)
Sokal, R. R. and F. J. Rohlf. Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 2nd ed. 859 pp. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman & Co. 1981
Thinh, L. V., D. J. Griffiths and Y. Ngan: Studies of the relationship between the ascidian Diplosoma virens and its associated microscopic algae. II: Aspects of the ecology of the animal host. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 32, 795–804 (1981)
Vogel, S.: Current-induced flow through the sponge, Halichondria. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 147, 443–456 (1974)
Vogel, S.: Life in moving fluids. Princeton: Princeton University Press 1981
Wellington, G. M.: An experimental analysis of the effects of light and zooplankton on coral zonation. Oecologia 52, 311–320 (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 344 of the Australian Institute of Marine Science
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, R.R. Light-enhanced growth of the ascidian Didemnum molle/Prochloron sp. symbiosis. Marine Biology 93, 437–442 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401111
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401111