Abstract
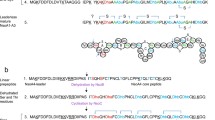
Lantibiotics form a group of modified peptides with unique structures, containing post-translationally modified amino acids such as dehydrated and lanthionine residues. In the gram-positive bacteria that secrete these lantibiotics, the gene clusters flanking the structural genes for various linear (type A) lantibiotics have recently been characterized. The best studied representatives are those of nisin (nis), subtilin (spa), epidermin (epi), Pep5 (pep), cytolysin (cyl), lactocin S (las) and lacticin 481 (lct). Comparison of the lantibiotic gene clusters shows that they contain conserved genes that probably encode similar functions.
The nis, spa, epi and pep clusters contain lanB and lanC genes that are presumed to code for two types of enzymes that have been implicated in the modification reactions characteristic of all lantibiotics, i.e. dehydration and thio-ether ring formation. The cyl, las and lct gene clusters have no homologue of the lanB gene, but they do contain a much larger lanM gene that is the lanC gene homologue. Most lantibiotic gene clusters contain a lanP gene encoding a serine protease that is presumably involved in the proteolytic processing of the prelantibiotics. All clusters contain a lanT gene encoding and ABC transporter likely to be involved in the export of (precursors of) the lantibiotics. The lanE, lanF and lanG genes in the nis, spa and epi clusters encode another transport system that is possibly involved in self-protection. In the nisin and subtilin gene clusters two tandem genes, lanR and lanK, have been located that code for a two-component regulatory system.
Finally, non-homologous genes are found in some lantibiotic gene clusters. The nisl and spal genes encode lipoproteins that are involved in immunity, the pepI gene encodes a membrane-located immunity protein, and epiD encodes an enzyme involved in a post-translational modification found only in the C-terminus of epidermin. Several genes of unknown function are also found in the las gene cluster.
A database has been assembled for all putative gene products of type A lantibiotic gene clusters. Database searches, multiple sequence alignment and secondary structure prediction have been used to identify conserved sequence segments in the LanB, LanC, LanE, LanF, LanG, LanK, LanM, LanP, LanR and LanT gene products that may be essential for structure and function. This database allows for a rapid screening of newly determined sequences in lantibiotic gene clusters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright L.M., Huala E. and Ausubel F.M. (1989) Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu. Rev. Genet. 23:311–336.
Banerjee S. and Hansen J.N. (1988) Structure and expression of a gene encoding the precursor of subtilin, a small protein antibiotic. J. Biol. Chem. 263:9508–9514.
Buchman G.W., Banerjee S. and Hansen J.N. (1988) Structure, expression, and evolution of a gene encoding the precursor of nisin, a small protein antibiotic. J. Biol. Chem. 263:16260–16266.
Chung Y.J. and Hansen J.N. (1992) Determination of the sequence of spaE and identification of a promoter in the subtilin (spa) operon in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bact. 174:6699–6702.
Chung Y.J., Steen M.T. and Hansen J.N. (1992) The subtilin gene of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 is encoded in an operon that contains a homolog of the hemolysin B transport protein. J. Bact. 174:1417–1422.
Comeau D.E., Ikenaka K., Tsung K. and Inouye M. (1985) Primary characterization of the protein products of the Escherichia coli ompB locus: structure and regulation of synthesis of the OmpR and EnvZ proteins. J. Bact. 164:578–584.
DeVos W.M., Jung G. and Sahl H.-G. (1991) In: Nisin and Novel Lantibiotics: Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Lantibiotics, Jung G. and Sahl H.-G. (eds.), Leiden: Escom Publishers, pp. 457–464.
DeVos W.M., Kuipers O.P., van derMeer J.R. and Siezen R.J. (1995) Maturation pathway of nisin and other lantibiotics: posttranslationally modified antimicrobial peptides exported by grampositive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 17:427–437.
DeVos W.M., Beerthuyzen M.M., Luesink E.J. and Kuipers O.P. (1995) Genetics of the nisin operon and the sucrose-nisin conjugative transposon Tn5276. In: Genetics of Streptococci, Enterococci and Lactococci (Ferretti J.J., Gilmore M.S., Klaenhammer T.R., Brown F., eds.) Dev.Biol.Stand. Basel, Karger, vol.85, pp 617–625.
Dodd H.M., Horn N. and Gasson M.J. (1990) Analysis of the genetic determinant for production of the peptide antibiotic nisin. J. Gen. Microbiol. 136:555–566.
Engelke G., Gutowski-Eckel Z., Hammelmann M. and Entian K.-D. (1992) Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic nisin: Genomic organization and and membrane localization of the NisB protein. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 3730–3743.
Engelke G., Gutowski-Eckel Z., Kiesau P., Siegers K., Hammelmann M. and Entian k.-D. (1994) Regulation of nisin biosynthesis and immunity in Lactococcus lactis 6F3. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60:814–825.
Fath M.J. and Kolter R. (1993) ABC transporters: bacterial exporters. Microbiol. Rev. 57:995–1017.
Felmlee T., Pellett S. and Welch R.A. (1985) Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J. Bacteriol. 163:94–105.
Garrido M.C., Herrero M., Kolter R. and Moreno F. (1988) The export of the DNA replication inhibitor microcin B17 provides immunity for the host cell. EMBO J. 7:1853–1862.
Gilmore m.S., Segarra R.A., Booth M.C., Bogie C.P., Hall L.R. and Clewell D.B. (1994) Genetic structure of the Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pAD1 encoded cytolytic toxin system and its relationship to lantibiotic determinants. J. Bacteriol. 176:7335–7344.
Gilmore M.S., Segarra R.A. and Booth M.C. (1990) An HlyB-type function is reguired for expression of the Enterococcus faecalis hemolysin/bacteriocin. Infect. Immunity 58:3914–3923.
Gilson L., Mahanty H.K. and Kolter R. (1990) Genetic analysis of an MDR-like export system: the secretion of colicin V. EMBO J. 9:3875–3884.
Gutowski-Eckel Z., Klein C., Siegers K., Hammelmann M. and Entian K.-D. (1994) Growth phase-dependent regulation and membrane localization of SpaB, a protein involved in biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60:1–11.
Havarstein L.S., Diep D.B. and Nes I.F. (1995) A family of bacteriocin ABC transporters carry out proteolytic processing of their substrates comcomitant with export. Mol. Microbiol. 16:229–240.
Hui F.M. and Morrison D.A. (1991) Genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: nucleotide sequence analysis shows comA, a gene required for competence induction, to be a member of the bacterial ATP-dependent transport protein family. J. Bacteriol. 173:372–381.
Hynes W.L., Ferretti J.J. and Tagg J.R. (1994) Cloning of the gene encoding streptococcin A-FF22, a novel lantibiotic produced by Streptococcus pyogenes, and determination of its nucleotide sequence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 1969–1971.
Hynes W.L., Friend V.L. and Ferretti J.J. (1994) Duplication of the lantibiotic structural gene in M-type 49 group A Streptococcus strains producing Streptococcin A-M49. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60:4207–4209.
Immonen T., Ye S., Ra R., Qiao M., Paulin L. and Saris P.E.J. (1995) The codon usage of the nisZ operon in Lactococcus lactis N8 suggests a non-lactococcal origin of the conjugative nisinsucrose transposou. DNA Sequence 5: 203–218.
Jack R.W. and Sahl H.-G. (1995) Unique peptide modifications involved in the biosynthesis of lantibiotics. Trends Biotech. 13:269–278.
Jack R.W., Tagg J.R. and Ray B. (1995) Bacteriocins of Grampositive bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 59:171–200.
Jung G. and Sahl H.-G. (1991) In: Nisin and Novel Lantibiotics: Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Lantibiotics, Jung G. and Sahl H.-G (eds.), Leiden: Escom Publishers, pp. 1–34.
Kaletta C. and Entian K.-D. (1989) Nisin, a peptide antibiotic: Cloning and sequencing of the nisA gene and posttranslational processing of its peptide product. J. Bact. 171: 1597–1601.
Kaletta C., Entian K.-D., Kellner R., Jung G., Reis M. and Sahl H.-G. (1989) Pep5, a new lantibiotic: structural gene isolation and prepeptide sequence. Arch. Microbiol. 152: 16–19.
Klein C., Kaletta C., and Entian K.-D. (1993) Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin is regulated by a histidine kinese/response regulator system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 296–303.
Klein C., Kaletta C., Schnell N. and Entian K.-D. (1992) Analysis of genes involved in biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 132–142.
Klein C. and Entian K.-D. (1994) Genes involved in self-protection against the lantibiotic subtilin produced by Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 2793–2801.
Kolter R. and Moreno F. (1992) Genetics of ribosomally synthesized peptide antibiotics. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 46: 141–163.
Kuipers O.P., Beerthuyzen M.M., Siezen R.J. and deVos W.M. (1993a) Characterization of the nisin gene cluster nisABTCIPR of Lactococcus lactis. Requirement of expression of the nisA and nisl genes for development of immunity. Eur. J. Biochem. 216: 281–291.
Kuipers O.P., Rollema H.S., deVos W.M. and Siezen R.J. (1993b) Biosynthesis and secretion of a precursor of nisin Z by Lactococcus lactis directed by the leader peptide of the homologous lantibiotic subtilin from Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett. 330: 23–27.
Kuipers O.P., Beerthuyzen M.M., deRuyter P.A., Luesink E. and DeVos W.M. (1995) Autoregulation of nisin biosynthesis in Lactococcus lactis by signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 27299–27304.
Kyte J. and Doolittle R.F. (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 157: 105–132.
Letoffe S., Delepelaire P. and Wandersman C. (1990) Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi: the specific secretion functions are analogous to those of Escherichia coli α-hemolysin. EMBO J. 9: 1375–1382.
Marugg J.D., Gonzalez C.F., Kunka B.S., Ledeboer A.M., Pucci M.J., Toonen M.Y., Walker S.A., Zoetmulder L.C.M. and Vandenbergh P.A. (1992) Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of genes involved in production of pediocin PA-1, a bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 2360–2367.
Meyer C., Bierbaum G., Heidrich C., Reis M., Sueling J., Iglesias-Wind M.I., Kempter C., Molitor E. and Sahl H.-G. (1995) Eur. J. Biochem., 232: 478–489.
Mulders J.W.M., Boerrigter I.J., Rollema H.S., Siezen R.J. and deVos W.M. (1991) Identification and characterization of the lantibiotic nisin Z, a natural nisin variant. Eur. J. Biochem. 201: 581–584.
Parkinson J.S. (1993) Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell Press 73: 857–871.
Peschel A., Augustin J., Kupke T., Stevanovic S. and Götz F. (1993) Regulation of epidermin biosynthetic genes by EpiQ. Mol. Microbiol. 9: 31–39.
Piard J.-Ch., Kuipers O.P., Rollema H.S., Desmazeaud M.J. and deVos W.M. (1993) Structure, organization, and expression of the lct gene for lacticin 481, a novel lantibiotic produced by Lactococcus lactis. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 16361–16368.
Reis M., Eschbach-Bludau M., Iglesias-Wind M.I., Kupke T. and Sahl H.-G. (1994) Producer immunity towards the lantibiotic Pep5: Identification of the immunity gene pepl and localization and functional analysis of its gene product. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 2876–2883.
Rince A., Dufour A., LePogam S., Thuault D., Bourgeois C.M> and LePennec J.P. (1994) Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of genes involved in production of lactococcin DR, a bacteriocin from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 1652–1657.
Ross K.F., Ronson C.W. and Tagg J.R. (1993) Isolation and characterization of the lantibiotic salivaricin A and its structural gene salA from Streptococcus salivarius 20P3. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 2014–2021.
Rost B. and Sander C. (1994) Combining evolutionary information and neural networks to predict secondary structure. Proteins 19: 55–72.
Sahl H.-G., Jack R.W. and Bierbaum G. (1995) Biosynthesis and biological activities of lantibiotics with unique post-translational modifications. Eur. J. Biochem. 230:827–853.
Schnell N., Entian K.-D., Götz F., Hörner T., Kellner R. and Jung G. (1989) Structural gene isolation and prepeptide sequence of gallidermin, a new lanthionine containing antibiotic. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 58: 263–268.
Schnell N., Engelke G., Augustin J., Rosenstein R., Ungermann V., Götz F. and Entian K.-D. (1992) Analysis of genes involved in the biosynthesis of lantibiotic epidermin. Eur. J. Biochem 204: 57–68.
Schnell N., Entian K.-D., Schneider U., Götz F., Zähner H., Kellner R. and Jung G. (1988) Prepeptide sequence of epidermin, a ribosomally synthesized antibiotic with four sulphide-rings. Nature 333: 276–278.
Segarra, R.A. (1992) Molecular characterization of the Enterococcus faecalis hemolysin/bacteriocin determinant. PhD Thesis, University of Oklahoma.
Segarra R.A., Booth M.C., Morales D.A., Huycke M.M. and Gilmore M.S. (1991) Molecular characterization of the Enterococcus faecalis cytolysin activator. Infect. Immunity 59: 1239–1246.
Seki T., Yoshikawa H., Takahashi H. and Saito H. (1987) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of phoP, the regulatory gene for alkaline phosphatase and phosphodiesterase in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bact. 169: 2913–2916.
Seki T., Yoshikawa H., Takahashi H. and Saito H. (1988) Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis phoR gene. J. Bact. 170: 5935–5938.
Shinde U. and Inouye M. (1993) Intramolecular chaperones and protein folding. Trends Biochem. Sci. 18: 442–446.
Siegers K. and Entian K.-D. (1995) Genes involved in immunity to the lantibiotic nisin produced by Lactococcus lactis 6F3. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 61: 1082–1089.
Siezen R.J., deVos M.W., Leunissen J.A.M. and Dijkstra B.W. (1991) Homology modelling and protein engineering strategy of subtilases, the family of subtilisin-like serine proteinases. Prot. Eng. 4:719–737.
Siezen R.J., Rollema H.S., Kuipers O.P. and deVos W.M. (1995a) Homology modelling of the Lactococcus lactis leader peptidase NisP and its interaction with the precursor of the lantibiotic nisin. Prot. Eng. 8: 117–125.
Siezen R.J., Leunissen J.A.M. and Shinde U. (1995b) Homology analysis of propeptides of subtilisin-like serine proteases (subtilases). In: Intramolecular Chaperones and Protein Folding (Shinde U. and Inouye M., eds.), R.G. Landes Company Biomedical Publishers, Austin, Texas, pp. 231–253.
Skaugen M., Nissen-Meyer J., Jung G., Stevanovic S., Sletten K., Abildgaard C.I.M. and Nes I.F. (1994) In vivo conversion of L-serine to D-alanine in a ribosomally synthesized polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 27183–27185.
Skaugen, M. (1994) Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ås, Norway
Steen M.T., Chung Y.J. and Hansen J.N. (1991) Characterization of the nisin gene as part of a polycistronic operon in the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis ATCC 11454. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57:1181–1188.
Stock J.B., Ninfa A.J. and Stock A.M. (1989) Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 53: 450–490.
Stoddard G.W., Petzel J.P., vanBelkum M.J., Kok J. and McKay L.L. (1992) Molecular analyses of the lactococcin A gene cluster from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis WM4. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58; 1952–1961.
Swanson R.V., Alex L.A. and Simon M.I. (1994) Histidine and aspartate phosphorylation: two-component systems and the limits of homology. TIBS 19: 485–490.
Van derKamp M., Van denHooven H.W., Konings R.N.H., Hilbers C.W., Van deVen F.J.M., Bierbaum G., Sahl H.-G., Kuipers O.P., Siezen R.J. and DeVos W.M. (1995) Elucidation of the primary structure of the lantibiotic epilancin-K7 from Staphylococcus epidermidis K7. Cloning of the epilancin-K7-encoding gene and NMR analysis of mature epilancin K7. Eut J. Biochem. 230:587–600.
Van derMeer J.R., Polman J., Beerthuyzen M.M., Siezen R.J., Kuipers O.P. and deVos W.M. (1993) Characterization of the Lactococcus lactis nisin A operon genes nisP, encoding a subtilisin-like serine protease involved in precursor processing, and nisR, encoding a regulatory protein involved in nisin biosynthesis. J. Bact. 175: 2578–2588.
Van derMeer J.R., Rollema H.S., Siezen R.J., Beerthuyzen M.M., Kuipers O.P. and deVos W.M. (1994) Influence of amino acid substitutions in the nisin leader peptide on biosynthesis and secretion of nisin by Lactococcus lactis. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 3555–3562.
Venema K., Kok J., Marugg J.D., Toonen M.Y., Ledeboer A.M., Venema G., and Chikindas M.L. (1995) Functional analysis of the pediocin operon of Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0: PedB is the immunity protein and PedD is the precursor processing enzyme. Mol. Microbiol., 17: 515–522.
VonHeijne G. (1989) The structure of signal peptides from bacterial lipoproteins. Protein Eng. 2:531–534.
Walker J.E., Sarste M., Runswick M.J. and Gay N.J. (1982) Distantly related sequences in the α-and β-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1: 945–951.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siezen, R.J., Kuipers, O.P. & de Vos, W.M. Comparison of lantibiotic gene clusters and encoded proteins. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 69, 171–184 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399422
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399422