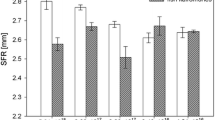
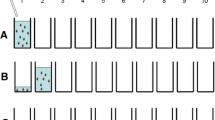
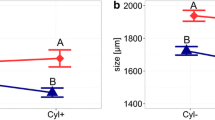
Summary
Data are presented which make it most probable that selection according to relative visibility (represented by body size and egg ratio) and relative mortality stabilize the coexistence of Daphnia hyalina hyalina Leydig, D. galeata gracilis Hellich and D. cucullata Sars in the prealpine Klostersee. The results are based on multiple and partial correlation analyses which showed positive partial correlation between relative size and/or relative egg ratio and/or relative abundance, and the index of selectivity (W) according to Vanderploeg and Scavia (1979). Further it turned out that besides size, abundance, and egg ratio, the lake temperature but not other environmental parameters are related with the mortality of Daphnia. From these data a verbal descriptive model is derived which explains the seasonal segregation and stable coexistence of the three species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archibald CP (1975) Experimental observations on the effects of predation by goldfish Carassius auratus on the zooplankton of a small saline lake. J Fish Res Board Can 32: 1589–1594
Bohl E (1974) Untersuchungen über die Mortalität der sympatrischen Daphnienarten D. hyalina und D. cucullata (Crustacea, Cladocera) durch Fischfraß unter besonderer Berücksichtigung ihrer Abhängigkeit von der Lichtintensität. Diploma thesis University of Munich
Bohl E (1979) Mechanismen der Nahrungsselektivität planktivorer Cypriniden. Doctoral thesis University of Munich
Bohl E (1980) Diel pattern of pelagic distribution and feeding in planktivorous fish. Oecologia (Berl) 44: 368–375
Brooks JL, Dodson SI (1965) Predation, body size and composition of plankton. Science 150: 28–35
Confer JL, Blades PI (1975) Reaction distance to zooplankton by Lepomis gibbosus. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 19: 2493–2497
Cooper WE (1965) Dynamics and production of a natural population of fresh water amphipod, Hyalella azteca. Ecol Monogr 35: 377–394
Gessner F (1953) Die Limnologie des Naturschutzgebietes Seeon. Arch Hydrobiol 47: 553–624
Hall DJ (1964) An experimental approach to the dynamics of a natural population of Daphnia galeata mendotae. Ecol 45: 94–112
Hall DJ, Cooper WE, Werner EE (1970) An experimental approach to the production dynamics and structure of freshwater animal communities. Limnology and Oceanography 15: 839–928
Hrbacek H, Hrbackova-Esslova M (1960) Fish stock as a protective agent in the occurrence of the slow developing dwarf species and strains of the genus Daphnia. Int Rev Hydrobiol 45: 355–358
Jacobs J (1967) Untersuchungen zur Funktion und Evolution der Zyklomorphose bei Daphnia, mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Selektion durch Fische. Arch Hydrobiol 62: 467–541
Jacobs J (1977a) Coexistence of similar zooplankton species by differential adaptation to reproduction and escape in an environment with fluctuating food and enemy densities. II. Field data analysis of Daphnia. Oecologia (Berl) 30: 313–329
Jacobs J (1977b) Coexistence of similar zooplankton species by differential adaptation to reproduction and escape in an environment with fluctuating food and enemy densities. I. A model. Oecologia (Berl) 29: 233–247
Jacobs J (1978) Coexistence of similar zooplankton species by differential adaptation to reproduction and escape in an environment with fluctuating food and enemy densities. III. Laboratory experiments. Oecologia (Berl) 35: 35–54
Jacobs J (1979) The influence of prey size, light intensity, and alternative prey, on the selectivity of plankton feeding fish. Verh. Internat Verein Limnol 20 (Kopenhagen), 2461–2466
Kettle D, O'Brien WJ (1978) Vulnerability of arctic zooplankton species to predation by small lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) J Fish Res Board Can 35: 1495–1500
Kucklentz V (1975) Untersuchungen über selectives Fressen bei Forellen und Elritzen. Doctoral thesis, University of Munich
Lampert W (1971) Untersuchungen zur Biologie und Populationsdynamik der Coregonen im Schluchsee. Arch Hydrobiol/Suppl 38: 237–314
Mellors WK (1975) Selective predation of ephippial Daphnia and the resistance of ephippial eggs to digestion. Ecol 56: 974–980
Metz JP (1974) Die Invertebratendrift an der Oberfläche eines Voralpenflusses und ihre selektive Ausnutzung durch die Regenbogenforellen (Salmo gairdneri). Oecologia (Berl) 14: 247–267
Murdoch WW, Avery S, Smyth EB (1975) Switching in predatory fish. Ecol 56: 1094–1105
Neill WE (1975) Resource partitioning by competing microcrustaceans in stable laboratory microoecosystems. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 19: 2885–2890
Nie NH, Hull CH, Jenkins JG, Steinbrenner K, Bent DH (1975) SPSS Statistical package for the social sciences. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Northcote TG, Clarotto R (1975) Limnetic macrozooplankton and fish predation in some coastal British Columbia lakes. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 19: 2378–2393
O'Brien WJ, Slade NA, Vinyard GL (1976) Apparent size as the determinant of prey selection by bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus). Ecol 57: 1304–1310
Reddy SR (1975) Effect of water temperature on the predatory efficiency of Gambusia affinis. Experientia 31: 801–802
Seghers BH (1975) Role of gill rakers in size-selective predation by lake white fish Coregonus clupeaformis (Mitchill). Verh Internat Verein Limnol 19: 2410–2405
Seitz A (1977) Die Bedeutung von Umweltfaktoren, Konkurrenz und Räuber-Beute-Beziehungen für die Koexistenz dreier Daphnienarten. Eine Freilandanalyse im Seeoner Klostersee. Doctoral thesis in Biology. University Munich
Seitz A (1979) On the calculation of birth rates and death rates in fluctuating populations with continuous recruitment. Oecologia (Berl) 41: 343–360
Seitz A (1980) The coexistence of three species of Daphnia in the Klostersee. I. Field studies on the dynamics of reproduction. Oecologia (Berl) 45: 117–130
Stavn RH (1975) The effects of predator pressure on species composition and vertical distribution of Daphnia in Piedmont Lakes of North Carolina, U.S.A. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 19: 2891–2897
Tappa DW (1965) The dynamics and the association of six limnetic species of Daphnia in Aziscoos Lake. Maine Ecol Monogr 35: 395–423
Threlkeld ST (1979) The midsummer dynamics of the two Daphnia species in Wintergreen Lake, Michigan Ecol 60: 165–179
Vanderploeg HA, Scavia D (1979) Two electivity indices for feeding with special reference to zooplankton gracing. J Fish Res Board Can 36: 362–365
Werner EE, Hall DJ (1974) Optimal foraging and the size selection of prey by the bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus) Ecol 55: 1042–1052
Wright JC (1965) The population dynamics and production of Daphnia in Canyon Ferry reservoir, Montana. Limnology and Oceanography 10: 583–590
Zaret TM (1972) Predators, invisible prey and the nature of polymorphism in the Cladocera. Limnology and Oceanography 17: 171–184
Zaret TM, Kerfoot WC (1975) Fish predation on Bosmina longirostris: Body size versus visibility selection. Ecol 56: 232–237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seitz, A. The coexistence of three species of Daphnia in the Klostersee. Oecologia 47, 333–339 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398526
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398526