Abstract
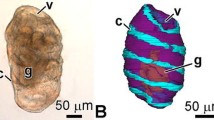
Structural changes occurring in the alimentary tract, perivisceral cavity, foot, hypobranchial gland, and gills of larval and post-larval Solemya reidi, a gutless protobranch bivalve, were examined using both light and electron microscopy at 1, 3, 5, 18, 34 and 42 d after fertilization. A fully developed mouth, esophagus, and anus, together with the rudiments of a stomach and rectum are present before metamorphosis. At metamorphosis, the cells making up the dorsal and lateral walls of the stomach dissociate, and by 18 d the mouth and anus are the only remaining portions of the alimentary tract. The larval test is ingested into the perivisceral cavity at metamorphosis and its autolysis continues through at least the 42nd day after fertilization. The foot, gills, and hypobranchial gland, poorly developed at metamorphosis, develop slowly and are still undergoing extensive morphogenesis at 42 d.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Allen, J. A. (1985). The recent Bivalvia: their form and evolution. In: Trueman, E. R., Clarke, M. R. (eds.) The mollusca, Vol. 10. Evolution. Academic Press, New York, p. 337–403
Allen, J. A., Sanders, H. L. (1969). Nucinella serrei Lamy (Bivalvia: Protobranchia) a monomyarian solemyid and possible living actinodont. Malacologia 7: 381–396
Allen, J. A., Sanders, H. L. (1982). Studies on the deep-sea Protobranchia; the subfamily Spinulinae (family Nuculanidae). Bull. Mus. comp. Zool. Harv. 150: 1–30
Beklemishev, W. N. (1969). Principles of comparative anatomy of invertebrates. Vol. 1 and 2. [Transl. from Russian by J. M. MacLennan]. Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh
Bernard, F. R. (1980). A new Solemya s. str. from the northeastern Pacific (Bivalvia: Cryptodonta). Venus Kyoto 39: 17–23
Bullock, T. H., Horridge, G. A. (1965). Structure and function in the nervous system of invertebrates, Vol. II. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco
Cranfield, H. J. (1973). A study of the morphology, ultrastructure and histochemistry of the foot of the pediveliger of Ostrea edulis. Mar. Biol. 22: 187–202
D'Asaro, C. N. (1967). The morphology of larval and postlarval Chione cancellata Linne (Eulamellibranchia: Veneridae) reared in the laboratory. Bull. mar. sci. Gulf Caribb. 17: 949–972
Drew, G. A. (1897). Notes on the embryology, anatomy, and habits of Yoldia limatula, Say. Johns Hopkins Univ. Circ. 17: 11–14
Drew, G. A. (1899a). The anatomy, habits, and embryology of Yoldia limatula, Say. Mem. biol. Lab. Johns Hopkins Univ. 4: 1–37
Drew, G. A. (1899b) Some observations on the habits, anatomy and embryology of members of the Protobranchia. Anat. Anz. 15: 493–519
Drew, G. A. (1901). The life history of Nucula delphinodonta (Mighels). Q. J. microsc. Sci. 44: 313–391
Elston, R. (1980). Functional anatomy, histology and ultrastructure of the soft tissues of the larval American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Proc. natn. Shellfish. Ass. 70: 65–93
Gureeva, M. A., Ivanov, A. V. (1986). On the coelomic mesoderm formation in embryos of Oligobrachia mashikoi (Pogonophora). Zool. Zh. 65: 780–788
Gustafson, R. G., Reid, R. G. B. (1986). Development of the pericalymma larva of Solemya reidi (Bivalvia: Cryptodonta: Solemyidae) as revealed by light and electron microscopy. Mar. Biol. 93: 411–427
Hampson, G. R. (1971). A species pair of the genus. Nucula (Bivalvia) from the eastern coast of the United States. Proc. malac. Soc. Lond. 39: 333–342
Ivanov, A. V. (1963). Pogonophora. Academic Press, New York
Jouin, C. (1979). Description of a free-living polychaete without gut: Astomus taenioides n. gen., n. sp. (Protodrilidae, Archiannelida). Can. J. Zool. 57: 2448–2456
Kuznetsov, A. P., Shileiko, A. A. (1984). Gutless Protobranchia (Bivalvia). Biol. Nauki (Mosk) 0 (2): 39–49
Lane, D. J. W., Nott, J. A. (1975). A study of the morphology, fine structure and histochemistry of the foot of the pediveliger of Mytilus edulis L. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 55: 477–495
Lane, D. J. W., Nott, J. A., Crisp, D. J. (1982). Enlarged stem glands in the foot of the post-larval mussel Mytilus edulis: adaptation for bysso-pelagic migration. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 62: 809–818
Morton, B. S. (1977). The hypobranchial gland in the Bivalvia. Can. J. Zool. 55: 1225–1234
Ott, J., Rieger, G., Rieger, R., Enderes, F. (1982). New mouthless interstitial worms from the sulfide system: symbiosis with prokaryotes. Pubbl. Staz. zool. Napoli (I: Mar. Ecol.) 3: 313–333
Owen, G. (1959). The ligament and digestive system in the taxodont bivalves. Proc. malac. Soc. Lond. 33: 215–223
Owen, G. (1961). A note on the habits and nutrition of Solemya parkinsoni (Protobranchia: Bivalvia). Q. Jl microsc. Sci. 102: 15–21
Pelseneer, P. (1891). Contribution à l'étude des lamellibranches. Archs. Biol. Paris 11: 147–312
Raven, C. P. (1966). Morphogenesis. The analysis of molluscan development. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Reid, R. G. B. (1980). Aspects of the biology of a gutless species of Solemya (Bivalvia: Protobranchia). Can. J. Zool. 58: 386–393
Reid, R. G. B., Bernard, F. R. (1980). Gutless bivalves. Science, N.Y. 208: 609–610
Reid, R. G. B., Brand, D. G. (1987). Observations on Australian Solemyidae. J. Aust. malac. Soc. 8: 41–50
Richards, K. L., Fleming, T. P., Jamieson, B. G. M. (1982). An ultrastructural study of the distal epidermis and the occurrence of subcuticular bacteria in the gutless tubificid Phallodrilus albidus (Oligochaeta: Annelida). Aust. J. Zool. 30: 327–336
Stempell, W. (1899). Zur Anatomie von Solemya togata Poli. Zool. Jb. (Abt. Anat. Ont. Tiere) 13: 89–170
Thompson, T. E. (1960). The development of Neomenia carinata Tullberg (Mollusca Aplacophora). Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 153: 263–278
Yonge, C. M. (1939). The protobranchiate Mollusca: A functional interpretation of their structure and evolution. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 230: 79–147
Yonge, C. M. (1962). On the primitive significance of the byssus in the Bivalvia and its effects in evolution. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 42: 113–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Lawrence, Tampa
Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution Contribution No. 601.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gustafson, R.G., Reid, R.G.B. Larval and post-larval morphogenesis in the gutless protobranch bivalve Solemya reidi (Cryptodonta: Solemyidae). Mar. Biol. 97, 373–387 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397768
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397768