Abstract
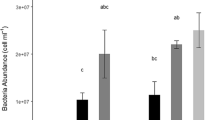
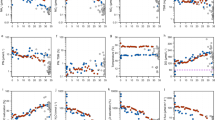
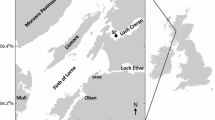
Rates of ammonium remineralization were determined using a 15N isotope dilution technique for two oceanic regions, one coastal region, and one estuarine region, covering a wide range of ambient nutrient, light, and temperature conditions. Results showed that NH +4 assimilative and regenerative fluxes were primarily in balance, even when the ambient nitrogenous pool was completely dominated by NO -3 . Variations in uptake and remineralization rates relative to time of day and season were also determined. Size fraction studies at several of the sites showed that the smallest size fraction (<10 μm) was usually the most important in remineralizing NH +4 , and the importance of the apparent bacterial fraction (<1 μm) may increase following blooms. The results support the concept that, over a wide variety of conditions, the fluxes of NH +4 remineralization and uptake are tightly coupled; phytoplankton are able to utilize NH +4 at the rate that it is produced by heterotrophic processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Alexander, V.: Relationships between turnover rates in the biological nitrogen cycle and algal productivity. In: Dynamics of the nitrogen cycle in lakes, pp. 37–50. Fairbanks, Alaska: Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska 1970. (Rep. Inst. mar. Sci. Univ. Alaska No. R 71-7)
Axler, R. P., G. W. Redfield and C. R. Goldman: The importance of regenerated nitrogen to phytoplankton productivity in a subalpine lake. Ecol. 62, 345–354 (1981)
Beers, J. R.: Ammonia and inorganic phosphorus, excretion by the planktonic chaetognath, Sagitta hispida Conant. J. Cons. perm. int. Explor. Mer. 29, 123–129 (1964)
Biggs, D. C.: Respiration and ammonium excretion of open-ocean gelatinous zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22, 108–117 (1977)
Biggs, D. C.: Non-biogenic fixed nitrogen in Antarctic surface waters Nature. Lond. 276 96–97 (1978)
Blackburn, T. H.: Method for measuring rates of NH +4 turnover in anoxic marine sediments, using a 15N−NH +4 dilution technique. Appl. environ. Microb. 37, 760–765 (1979)
Bremner, J. M.: Inorganic forms of nitrogen. In: Methods of soil analysis, part 2, Vol. 9, pp 1179–1237. Ed. by C. A. Black. Madison, Wisconsin: American Soc. of Agronomy 1965
Bremner, J. M. and A. P. Edwards. Determination and isotoperatio analysis of different forms of nitrogen in soils: I. Apparatus and procedure for distillation and determination of ammonium. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29, 504–507 (1965)
Bremner, J. M. and D. R. Keeney: Steam distillation methods for determination of ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite. Anal. chim. Acta 32, 485–495 (1965)
Bremner, J. M. and D. R. Keeny: Determination and isotoperatio analysis of different forms of nitrogen, in soils. 3. Exchangeable ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite by extraction-distillation methods. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 30, 577–582 (1966)
Brezonik, P. L.: Nitrogen: sources and transformations in natural waters. In: Nutrients in natural waters, pp 1–47. Ed. by H. E. Allen and J. R. Kramer. New York: Wiley 1972
Caperon, J., D. Schell, J. Hirota and E. Laws: Ammonium excretion rates in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii, measured by a 15N isotope dilution technique. Mar. Biol. 54, 33–40 (1979)
Corner, E. D. S. and B. S Newell: On the nutrition and metabolism of zooplankton. IV. The forms of nitrogen excreted by Calanus. J. mar. biol. Assoc. U.K. 47, 113–120 (1967)
Dugdale, R. C. and J. J. Goering: Uptake of new and regenerated forms of nitrogen in primary productivity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 12, 196–206 (1967)
Eppley, R. W. and B. J. Peterson: Particulateorganic matter flux and planktonic new production in the deep sea. Nature, Lond. 282, 677–680 (1979)
Glibert, P. M., D. C. Biggs and J. J. McCarthy: Utilization of ammonium and nitrate during austral summer in the Scotia Sea. Deep-Sea Res. 29, 837–850 (1982a)
Glibert, P. M. and J. C. Goldman: Rapid ammonium uptake by marine phytoplankton. Mar. Biol. Lett. 2, 25–31 (1981)
Glibert, P. M., J. C. Goldman and E. J. Carpenter: Seasonal variations in the utilization of ammonium and nitrate by phytoplankton in Vineyard Sound Massachusetts. Mar. Biol. (1982b). (In press)
Glibert, P. M., F. Lipschultz, J. J. McCarthy and M. A. Altabet: Isotope dilution models of uptake and remineralization of ammonium by marine plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27, 639–650 (1982c)
Goldman, J. C., C. D. Taylor and P. M. Glibert: Nonlinear timecourse uptake of carbon and ammonium by marine phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 6, 137–148 (1981)
Haines, E. B.: Nutrient inputs to the coastal zone: the Georgia and South Carolina shelf. In: Estuarine research, vol. 1, pp 303–324. Ed. by L. E. Cronin. New York: Academic Press 1975
Harris, E.: The nitrogen cycle in Long Island Sound. Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Coll. 17, 31–65 (1959)
Harrison, W. G.: Experimental measurement of nitrogen remineralization in coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 684–694 (1978)
Harrison, W. G.: Nutrient regeneration and primary production in the sea, pp 433–460 Ed. by P. G. Falkowski New York Plenum Press 1980
Jacobs, S. S., A. L. Gordon and A. F. Amos: Effect of glacial ice melting on the Antarctic surface water. Nature, Lond. 277, 468–471 (1979)
Jawed, M.: Body nitrogen and nitrogenous excretion in Neomysis rayii Murdoch and Euphausia pacifica hansen. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 748–754 (1969)
Johannes, R. E.: Phosphorus excretion and body size in marine animals: Microzooplankton and nutrient regeneration. Science, N. Y. 146, 923–924 (1964)
Johannes, R. E.: Nutrient regeneration in lakes and oceans. Adv. Microbiol. Sea 1, 203–212 (1968)
mcCarthy, J. J. and J. C. Goldman: Nitrogenous ntrition of marine phytoplankton in nutrient depleted waters. Science, N.Y. 203, 670–672 (1979)
McCarthy, J. J. and D. Kamykowski: Urea and other nitrogenous nutrients in La Jolla Bay during February, March, and April 1970. Fish. Bull. U.S. 70, 1261–1274 (1972)
McCarthy, J. J., W. R. Taylor and J. L. Taft: The dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorus cycling in the open waters of the Chesapeake Bay. In. Marine chemistry in the coastal, environment, pp 664–681. Ed. by T. M. Church. Philadelphia, Penn: Am. Chem. Soc. 1975
McCarthy, J. J., W. R. Taylor and J. L. Taft: Nitrogenous nutrition, of the plankton in the chesapeake Bay. I. Nutrient availability and phytoplankton preferences. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22, 996–1011 (1977)
McCarthy, J. J. and T. E. Whitledge: Nitrogen excretion by the anchovy (Engraulis mordax and ringens) and jack mackeral (Trachurus symmetricus). Fish Bull., U.S. 70, 395–401 (1972)
Nixon, S. W., C. A. Oviatt and S. S. Hale: Nitrogen regeneration and the metabolism of coastal marine bottom communities. In: The role of terrestrial and aquatic organisms in decomposition processes, pp 269–283 Ed. by J. M. Anderson and A. Macfayden. Oxford, England: Blackwell 1975
Olson, R. J.: Nitrate and ammonium uptake in Atarctic, waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25, 1064–1074 (1980)
Paasche, E. and S. Kristiansen: Ammonium regeneration by microzooplankton in the Oslofjord, Norway. Mar. Biol. 69 55–63 (1982)
Parker, B. C., L. E. Heiskell W. J. Thompson, and E. J. Zeller: Nonbiogenic fixed nitrogen in Antarctica and some ecological implications. Nature, Lond. 271, 651–652 (1978)
Seki, H., T. Tsuji and A. Hattori: Effect of zooplankton grazing on the formation of the anoxic layer in Tokyo Bay. Estuar. coast. mar. Sci. 2, 145–151 (1974)
Smith, S. L.: Nutrient regeneration by zooplankton during a red tide off Peru, with notes on biomass and species composition of zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 49, 125–132 (1978a)
Smith, S. L.: The role of zooplankton in the nitrogen dynamics of a shallow estuary. Estuar coast. mar. Sci. 7, 555–565 (1978b)
Solórzano, L.: Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 799–801 (1969)
Strickland, J. D. H. and T. R. Parsons: A practical handbook of seawater analysis, 310 pp. Ottowa: Fish. Res. Bd Can. 1972
Walsh, J. J. and R. C. Dugdale: A simulation model of nitrogen flow in the Peruvian upwelling system. Inv. Pesq. 35, 309–330 (1971)
Wheeler, P. A., P. M. Glibert, and J. J. McCarthy: Ammonium uptake and incorporation by Chesapeake Bay phytoplankton: Short-term uptake kinetics. Limnol. Oceanogr. (In press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S.K. Pierce, College Park
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glibert, P.M. Regional studies of daily, seasonal and size fraction variability in ammonium remineralization. Mar. Biol. 70, 209–222 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397687
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397687