Abstract
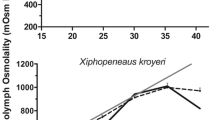
The effects of salinity on oxygen consumption was investigated in cultured Penaeus monodon Fabricius and P. stylirostris Stimpson postlarvae (32 and 35 d after metamorphosis, respectively). In both species, no difference appeared between non-acclimated and fully-acclimated individuals. The metabolic rate was unaffected by salinity variations, but P. stylirostris displayed a tendency (non-significant at P<0.05) to increase respiration at lower salinities. These observations are discussed in reference to the ecology of the young prawns.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Anonymous: Acclimation of Penaeus monodon postlarvae in freshwater, 6pp. Iloilo, The Philippines: Freshwater Fisheries Station, Aquaculture Department, South East Asian Fisheries Development Center 1980. (Limited publication)
Bages, M. and L. Sloane: Effects of dietary protein and starch levels on growth and survival of Penaeus monodon Fabricius postlarvae. Aquaculture, Amsterdam (In press). (1981)
Bertalanffy, L. von: Quantitative laws in metabolism and growth. Q. Rev. Biol. 32, 217–231 (1957)
Bulnheim, H. P.: Respiratory metabolism of Idotea balthica (Crustacea, Isopoda) in relation to environmental variables, acclimation processes and moulting. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 26, 464–480 (1974)
Chung, K. S.: A note on salinity preference of Penaeus brasiliensis. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 46, p. 389 (1980)
Gyllenberg, G. and G. Lundqvist: The effects of temperature and salinity on the oxygen consumption of Eurytemora hirundoides (Crustacea, Copepoda). Annls zool. fenn. 16, 205–208 (1979)
Hagerman, L.: The oxygen consumption of Crangon vulgaris (Fabricius) (Crustacea, Natantia) in relation to salinity. Ophelia 7, 283–292 (1970)
Jones, M. B.: Survival and oxygen consumption in various salinities of three species of Idotea (Crustacea, Isopoda) from different habitats. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 48, 501–506 (1974)
Kinne, O.: Physiology of estuarine organisms with special reference to salinity and temperature: general aspects. In: Estuaries, pp. 525–540. Washington, D.C.: American Association for the Advancement of Science 1967. (Publs Am. Ass. Advmt Sci. No. 83)
Kutty, M. N., G. Murugapoopathy and T. S. Krishnan: Influence of salinity and temperature on the oxygen consumption in young juveniles of the Indian prawn Penaeus indicus. Mar. Biol. 11, 125–131 (1971)
Lance, J.: Respiration and osmotic behaviour of the copepod Acartia tonsa in diluted sea-water. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 14, 155–165 (1965)
Lasserre, P. et J. Renaud-Mornant: Interprétation écophysiologique des effets de température et de salinité sur l'intensité respiratoire de Derocheilocaris remanei biscayensis Delamare, 1953 (Crustacea, Mystacocarida). C.r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris (sér. D). 272, 1159–1162 (1971)
Leffler, Ch. W.: Ionic and osmotic regulation and metabolic response to salinity of juvenile Callinectes sapidus Rathburn. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 52, 545–549 (1975)
Mair, J. McD.: Salinity and water type preference of four species of postlarval shrimp (Penaeus) from West Mexico. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 45, 68–82 (1980)
McFarland, W. N. and P. E. Pickens: The effects of season, temperature and salinity on standard and active oxygen consumption of the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes vulgaris (Say). Can. J. Zool. 43, 571–585 (1965)
Rao, K. P.: Oxygen consumption as a function of size and salinity in Metapenaeus monoceros Fab. from marine and brackishwater environments. J. exp. Biol. 35, 307–313 (1958)
Singh, T.: The isoosmotic concept in relation to the aquaculture of the giant prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 20, 251–256 (1980)
Venkataramiah, A., G. J. Lakshmi, P. Biesot, J. D. Valleau and G. Gunter: Studies on the time course of salinity and temperature adaptation in the commerical brown shrimp Penaeus aztecus Ives, 308 pp. Contract Report H-77-1 for Office, Chief of Engineers, U.S. Army Washington, D.C. (Contract DACW 39-73-C-0115). Vicksburg, Miss.: U.S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station 1977
Venkataramiah, A., G. J. Lakshmi and G. Gunter: A review of the effects of some environmental and nutritional factors on brown shrimp Penaeus aztecus Ives in laboratory cultures. Proc. 9th Eur. mar. Biol. Symp. 523–547 (1975). (Ed. by H. Barnes, Aberdeen: Aberdeen University Press)
Vlasblom, A. G. and J. H. B. W. Elgershuizen: Survival and oxygen consumption of Praunus flexuosus and Neomysis integer and embryonic development of the latter species, in different temperature and chlorinity combinations. Neth. J. Sea Res. 11, 305–315 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaudy, R., Sloane, L. Effect of salinity on oxygen consumption in postlarvae of the penaeid shrimps Penaeus monodon and P. stylirostris without and with acclimation. Mar. Biol. 65, 297–301 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397125
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397125