Abstract
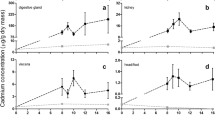
Specimes of bay scallops, Argopecten irradians, collected from shallow-water eel-grass beds near Beaufort, North Carolina (USA) in September 1979, were exposed to 0.7 ppm cadmium in flowing seawater for 5 d. This exposure resulted in a massive extrusion of the calcified concretions of most of the kidney epithelial cells, although marked morphological damage consisting of cytoplasmc degeneration was apparent in only a few focal areas of the kidney. In addition, unique cytoplasmic membrane-bound bodies were observed in epithelial cells of cadmium-treated but not control scallop kidneys. In some cells, these bodies appeared to fuse with the main concretion vacuole. Kidneys of cadmium-treated scallops accumulated cadmium to 200 ppm on a wet wt basis; of this 60% was associated with concretions (2 000 ppm dry wt) and 38% with the membranous pellet obtained after ultracentrifugation at 105 000 g for 1 h. Approximately 2% of total kidney cadmium was associated with the cytosolic fractions but, unlike zinc or manganese, which were bound to either high or low molecular weight species, a large component of the cadmium in this fraction was bound to a protein peak of approximately 21 000 daltons. Results of this study indicate that kidney concretions of A. irradians play a major role in the control of renal cadmium accumulation and excretion and hence the toxicity of cadmium to this organism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Andrews, P.: Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 91, 222–233 (1964)
Bahner, L. H., C. D. Craft and D. R. Nimmo: A saltwater flowthrough bioassay method with controlled temperature and salinity. Progve Fish Cult. 37, 126–131 (1975)
Carmichael, N. G., K. S. Squibb, D. W. Engel and B. A. Fowler: Metals in the molluscan kidney: uptakte and subcellular distribution of 109Cd, 54Mn and 65Zn by the clam, Mercenaria mercenaria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65A, 203–206 (1980)
Carmichael, N. G., K. S. Squibb and B. A. Fowler: Metals in the molluscan kidney: a comparison of two closely related bivalve species (Argopecten) using X-ray microanalysis and atomic absorption spectroscopy. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 39, 1149–1155 (1979)
Cherian, M. G., R. A. Goyer and L. Delaquerriere-Richardson: Cadmium-metallothionein-induced nephropathy. Toxic. appl. Pharmac. 38, 399–408 (1976)
Engel, D. W. and B. A. Fowler: Copper and cadmium-induced changes in the metabolism and structure of molluscan gill tissue. In: Marine pollution: functional responses, pp 609–624. Ed. by W. B. Vernberg, F. P. Thurberg and A. Calabrese. New York: Academic Press 1979
Fowler, B. A.: The international conference on environmental cadmium: an overview. Envir. Hlth Perspectives 28, 301–304 (1979)
Fowler, B. A. and G. F. Nordberg: The renal toxicity of cadmium metallothionein: morphometric and x-ray microanalytical studies. Toxic. appl. Pharmac. 45, 609–624 (1978)
George, S.G., E. Carpene, T. L. Coombs, J. Overnell and A. Youngson: Characterization of cadmium-binding proteins from mussels, Mytilus edulis (L), exposed to cadmium. Biochim. biophys. Acta 580, 225–233 (1979)
George, S. G. and B. J. S. Pirie: The occurrence of cadmium in sub-cellular particles in the kidney of the marine mussel, Mytilus edulis, exposed to cadmium. Biochim. biophys. Acta 580, 234–244 (1979)
George, S. G., B. J. S. Pirie and T. L. Coombs: Isolation and elemental analysis of metal-rich granules from the kidney of the scallop, Pecten maximus (L.). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 42, 143–156 (1980)
Howard, A. G. and G. Nickless: Heavy metal complexation in polluted molluscs. I. Limpets (Patella vulgata and Patella intermedia). Chem. biol. Interactions 16, 107–114 (1977a)
Howard, A. G. and G. Nickless: Heavy metal complexation in polluted molluscs. II. Oysters (Ostrea edulis and Crassostrea gigas). Chem. biol. Interactions 17, 257–263 (1977 b)
Marshall, A. T. and V. Talbot: Accumulation of cadmium and lead in the gills of Mytilus edulis: x-ray microanalysis and chemical analysis. Chem. biol. Interactions 27, 111–123 (1979)
Overnell, J. and T. L. Coombs: Purification and properties of plaice metallothionein, a cadmium-binding protein from the liver of the plaice (Pleuronectes platessa). Biochem. J. 183, 277–283 (1979)
Ridlington, J. W. and B. A. Fowler: Isolation and partial characterization of cadmium-binding protein from the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Chem. biol. Interactions 25, 127–138 (1979)
Squibb, K. S., J. W. Ridlington, N. G. Carmichael and B. A. Fowler: Early cellular effects of circulating cadmium-thronein on kidney proximal tubules. Envir. Hlth Perspectives 28, 287–296 (1979)
Webb, M.: The metallothioneins. In: The chemistry, biochemistry and biology of cadmium, pp 285–340. Ed. by M. Webb. New York: Elsevier/North-Holland 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carmichael, N.G., Fowler, B.A. Cadmium accumulation and toxicity in the kidney of the bay scallop Argopecten irradians . Marine Biology 65, 35–43 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397065
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397065