Abstract
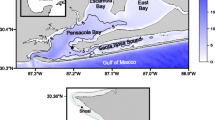
Pelagic primary production and benthic and pelagic aerobic metabolism were measured monthly at one site in the estuarine plume region of the nearshore continental shelf in the Georgia Bight. Benthic and water-column oxygen uptake were routinely measured and supplemented with seasonal measures of total carbon dioxide flux. Average respiratory quotients were 1.18:1 and 1.02:1 for the benthos and water column, respectively. Benthic oxygen uptake ranged from 1.23 to 3.41 g O2 m-2 d-1 and totalled 756 g O2 m-2 over an annual period. Water column respiration accounted for 60% of total system metabolism. Turnover rates of organic carbon in sediment and the water column were 0.09 to 0.18 yr-1 and 6.2 yr-1, respectively. Resuspension appeared to control the relative amounts of organic carbon, as well as the sites and rates of organic matter degradation in the benthos and water column. Most of the seasonal variation in benthic and pelagic respiration could be explained primarily by temperature and secondarily by primary productivity. On an annual basis, the shelf ecosystem appeared to be heterotrophic; primary production was 73% of community metabolism, which was 749 g C m-2 yr-1. The timing of heterotrophic periods through the year appeared to be closely related to both river discharge and the periodicity of growth and death of marsh macrophytes in the adjacent estuary. The results of this study support the estuarine “outwelling” hypothesis of Odum (1968).
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Blanton, J. O.: Ocean currents along a nearshore frontal zone on the continental shelf of the southeastern United States. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 11 (12), 1627–1637 (1981)
Blanton, J. O. and L. P. Atkinson: Physical transfer processes between Georgia tidal inlets and nearshore waters. In: Estuarine interactions, pp 514–532. Ed. by M. L. Wiley. New York: Academic Press 1978
Boynton, W. R., W. M. Kemp and C. Osborne: Nutrient fluxes across the sediment-water interface in the turbid zone of a coastal plain estuary. In: Estuarine perspectives, pp 93–110. Ed. by V. S. Kennedy. New York: Academic Press 1980
Carey, A. G.: Energetics of the benthos of Long Island Sound. I. Oxygen utilization of sediment. Bull. Bingham oceanogr. Collect. 19, 136–144 (1967)
Christensen, J. P. and T. T. Packard: Oxygen utilization and plankton metabolism in a Washington fjord. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 4, 339–347 (1976)
Davies, J. M. and P. J. le B. Williams: Verification of 14C2 and O2 derived primary production measurements using an eclosed ecosystem. J. Plankton Res. 6, 457–474 (1984)
Day, J. W., W. G. Smith, P. R. Wagner and W. Stowe: Community structure and carbon budget of a salt marsh and shallow bay estuarine system in Louisiana, 80 pp. Publ. No. LSU-SG-72-04. Center for Wetland Resources, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge. 1973
Edwards, R.: Ecology of a coastal lagoon complex in Mexico. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 6, 75–92 (1978)
Eppley, R. W., E. Renger and P. R. Betzer: The residence time of particulate organic carbon in the surface layer of the ocean. Deep-Sea Res. 30, 311–323 (1983)
Fallon, R. D., S. Y. Newell and C. S. Hopkinson: Bacterial production in marine sediments: will cell-specific measures agree with whole-system metabolism?. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 11, 119–127 (1983)
Fisher, T. R., P. R. Carlson and R. T. Barber: Sediment nutrient regeneration in three North Carolina estuaries. Estuar cstl Shelf Sci. 14, 101–116 (1982)
Gallagher, J. L., R. J. Reimold, R. A. Linthurst and W. J. Pfeiffer: Aerial production, mortality and mineral accumulation export dynamics in Spartina alterniflora and Juncus roemerianus plant stands in a Georgia salt marsh. Ecology 61, 303–312 (1980)
Garside, C. and T. C. Malone: Monthly oxygen and carbon budgets of the New York Bight Apex. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 6, 93–104 (1978)
Haines, E. B.: Nutrient inputs to the coastal zone: the Georgia and South Carolina Shelf. In: Estuarine research, Vol. I, pp 303–324. Ed. by L. Cronin. New York: Academic Press 1975
Haines, E. B.: The origins of detritus in Georgia salt marsh estuaries. Oikos 29, 254–260 (1977)
Haines, E. B. and W. M. Dunstan: The distribution and relation of particulate organic matter and primary productivity in the Georgia Bight. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 3, 431–441 (1975)
Happ, G., J. G. Gosselink and J. W. Day: The seasonal distribution of organic carbon in a Louisiana estuary. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 5, 695–705 (1977)
Hargrave, B. T.: Similarity of oxygen uptake by benthic communities. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 801–805 (1969)
Hargrave, B. T.: Coupling carbon flow through some pelagic and benthic communities. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can 30, 1317–1326 (1973)
Hargrave, B. T.: Seasonal changes in oxygen uptake by settled particulate matter and sediments in a marine bay. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 35, 1621–1628 (1978)
Hargrave, B. T. and G. A. Phillips: Annual in situ carbon dioxide and oxygen flux across a subtidal marine sediment. Estuar. cstl Shelf Sci. 12, 725–737 (1981)
Hartwig, E. O.: Nutrient cycling between the water column and a marine sediment. I. Organic carbon. Mar. Biol. 34, 285–295 (1976)
Hartwig, E. O.: Factors affecting respiration and photosynthesis by the benthic community of a subtidal siliceous sediment. Mar. Biol. 46, 283–293 (1978)
Heath, G. R., T. C. Moore and J. Dauphin: Organic carbon in deep-sea sediments. In: The fate of fossil fuel CO2 in the oceans, pp 605–625. Ed. by N. Anderson and A. Malahoff. New York: Plenum Press 1977
Hopkinson, C. S., J. W. Day and B. T. Gael: Respiration studies in a Louisiana salt marsh. An. Cent. Cienc. del Mar y Limnol. Unit. Nat. Auton. Mexico 5, 225–238 (1978)
Hopkinson, C. S., J. G. Gosselink and R. T. Parrondo: Production of coastal Louisiana marsh plants calculated from phenometric techniques. Ecology 61, 1091–1098 (1980)
Hopkinson, C. S. and F. A. Hoffman: The estuary extended — a recipient-system study of estuarine outwelling in Georgia. In: The estuary as a filter. pp 313–330. Ed. by V. S. Kennedy. New York: Academic Press 1984
Hopkinson, C. S. and R. L. Wetzel: In situ measurements of nutrient and oxygen fluxes in a coastal marine benthic community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 10, 29–35 (1982)
Howarth, R. W. and J. M. Teal: Surfate reduction in a New England salt marsh. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24, 999–1013 (1979)
Howes, B. L., J. Dacey and G. King: Carbon flow through oxygen and SO4 reduction pathways in salt marsh sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29, 1037–1051 (1984)
Hunt, C. D.: Variability in the benthic Mn flux in coastal marine ecosystems resulting from temperature and primary production. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28, 913–923 (1983)
Johnson, K. M., C. Burney and J. Sieburth: Precise and accurate determination by infrared photometry of CO2 dynamics in marine ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 10, 251–256 (1983)
Jørgensen, B. B.: The sulfur cycle of a coastal marine sediment (Limfjorden, Denmark). Limnol. Oceanogr. 22, 814–832 (1977)
Kelly, J. R. and S. W. Nixon: Experimental studies of the effect of organic deposition on the metabolism of a coastal marine bottom community. Mar. Ecol. Proc. Ser. 17, 157–169 (1984)
Kemp, W. M. and W. R. Boynton: Influence of biological and physical processes on dissolved oxygen dynamics in an estuarine system: implications for measurement of community metabolism. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 11, 407–431 (1980)
Kjerfve, B. and H. N. McKellar: Time series measurements of estuarine material fluxes. In: Estuarine perspectives, pp 341–358. Ed. by V. S. Kennedy. New York: Academic Press 1980
Leiper, A. S.: Seasonal changes in the structure of three sublittoral marine benthic communities off Sapelo Island, Georgia, 296 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of Georgia, Athens 1973
Manheim, F. T., R. H. Meade and G. Bond: Suspended matter in surface water of the Atlantic continental margin from Cape Cod to the Florida Keys. Science, N.Y. 167, 371–376 (1970)
Mulholland, P. J.: Formation of particulate oceanic carbon in water from a southeastern swamp-stream. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26, 790–795 (1981)
Muller, P. J. and E. Suess: Productivity, sedimentation rate and sedimentary organic matter in the oceans. I. Organic carbon preservation. Deep-Sea Res. 49, 1347–1362 (1979)
Murray, J. W., V. Grundmanis and W. Smethie: Interstitial water chemistry in sediments of Saanich Inlet. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 42, 1011–1026 (1978)
Nixon, S. W.: Between coastal marshes and coastal waters — a review of twenty years of speculation and research on the role of salt marshes in estuarine productivity and water chemistry. In: Estuarine and wetland processes, pp 437–525. Ed. by P. Hamilton and K. MacDonald: New York: Plenum Press 1980
Nixon, S. W.: Remineralization and nutrient cycling in coastal marine ecosystems. In: Nutrient enrichment in estuaries, pp 111–138. Ed. by B. Nielson and L. Cronin. Clifton, New Jersey: Humana Press 1981
Nixon, S. W., J. Kelly, B. Furnas, C. Oviatt and S. Hale: Phosphorus regeneration and the metabolism of coastal marine bottom communities. In: Marine benthic communities, pp 219–242. Ed. by K. Tenore and B. Coull. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press 1980
Nixon, S. W. and C. A. Oviatt: Ecology of a New England salt marsh. Ecol. Monogr. 43, 463–498 (1973)
Nixon, S. W., C. Oviatt and S. Hale: Nitrogen regeneration and the metabolism of coastal marine bottom communities. In: The role of terrestrial and aquatic organisms in decomposition processes, pp 269–283. Ed. by J. Anderson and A. Macfadyen. London: Blackwell Scientific 1976
Odum, E. P.: A research challenge: evaluating the productivity of coastal and estuarine water. In: Proceedings, 2nd Sea Grant Conference, pp 63–64. Kingston: Grad. School of Oceanogr., University of Rhode Island 1968
Odum, E. P.: Fundamentals of ecology, 574 pp. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co. 1971
Oertel, G. F.: Sediment-hydrodynamic interrelationships at the entrance of the Doboy Sound estuary, Sapelo Island, Georgia, 172 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of Iowa 1971
Pamatmat, M. M.: Benthic community metabolism: a review and assessment of present status and outlook. In: Ecology of marine benthos, pp 89–111. Ed. by B. Coull. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press 1977
Pamatmat, M. M. and K. Banse: Oxygen consumption by the sea bed. 2. In situ measurement to a depth of 180 m. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 250–259 (1968)
Patten, B. C.: Plankton energetics of Raritan Bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 6, 369–387 (1961)
Peterson, B. J.: Aquatic primary productivity and the 14CO2 method: A history of the productivity problem. A. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 11, 359–385 (1980)
Pilkey, O. H. and D. Frankenberg: The relict-recent sediment boundary on the Georgia continental shelf. Bull. Georgia Acad. Sci. 22, 37–40 (1964)
Pinet, P. R. and R. W. Frey: Organic carbon in surface sands seaward of Altamaha and Doboy Sounds, Ga. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 88, 1731–1739 (1977)
Pomeroy, L. R., and R. E. Johannes: Total plankton respiration. Deep-Sea Res. 13, 971–973 (1966)
Pomeroy, L. R. and R. G. Wiegert (Eds.): Ecosystem and population ecology of a salt marsh: a synthesis, 271 pp. New York: Springer-Verlag 1981
Ragotzkie, R. A.: Plankton productivity in estuarine waters of Georgia. Publ. Inst. mar. Sci. Univ. Texas 6, 146–158 (1959)
Raine, R. C. T. and J. W. Patching: Aspects of carbon and nitrogen cycling in a shallow marine environment. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 47, 127–139 (1980)
Reimer, C. E. and E. Suess: The partitioning of organic carbon fluxes and sedimentary organic matter decomposition rates in the ocean. Mar. Chem. 13, 141–148 (1983)
Riley, G. A.: Plankton studies. II. The western north Atlantic, May–June 1939. J. mar. Res. 2, 145–162 (1939)
Riley, G. A.: Plankton studies. III. Long Island Sound. Bull. Bingham oceanogr. Collect. 7, 1–93 (1941)
Rybak, J. I.: Bottom sediments of the lakes of various trophic types. Ekol. Polska Ser. 17, 611–662 (1969)
SAS: SAS User's Guide, 1979 edition, 494 pp. Raleigh, North Carolina: SAS Institute, Inc. 1979
Schubauer, J. P. and C. S. Hopkinson: Above- and belowground emergent macrophyte production and turnover in a coastal marsh ecosystem, Georgia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29, 1052–1065 (1984)
Seki, H., J. Skelding and T. R. Parons: Observations on the decomposition of a marine sediment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 13, 440–447 (1968)
Smayda, T. J.: Phytoplankton studies in lower Narragansett Bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2, 342–359 (1957)
Smith, K. L.: Respiration of a sublittoral community. Ecology 54, 1065–1075 (1973)
Smith, K. L.: Benthic community respiration in the N.W. Atlantic Ocean: in situ measurements from 40 to 5 200 m. Mar. Biol. 47, 337–347 (1978)
Sotille, W. S.: Studies of microbial production and utilization of dissolved organic carbon in a Georgia salt marsh-estuarine ecosystem, 153 pp. Ph.D. thesis. University of Georgia, Athens 1973
de Souza Lima, H. and P. J. le B. Williams: Oxygen consumption by the planktonic population of an estuary — Southampton water. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 6, 515–521 (1978)
Stainton, M. P.: A syringe gas-stripping procedure for gaschromatographic determination of dissolved inorganic and organic carbon in fresh water and carbonates in sediments. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can 30, 1441–1445 (1973)
Strickland, J. and T. Parsons: A practical handbook of seawater analysis, 311 pp. Ottawa: Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 167 (3rd ed.) 1972
Taft, J. L., W. R. Taylor, E. O. Hartwig and R. Loftus: Seasonal oxygen depletion in Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 3, 242–247 (1980)
Thomas, J. P.: The influence of the Altamaha River on primary production beyond the mouth of the river, 80 pp. M.S. thesis, University of Georgia, Athens 1966
Turner, R. E.: Community plankton respiration in a salt marsh estuary and the importance of macrophytic leachates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 442–452 (1978)
Turner, R. E.: Community plankton respiration in a salt marsh estuary and the importance of macrophytic leachates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23, 442–451 (1978)
Valiela, I. and J. Teal: The nitrogen budget of a salt marsh ecosystem. Nature, Lond. 280, 652–656 (1979)
Van Es, F. B.: Community metabolism of intertidal flats in the Ems-Dollard estuary. Mar. Biol. 66, 95–108 (1982)
Williams, P. J. le B.: Microbial contribution to overall marine plankton metabolism: direct measurements of respiration. Oceanologica Acta 4, 359–364 (1981)
Williams, R. B.: Annual phytoplankton production in a system of shallow temperate estuaries. In: Some contemporary studies in marine science, pp 699–716. Ed. by H. Barnes. London: George Allen and Unwin Ltd. 1966
Williams, R. B. and M. R. Murdoch: Phytoplankton production and chlorophyll concentration in the Beaufort Channel, North Carolina. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11, 73–82 (1966)
Woodwell, G. M., R. Houghton, C. Hall, D. Whitney, R. Moll and D. Juers: The Flax Pond ecosystem study: the annual metabolism and nutrient budgets of a salt marsh. In: Ecological processes in coastal environments, pp 491–511. Ed. by R. L. Jefferies and A. J. Davy. Melbourne: Blackwell Scientific Publ. 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Lawrence, Tampa
This is Contribution No. 530 from the University of Georgia Marine Institute. This work was supported by the Georgia Sea Grant College Program maintained by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, US Department of Commerce
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hopkinson, C.S. Shallow-water benthic and pelagic metabolism:. Marine Biology 87, 19–32 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397002
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397002