Abstract
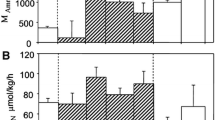
The large bathypelagic mysid Gnathophausia ingens was collected in January 1980 at 400 to 700 m depth from the San Clemente Basin off southern California. Instars 7-8 and Instars 10-12 were starved in the laboratory for up to 19 wk. Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion rates, and water, protein, lipid, and ash contents were determined periodically during starvation. Protein and lipid were metabolized in approximately equal amounts by starved individuals after the initial weeks of food deprivation. Unidentified components (probably non-protein nitrogenous compounds) apparently were oxidized within the first 7 wk of starvation. Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion by Instars 7-8 decreased steadily during 19 wk of starvation. In contrast, stable or increasing respiration and excretion rates were observed for fed mysids. The mean respiration rate of Instars 10-12 did not change significantly during 13 wk of starvation, although ammonia excretion rates decreased. Low metabolic rates and large lipid reserves probably help G. ingens to withstand long periods of starvation in the mesopelagic environment. Calculations based on the laboratory data demonstrate that small, infrequent meals could account for the rates of metabolism and growth observed for G. ingens in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Aldrich, J. C.: Individual variability in oxygen consumption rates of fed and starved Cancer pagurus and Maia squinado. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 51 A, 175–183 (1975)
Ansell, A. D.: Changes in oxygen consumption, heart rate and ventilation accompanying starvation in the decapod crustacean Cancer pagurus. Neth. J. Sea Res. 7, 455–475 (1973)
Bayne, B. L. and C. Scullard: Rates of nitrogen excretion by species of Mytilus (Bivalvia: Mollusca). J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57, 355–369 (1977)
Brett, J. R. and T. D. D. Groves: Physiological energetics. In: Fish physiology, Vol. 8. pp 279–352. Ed. by W. S. Hoar and D. J. Randall. New York: Academic Press 1979
Carter, J. A. and G. B. Dunphy: A preliminary analysis of dietary effects on serum ninhydrin-positive compounds of immature lobsters Homarus americanus (Milne Edwards). Can. J. Zool. 56, 359–363 (1977)
Chaisemartin, Mobilisation des réserves de métabolites chez les Astacidae: influences comparées de la stabulation à jeun et de certains états pathologiques. C. r. Séanc. Soc. Biol. 165, 671–676 (1971)
Childress, J. J.: Respiratory rate and depth of occurrence of midwater animals. Limnol. Oceanogr. 16, 104–106 (1971a)
Childress, J. J.: Respiratory adaptations to the oxygen minimum layer in the bathypelagic mysid Gnathophausia ingens. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 141, 109–121 (1971b)
Childress, J.J.: The respiratory rates of midwater crustaceans as a function of depth of occurrence and relation to the oxygen minimum layer off southern California. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 50a, 787–799 (1975)
Childress, J. J., A. T. Barnes, L. B. Quetin and B. Robison: Thermally protecting cod ends for the recovery of living deepsea animals. Deep-Sea Res. 25, 419–422 (1978)
Childress, J. J. and M. H. Nygaard: The chemical composition of midwater fishes as a function of depth of occurrence off southern California. Deep-Sea Res. 20, 1093–1109 (1974)
Childress, J. J. and M. H. Price: Growth rate of the bathypelagic crustacean Gnathophausia ingens (Mysidacea: Lophogastridae). I. Dimensional growth and population structure. Mar. Biol. 50, 47–62 (1978)
Childress, J. J. and M. H. Price: Growth rate of the bathypelagic crustacean Gnathophausia ingens (Mysidacea: Lophogastridae). II. Accumulation of material and energy. Mar. Biol. 76, 165–177 (1983)
Childress, J. J. and G. N. Somero: Depth-related enzymic activities in muscle, brain and heart of deep-living pelagic marine teleosts. Mar. Biol. 52, 273–283 (1979)
Conover, R. J.: Food relations and nutrition of zooplankton. Occ. Publs Narragansett mar. Lab., Univ. Rhode Isl. 2, 81–91 (1964)
Conover, R. J. and E. D. S. Corner: Respiration and nitrogen excretion by some marine zooplankton in relation to their life cycles. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 48, 49–75 (1968)
Corner, E. D. S. and B. S. Newell: On the nutrition and metabolism of zooplankton. IV. The forms of nitrogen excreted by Calanus. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 47, 113–120 (1967)
Cowey, C. B. and E. D. S. Corner: Amino acids and some other nitrogenous compounds in Calanus finmarchicus. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 43, 483–493 (1963)
Cuzon, G., C. Cahu, J. F. Aldrin, J. L. Messager, G. Stephan and M. Mevel: Starvation effect on metabolism of Penaeus japonicus. Proc. Wld Maricult. Soc. (New Orleans) 11, 410–423 (1980)
Cuzon, G. et H. J. Ceccaldi: Influence de la stabulation à jeun sur le métabolisme dela crevette Crangon crangon (L.). C. r. Séanc. Biol. 167, 66–68 (1973)
Dall, W.: Indices of nutritional state in the western rock lobster, Panulirus longipes (Milne Edwards). I. Blood and tissue constituents and water content. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 16, 167–180 (1974)
Elliott, J. M. and W. Davison: Energy equivalents of oxygen consumption in animal energetics. Oecologia 19, 195–201 (1975)
Ennis, G. P.: Lobster (Homarus americanus) fishery and biology in Bonavista Bay, Newfoundland 1966–70. Tech. Rep. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 289, 1–46 (1971)
Folch, J., M. Lees and G. H. S. Stanley: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1956)
Hernandorena, A. and S. J. Kaushik: Ammonia excretion of Artemia sp. (Crustacea: Branchiopoda) under axenic conditions. Mar. Biol. 63, 23–27 (1981)
Hiatt, H. W.: The biology of the lined shore crab, Pachygrapsus crassipes Randall. Pacif. Sci. 2, 135–213 (1948)
Hiller-Adams, P.: Effects of feeding and food deprivation on the bathypelagic mysid Gnathophausia ingens, 138 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Santa Barbara 1982
Hiller-Adams, P. and J. J. Childress: Effects of season on the bathypelagic mysid Gnathophausia ingens: water content, respiration, and excretion. Deep-Sea Res. 30, 629–638 (1983a)
Hiller-Adams, P. and J. J. Childress: Effects of feeding, feeding history, and food deprivation on respiration and excretion rates of the bathypelagic mysid Gnathophausia ingens. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole (in press) (1983b)
Hughes, J. T. and G. C. Matthieson: Observations on the biology of the American lobster Homarus americanus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 7, 414–421 (1962)
Ikeda, T.: Changes in respiration rate and in composition of organic matter in Calanus cristatus (Crustacea: Copepoda) under starvation. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 21, 280–298 (1971)
Ikeda, T.: Nutritional ecology of marine zooplankton. Mem. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 22, 1–97 (1974)
Kleiber, M.: The fire of life, 454 pp. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1961
Linford, E.: Biochemical studies on marine zooplankton. II. Variations in the lipid content of some Mysidacea. J. Cons. perm. int. Explor. Mer 30, 16–27 (1965)
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Roseborough, A. L. Farr and R. J. Randall: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Mayzaud, P.: Respiration and nitrogen excretion of zooplankton. II. Studies on the metabolic characteristics of starved animals. Mar. Biol. 21, 19–28 (1973)
Mayzaud, P.: Respiration and nitrogen excretion of zooplankton. IV. The influence of starvation on the metabolism and the biochemical composition of some species. Mar. Biol. 37, 47–58 (1976)
Needham, A. E.: Nitrogen output and ecdysis in Crustacea. Nature, Lond. 178, 495–496 (1957)
Parry, G.: Excretion. In: The physiology of Crustacea, pp 341–366. Ed. by T. H. Waterman. New York: Academic Press 1960
Raymont, J. E. G., J. Austin and E. Linford: Biochemical studies on marine zooplankton III. Seasonal variation in the biochemical composition of Neomysis integer. In: Some contemporary studies in marine science, pp 597–605. Ed. by H. Barnes. London: George Allen & Unwin 1966
Régnault, M.: Ammonia excretion of the sand shrimp Crangon crangon (L.) during the moult cycle. J. comp. Physiol. 133, 199–204 (1979)
Régnault, M.: Respiration and ammonia excretion of the shrimp Crangon crangon L.: metabolic response to prolonged starvation. J. comp. Physiol. 141, 549–555 (1981)
Rice, A. L. and A. J. Provenzano: The zoeal stages and the glaucothoe of Paguristes sericeus A. Milne-Edwards (Anomura, Diogenidae). Crustaceana 1965 (8), 239–254 (1965)
Roberts, J. L.: Thermal acclimation of metabolism in the crab Pachygrapsus crassipes Randall. I. The influence of body size, starvation, and molting. Physiol. Zoöl. 30, 232–242 (1957)
Schafer, H. J.: Storage materials utilized by starved pink shrimp, Penaeus duorarum Burkenroad. In: Proceedings of the World Conference on Biology and Culture of Shrimps, Mexico. F.A.O. Fish. Rep. 57, 393–403 (1968)
Smith, K. L. and R. Hessler: Respiration of benthopelagic fishes: in situ measurements at 1 230 m. Science, N.Y. 184, 72–73 (1974)
Stewart, J. E., G. W. Horner and B. Arie: Effects of temperature, food and starvation on several physiological parameters of the lobster Homarus americanus. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 29, 439–442 (1972)
Strickland, J. D. H. and T. R. Parsons: A practical handbook of seawater analysis, 2nd ed. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 167, 1–310 (1972)
Sullivan, K. M. and G. N. Somero: Enzyme activities of fish skeletal muscle and brain as influenced by depth of occurrence and habitats of feeding and locomotion. Mar. Biol. 60, 91–99 (1980)
Torres, J. J., B. W. Belman and J. J. Childress: Oxygen consumption rates of midwater fishes as a function of depth of occurrence. Deep-Sea Res. 26A, 185–197 (1979)
Wilcox, J. R. and H. P. Jeffries: Hydration in the sand shrimp Crangon crangon: relation to diet. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 150, 522–530 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N. D. Holland, La Jolla
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiller-Adams, P., Childress, J.J. Effects of prolonged starvation on O2 consumption, NH +4 excretion, and chemical composition of the bathypelagic mysid Gnathophausia ingens . Mar. Biol. 77, 119–127 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396309
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396309