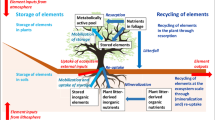
Abstract
This paper discusses the buffering, oxygen-donating, and sorption capacities of soils and sediments as an inter-connected system for regulating the retention and release of chemical pollutants. In this context, the author discusses the chemical conditions under which sediments may serve as a source or a sink for toxic materials, and conditions under which soils may retain or release them. It is demonstrated that nonlinear, time-delayed ecological transformations in soils and sediments often can be understood in terms of the interlinked system. The author discusses some possible future long-term environmental problems that might beset Europe, and some implications for a monitoring strategy for foresseing such problems.
Because the release of adsorbed toxic chemicals from heavily polluted sediments and soils can occur suddenly owing to changes in oxygen status (i.e., redox potential) or acidity, strategies for preventing the long-term release of such materials should not only consider current conditions of pH and redox potential, but also, how those conditions might change in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcamo, J., M., Amann, J.-P., Hettelingh, M., Holmberg, L., Hordijk, J., Kamari, L., Kauppi, P., Kauppi, G., Kornai, and A., Makela. 1987. Acidification in Europe: a simulation model for evaluating control strategies. Ambio 16: 232–245.
Almer, B., W., Dickson, C., Ekstrom, and E., Hornstrom. 1978. Sulfur Pollution and the Aquatic Ecosystem. In: Sulfur in the Environment, Part 2, J., Nriagu (ed.). New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Andersson, F. 1986. Acidic deposition and its effects on the forests of nordic Europe. Water, Air and Soil Pollution 30:17–29.
Bayley, S.E., R.S., Behr, and C.A., Kelly. 1986. Retention and release of S from a freshwater wetland. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 31:101–114.
Beanlands, G.E. and P.N., Duinker. 1983. An Ecological Framework for Environmental Impact Assessment in Canada. Institute for Environmental Studies of Dalhousie University, Halifax; Federal Environmental Assessment Review Office, Hull, Quebec.
Behrendt, H. 1988. Changes in nonpoint nutrient loading into European freshwaters: trends and consequences since 1950 and not-impossible changes until 2080. Report no. WP-88-000. Laxenburg, Austria: International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.
Berman, M. and R., Bartha. 1986. Control of the methylation process in a mercurypolluted aquatic sediment. Environmental Pollution (Series B) 11: 41–53.
Bjoernberg, A., L., Hakanson, and K., Lundbergh. 1988. A theory on the mechanisms regulating the bioavailability of mercury in natural waters. Environmental Pollution 49: 53–61.
Braekke, F.H. 1981. Hydrochemistry of high altitude catchments in South Norway. 1. Effects of summer droughts and soil-vegetation characteristics. Rep. Norw. For. Res. Inst. 36.8,26pp.
Braekke, F.H. Ed. 1976. Impact of Acid Precipitation on Forest and Freshwater Ecosystems in Norway. SNSF-Projekt, Research Rept. 6/76, 1432 Aas, Norway.
Breeuwsma, A. and O.F., Schoumans. 1987. Forecasting Phosphate Leaching from Soils on a Regional Scale, pp: 973–982. In: Vulnerability of Soils and Groundwater to Pollutants; International Conference, Noordwijk aan Zee, The Netherlands, March 30–April 3, 1987. The Hague: National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Hygiene.
Brooks, H. 1986. The Typologies of Surprises in Technology, Institutions, and Development, chapter 11, pp: 325–348. In: Sustainable Development of the Biosphere, W.C., Clark and R.E., Munn (eds.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Brown, K.A. 1980. The Distribution of Sulfur Compounds in a Peat Bog in Relation to Stream Water Chemistry. Report of Central Electricity Research Laboratories, RD/L/N 150/80. Central Electricity Generating Board. Surrey, England, 18pp.
Brown Weiss, E. 1984. The planetary trust: conservation and intergenerational equity. Ecology Law Quarterly 11: 495–581.
Brugam, R.B. and M., Lusk. 1986. In: Diatoms and Lake Acidity, pp: 115–129, J.P., Smol, R.W., Battarbee, R.B., Davis, and J., Merilainsen (eds.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Junk.
Calles, U.M. 1983. Dissolved inorganic substances. A study of mass balance in three small drainage basins. Hydrobiologia 101:13–18.
Charles, D.F. and S.A., Norton. 1986. Paleolimnological Evidence for Trends in Atmospheric Deposition of Acids and Metals., chapter 9, pp: 335–431. In: Acid Deposition Long-Term Trends, National Research Council. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Chemical and Engineering News. 1987, vol. 65, no. 41 (October 12), pp: 14–15. Hazardous waste found in household garbage. (Summary of a report of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.)
Chen, K.Y., S.K., Gupta, A.Z., Sycip, J.C.S., Lu, M., Knezevic, and W.-W., Choi. 1976. Research Study on the Effect of Dispersion, Settling, and Resedimentation on Migration of Chemical Constituents during Open-Water Disposal of Dredged Materials. U.S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, Contract Rep. D-76-1, CE, Vicksburg, Miss.
Clark, W.C., 1986a. Editorial. Environment 28, no.10 (December).
Clark, W.C. 1986b. Sustainable Development of the Biosphere: Themes for a Research Program, chapter 1, pp: 5–48. In: Sustainable Development of the Biosphere, W.C., Clark and R.E., Munn (eds.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Compeau, G. and R., Bartha. 1984. Methylation and demethylation of mercury under controlled redox, pH, and salinity conditions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 48: 1203–1207.
Crutzen, P.J. and T.E., Graedel. 1986. The Role of Atmospheric Chemistry in Environment-Development Interactions, chapter 8, pp: 213–249. In: Sustainable Development of the Biosphere, W.C., Clark and R.E., Munn (eds.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
DeGroot, A.J. 1977. Assessment of Certain European Dredging Practices and Dredged Material Containment and Reclamation Methods. Appendix E: Heavy Metals in the Dutch Delta, an Integrated Program for Research. Final Report, Contract DAJA 37-75-C-0382, U.S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, CE, Vicksburg, Miss.
DeHaan, F.A.M. 1987. Effects of Agricultural Practices on the Physical, Chemical and Biological Properties of Soils: Part III—Chemical Degradation of Soil as a Result of the Use of Mineral Fertilizers and Pesticides: Aspects of Soil Quality Evaluation, pp: 211–236. In: Scientific Basis for Soil Protection in the European Community, H., Barth and P.L., L'Hermite (eds.). London: Elsevier Applied Science.
DeVries, W. and A., Breeuwsma. 1986. Relative importance of natural and anthropogenic proton sources in soils in the Netherlands. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 28:173–184
DeWit, C.T. 1981. Oude wijn in nieuwe zakken. Landbouwkundig Tijdschrift 93:257–62.
Dickson, W. 1980. Properties of acidified waters, pp: 75–83. In Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation; Proc. of an International Conference, Sandefjord, Norway, March 11–14, 1980. Oslo: SNSF Project.
Dillon, P.J., R.A., Reid, and E. de, Grosbois 1987. The rate of acidification of aquatic ecosystems in Ontario, Canada, Nature 239: 45–48.
Fleischer, S. and S. Hamrin. 1987. Land use and nitrogen losses — a study within the Laholm Bay drainage basin of southwest Sweden. Verh. Internat. Verein Limnol. 23 (in press).
Fleischer, S., S., Hamrin, T., Kindt, L., Rydberg, and L., Stibe. 1987. Coastal eutrophication in Sweden reducing nitrogen in land runoff. Ambio 16: 246–251.
Foerstner, U. 1986 (in press). Changes in Metal Mobilities in Aquatic and Terrestrial Cycles. In: Proceeding of the International Seminar on “Speciation, Separation and Recovery of Metals”, J.W., Patterson (ed.). Chelsea, Mich., U.S.A.: Lewis Publishers.
Foerstner, U. 1980 Cadmium in Polluted Sediments, chapter 9, pp: 305–363. In: Cadmium in the Environment, J.O., Nriagu (ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Gambrell, R.P., R.A., Khalid, and W.H., PatrickJr. 1980. Chemical availability of mercury, lead, and zinc in Mobile Bay sediment suspensions as affected by pH and oxidation-reduction conditions. Environmental Science and Technology 14: 431–436.
Gambrell, R.P., R.A., Khalid, M.G., Verloo, and W.H., Patrick, Jr. 1977. Transformations of Heavy Metals and Plant Nutrients in Dredged Sediments as Affected by Oxidation-Reduction Potential and pH. Vol. II: Materials and Methods, Results and Discussion. U.S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, Contract Rep.D-77-4, CE, Vicksburg, Miss.
Haines, T.A. 1986. Fish Population Trends in Response to Surface Water Acidification, chapter 8, pp: 300–334. In: Acid Deposition Long-Term Trends, National Research Council. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Hakanson, L., A., Nilsson, and T., Andersson. 1988. Mercury in fish in Swedish lakes. Environmental Pollution49: 145–162.
Hem, J.D. 1972. Chemistry and occurrences of cadmium and zinc in surface water and groundwater. Water Resources Research 8: 661–679.
Henkens, Ch.H. 1983. Cadmium in meststoffen. Bedrijfsontwikkeling 14: 484.
Hunt, C.D. and D.L., Smith. 1983. Remobilization of metals from polluted marine sediments. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 40(Suppl. 2): 132–142.
Husar, R.B. 1986. Emissions of Sulfur Dioxide and Nitrogen Oxides and Trends for Eastern North America, chapter 2, pp: 48–92. In: Acid Deposition Long-Term Trends, National Research Council. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Huygen, C. and F.W. van Ijssel. 1981. Luchtverontreiniging bij kassen door bodemontsmetting met methylbromide. IMG-TNO, Delft, Report no. G 1048.
IB, 1987a. Dutch Institute for Soil Fertility, Haren. Reported in Environmental Statistics of The Netherlands 1987, p. 64. Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics, Department of Environmental Statistics, The Hague.
IB, 1987b. Dutch Institute for Soil Fertility, Haren. Reported in Environmental Statistics of The Netherlands 1987, p. 63. Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics, Department of Environmental Statistics, The Hague.
IIASA. 1988. IIASA's Acid Rain Project has estimated SO 2 emissions for West Germany, Switzerland, Austria, and Czechoslovakia for the years 1975, 1980, and 1985, based on the Official Energy Pathways reported by the respective countries. Total emissions in 1975 were 6,545 kilotons. Between 1975 and 1980 total emissions increased by about 4%. However, between 1980 and 1985 emissions decreased by about 6%. Overall, between 1975 and 1985, emissions decreased by about 2%.
Jansson, M., L., Leonardsson, and U., Rönner. 1986. Denitrification in rivers draining arable land decreases the nitrogen loading in Swedish coastal waters. Vatten 12:25–32.
John, M.K. 1972. Uptake of soil-applied cadmium and its distribution in radishes. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 52: 715–719.
John, M.K., C.J. Van, Laerhoven, and H.H., Chuah. 1972. Factors affecting plant uptake and phytotoxicity of cadmium added to soils. Environmental Science and Technology 6:1005–1009.
Kersten, M., and U., Foerstner. 1987. Cadmium Associations in Freshwater and Marine Sediments. In: Cadmium in the Aquatic Environment, J.O., Nriagu and J.B., Sprague (eds.). New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Khalid, R.A. 1980. Chemical Mobility of Cadmium in Sediment-Water Systems, chapter 8, pp: 257–304. In: Cadmium in the Environment, J.O., Nriagu (ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Lu, J.C.S. and K.Y., Chen. 1977. Migration of trace metals in interfaces of seawater and polluted surficial sediments. Environmental Science and Technology 11: 174–182.
MacLean, A.J. 1976. Cadmium in different plant species and its availability in soils as influenced by organic matter and additions of lime, P, Cd and Zn. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 56: 129–138.
Manabe, S. and T., Wetherald. 1986. Reduction in summer soil wetness induced by an increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Science 232: 626–628.
Miljostyrelsen. 1984. Oxygen depletion and fish kill in 1981— extent and causes (in Danish). (Miljostyrelsen = The National Agency of Environmental Protection Denmark.)
Miller, J.E., J.J., Hassett, and D.E., Koeppe. 1976. Uptake of cadmium by soybeans as influenced by soil cation exchange capacity, pH, and available phosphorus. Journal of Environmental Quality 5: 157–160.
Mooney, H.A., P.M., Vitousek, and P.A., Matson. 1987. Exchange of materials between terrestrial ecosystems and the atmosphere. Science 238:926–932.
National Research Council (NRC). 1985. Acid Deposition Effects on Geochemical Cycling and Biological Availability of Trace Elements Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
National Research Council (NRC). 1984. Acid Deposition: Processes of Lake Acidification. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
OECD. 1985. The State of the Environment 1985. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris.
Olsthoorn, A.A. and R., Thomas. 1986. Milieuverontreiniging door cadmuim 1981–200. Amsterdam. Instituut voor Milieuvraagstukken, Vrije Universiteit.
Paces, T. 1985. Acidification in Central Europe and Scandinavia: a competition between anthropogenic, geochemical and biochemical processes. Ambio 14: 354–356.
Parry, M. and T., Carter. 1987. The Assessment of Effects of Climatic Variations on Agriculture: Aims, Methods and Summary of Results. In: The Impact of Climatic Variations on Agriculture. Volume 1. Assessments in Cool Temperate and Cold Regions, M.L., Parry, T.R., Carter, and N.T., Konijn (eds.). Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Reidel.
Pinay, G. and H. DeCamps. 1988 (in press). The role of riparian woods in regulating nitrogen fluxes between the alluvial aquifer and surface water: a conceptual model. Regulated Rivers, September 1988.
Prause, B., E., Rehm, and M., Schulz-Baldes. 1985. The remobilization of Pb and Cd from contaminated dredge spoil after dumping in the marine environment. Environmental Technology Letters 6: 261–266.
Renberg, I. 1986. In: Diatoms and Lake Acidity, pp: 213–219, J.P., Smol, R.W., Battarbee, R.B., Davis, and J., Merilainsen (eds.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Junk.
Rippon, J.E., R.A., Skeffington, M.J., Wood, K.A., Brown and D.J.A., Brown. 1980. Hydrogen, Sulphur, and Nitrogen Budgets in Soils and Catchments, pp. 276–277. In: Ecological Impacts of Acid Precipitation, D., Drablos and A., Tollan (eds.). SNSF Project, Oslo, Norway.
Salomons, W. 1983. Trace metals in the Rhine, their past and present (1920–1983) influence on aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. In: Proc. Intern. Conf. Heavy Metals in the Environment, Heidelberg, pp. 764–771. CEP—Consultants, Edinburgh.
Salomons, W. and J.A.Van, Pagee. 1981. Biogeochemical processes affecting metal concentrations in lake sediments (IJsselmeer, The Netherlands). Science Total Environment 16:217–229.
Sauerbeck, D. 1987. Effects of Agricultural Practices on the Physical, Chemical and Biological Properties of Soils: Part II—Use of Sewage Sludge and Agricultural Wastes, pp: 181–210. In: Scientific Basis for Soil Protection in the European Community, H., Barth and P.L., L'Hermite (eds.). London: Elsevier Applied Science.
Schoumans, O.F., A., Breeuwsma, and H.de, Vries. 1987. Use of soil survey information for assessing the phosphate sorption capacity of heavily manured soils, pp: 1079–1088. In: Vulnerability of Soils and Groundwater to Pollutants; International Conference, Noordwijk aan Zee, The Netherlands, March 30-April 3, 1987. The Hague: National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Hygiene.
Schroder, H. 1985. Nitrogen losses from Danish agriculture—trends and consequences. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 14: 279–289.
Stevenson, F.J. 1972. Organic matter reactions involving herbicides in soils. Journal of Environmental Quality 1: 333.
Tamm, C.O. and L., Hallbaecken. 1988. Changes in soil acidity in two forest areas with different acid deposition: 1920s to 1980s. Ambio 17: 56–61.
Tyler, G., D. Berggren, B. Bergkvist, U. Falkengren-Grerup, L. Folkeson, and A. Ruehling. 1985. Soil acidification and metal solubility on forests of south Sweden. The NATO Advanced Research Institute Workshop: Effects of air pollutants, especially acidic deposition on forests, agriculture and wetlands; Toronto, May 12–17, 1985.
Vitt, D.H. and S., Bayley. 1984. The vegetation and water chemistry of four oligotrophic basin mires in northwestern Ontario. Canadian Journal of Botany 62:1485–1500.
VROM, 1980. Dutch Ministry of Housing, Physical Planning and Environment, Leidschendam. Reported in Environmental Statistics of The Netherlands 1987, pp. 68–69. Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics, Department of Environmental Statistics, The Hague.
V & W, 1987. Dutch Ministry of Transport and Public Works, The Hague. Reported in Environmental Statistics of The Netherlands 1987, pp. 50, 57. Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics, Department of Environmental Statistics, The Hague.
Wallace, A., E.M., Romney, G.V., Alexander, S.M., Soufi, and P.M., Patel. 1977. Some interactions in plants among cadmium, other heavy metals, and chelating agents. Agronomy Journal, 69: 18–20.
Wieder, R.K. and G.E., Lang. 1984. Influence of wetlands and coal mining on stream water chemistry. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 23: 381–396.
Williams, R.K., and D.J., David. 1976. The accumulation in soil of cadmium residues from phosphate fertilizers and their effect on the cadmium content of plants. Soil Science 121: 86–93.
Williams, C.H. and D.J., David. 1973. The effect of superphosphate on the cadmium content of soils and plants. Australian Journal of Soil Research 11: 43–56.
WL, 1987. Delft Hydraulics, Delft. Reported in Environmental Statistics of The Netherlands 1987, p. 64. Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics, Department of Environmental Statistics, The Hague.
Wollast, R. 1983. Interactions in Estuaries and Coastal Waters, chapter 14, pp: 385–410. In: The Major Biogeochemical Cycles and Their Interactions, SCOPE 21, B., Bolin and R.B., Cook (eds.). New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Wood, J.M. 1980. The Role of pH and Oxidation-Reduction Potentials in the Mobilization of Heavy Metals. In: Polluted Rain, M.W., Miller, and P.E., Morrow (eds.). New York: Plenum Publishing Corp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stigliani, W.M. Changes in valued “Capacities” of soils and sediments as indicators of nonlinear and time-delayed environmental effects. Environ Monit Assess 10, 245–307 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395083
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395083