Abstract
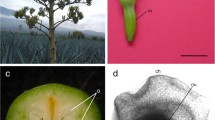
A technique has been developed for isolating embryo sacs (ESs) by enzymatic maceration. Ovules were macerated in a mixture of pectinase, cellulase and, in some cases, snailase and pectolyase Y-23. The ovular tissues were removed and the ESs were isolated in toto. Embryo sacs were isolated from both fixed and fresh ovules of Antirrhinum majus L., Helianthus annuus L. and Nicotiana tabacum L. Fluorochromasia by fluorescein diacetate showed that the ESs isolated from fresh ovules were viable. The method has promise for various histochemical and cell-physiological studies and quite possibly also for in-vitro culture of ESs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ES:
-
embryo sac
- FDA:
-
fluorescein diacetate
- FPA:
-
formalin-propionic acid 50% alcohol (5:5:10, by vol.)
- H33258:
-
Hoechst 33258
References
Arndt-Jovin, D.T., Jovin, T.M. (1977) Analysis and sorting of living cells according to deoxyribonucleic acid content. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 25, 585–589
Bradley, M.V. (1948) An aceto-carmine squash technic for mature embryo sacs. Stain Technol. 23, 29–40
Cowell, J.K., Franks, L.M. (1980) A rapid method for accurate DNA measurements in single cells in situ using a simple microfluorimeter and Hoechst 33258 as a quantitative fluorochrome. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 28, 206–210
Enaleeva, N.Kh., Dushaeva, N.A. (1975) Cytoembryological studies in Nicotiana tabacum L. by means of enzymatic maceration. In: Apomixis and cytoembryology of plants (in Russ.), vol. 3, pp. 171–175, Saratov University Press, USSR
Forbes, I. (1960) A rapid enzyme-smear technique for the detection and study of plural embryo sacs in mature ovaries in several Paspalum species. Agron. J. 52, 300–301
Galbraith, D.W., Mauch, T.J., Shields, B.A. (1981) Analysis of the initial stages of plant protoplast development using 33258 Hoechst: reactivation of the cell cycle. Physiol. Plant. 51, 380–386
Heslop-Harrison, J. (1972) Sexuality of angiosperms. In: Plant Physiology, vol. 6C, pp. 133–289, Steward, F.C., ed. Academic Press, New York London
Heslop-Harrison, J., Heslop-Harrison, Y. (1970) Evaluation of pollen viability by enzymatically-induced fluorescence; intracellular hydrolysis of fluorescein diacetate. Stain Technol. 45, 115–120
Heslop-Harrison, Y.,(1977) The pollen-stigma interaction: pollen-tube penetration in Crocus. Ann. Bot. 41, 913–922
Heslop-Harrison, Y., Heslop-Harrison, J. (1982) The microfibrillar component of the pollen intine: some structural features. Ann. Bot. 50, 831–842
Howard, R.J., Battye, F.L., Mitchell, G.F. (1979) Plasmodium-infected blood cells analyzed and sorted by flow fluorimetry with deoxyribonucleic acid binding dye 33258 Hoechst. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 27, 803–813
Kapil, R.N., Bhatnagar, A.K. (1981) Ultrastructure and biology of female gametophyte in flowering plants. Int. Rev. Cyt. 70, 291–341
Laloue, M., Coortois, M.D., Manigault, P. (1980) Convenient and rapid fluorescent staining of plant cell nuclei with 33258 Hoechst. Plant Sci. Lett. 17, 175–179
Larkin, P.J. (1976) Purification and viability determination of plant protoplasts. Planta 128, 213–216
Meadows, M.G. (1983) Characterization of cells and protoplasts of the B73 maize cell line. Plant Sci. Lett. 28, 337–348
Meadows, M.G., Potrykus, J. (1981) Hoechst 33258 as a vital stain for plant cell protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep. 1, 77–79
Murty, U.R., Schertz, K.F., Bashaw, E.C. (1979) Apomictic and sexual reproduction in Sorghum. Ind. J. Genet. Plant Breeding 39, 271–278
Nagata, T., Takebe, I. (1970) Cell wall regeneration and cell division in isolated tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Planta 92, 301–308
Ockendon, D.T., Gates, P.J. (1976) Reduced pollen viability in the onion (Allium cepa). New Phytol. 76, 511–517
Raghavan, V. (1976) Experimental embryogenesis in vascular plants. Academic Press, London New York San Francisco
Raghavan, V. (1976) Totipotency of plant cells: evidence for the totipotency of male germ cells from anther and pollen culture studies. In: Plant cell and tissue culture: Principles and applications, pp. 155–178, Sharp, W.R., ed. Ohio State University Press, Columbus, USA
Shivanna, K.R., Heslop-Harrison, J. (1981) Membrane state and pollen viability. Ann. Bot. 47, 759–770
Smith, B.A., Reider, M.L., Fletcher, J.S. (1982) Relationship between vital staining and subculture growth during the senescence of plant tissue cultures. Plant Physiol. 70, 1228–1230
Solntseva, M.P., Levkovsky, V.P. (1978) The variant of preparing constant Feulgen's stained slides of total embryo sacs isolated by plant tissue maceration. [In Russ.] Bot. Zh. 63, 827–831
Tyrnov, V.S., Enaleeva, N.Kh. (1979) The possibility of isolation and culture of female gametophyte in angiosperms. In: Theses of Reports, 3rd All-Union Conf. on Plant Cell Culture (in Russ.), pp. 164–165
Tyrnov, V.S., Enaleeva, N.Kh., Khokhlov, S.S. (1975) A study of in vitro isolated embryo sacs in angiosperms. In: Theses of Reports, XII Int. Bot. Congr. (in Russ.), p. 266, Nauka, Leningrad Division
Widholm, J.M. (1972) The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol. 47, 189–194
Yang, H.Y., Zhou, C. (1982) In vitro induction of haploid plants from unpollinated ovaries and ovules. Theor. Appl. Genet. 63, 97–104
Yang, H.Y., Zhou, C. (1984) Observations on megasporogenesis and megagametophyte development in Paulownia sp. and Sesamum indicum by enzymatic maceration technique. Acta Bot. Sin. 26, 342–346
Zhou, C., Yang, H.Y. (1982) Enzymatic isolation of embryo sacs in angiosperms: isolation and microscopical observation on fixed materials. Acta Bot. Sin. 24, 403–407
Zhou, C., Yang, H.Y. (1984) The enzymatic isolation of embryo sacs from fixed and fresh ovules of Antirrhinum majus L. Acta Biol. Exp. Sin. 17, 141–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Yang, H.Y. Observations on enzymatically isolated, living and fixed embryo sacs in several angiosperm species. Planta 165, 225–231 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395045
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395045