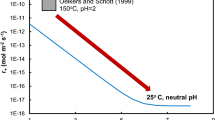
Abstract
In a study of silica dissolution from diatoms, the rate coefficient (K) h-1 of raw diatom cells was estimated as 4 to 5 times smaller than that of the acid-digested siliceous skeletons. The dissolution rate coefficient at early stage (K1) can be predicted as a function of temperature (T°C): in K1=α+βT, where α is the frequency factor depending on the properties of diatom species, ranging from -7.35 to-`0.38, and the temperature coefficient β is 0.0833 for all species. Activation energies were calculated to be 1.37 to 1.38 Kcal mol-1. This equation suggests that the rate coefficient K1 increases by a factor of 2.27 for each 10 C° rise in temperature. This equation will also be applied to a new approach for the fate and behavior of biogenous silica settling through a water column by introducing the term temperature into a model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Burton, J. D. and P. S. Liss: Oceanic budget of dissolved silicon. Nature, Lond. 220, 905–906 (1968)
Calvert, S. E.: Silica balance in the ocean and diagenesis. Nature, Lond. 219, 919–920 (1968)
Gilbert, J. Y. and W. E. Allen: The phytoplankton of the Gulf of California obtained by the E. W. Scripps in 1939 and 1940. J. mar. Res. 5, 89–110 (1943)
Gregor, B.: Silica balance of the ocean. Nature, Lond. 219, 360–361 (1968)
Grill, E. V. and F. A. Richards: Nutrients regeneration from phytoplankton decomposing in seawater. J. mar. Res. 22, 51–69 (1964)
Harriss, R.: Biological buffering of oceanic silica. Nature, Lond. 212, 275–276 (1966)
Hecky, R. E., K. Mopper, P. Kilham and E. T. Degens: The amino acid and sugar composition of diatom cell-walls. Mar. Biol. 19, 323–331 (1973)
Honjo, S. and M. R. Roman: Marine copepod fecal pellets: production, preservation and sedimentation. J. mar. Res. 36, 45–57 (1978)
Hurd, D. C.: Factors affecting solution rate of biogenic opal in seawater. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 15, 411–417 (1972)
Jørgensen, E. G.: Solubility of silica in diatoms. Physiol. Plant. 8, 846–851 (1955)
Kamatani, A.: Regeneration of inorganic nutrients from diatom decomposition. J. oceanogr. Soc. Japan 25, 63–74 (1969)
Kamatani, A.: Physical and chemical characteristics of biogenous silica. Mar. Biol. 8, 89–95 (1971)
Kamatani, A. and J. P. Riley: The rate of dissolution of diatom silica walls in seawater. Mar. Biol. 55, 29–35 (1979)
Kamatani, A., J. P. Riley and G. Skirrow: The dissolution of opaline silica of diatom tests in seawater. J. oceanogr. Soc. Japan 36, 201–208 (1980)
Kobubo, S.: Plankton diatoms, pp 330, Tokyo, Koseisha Koseikaku 1965
Kozlova, O. G. and V. V. Mukhina: Diatoms and silicoflagellates in suspension and floor sediments of the Pacific Ocean. Int. Geol. Res. 9, 1322–1342 (1967)
Lawson, D. S., D. C. Hurd and H. S. Pankratz: Silica dissolution rates of decomposing phytoplankton assemblages at various temperatures. Am. J. Sci. 278 1373–1393 (1978)
Lerman, A., D. Lal and M. F. Dacey: Stokes settling and chemical reactivity of suspended particles in natural waters. In: Suspended solid in water, pp 17–47. Ed. by R. J. Gibbs. New York: Plenum Press 1974
Lewin, J. C.: The dissolution of silica from diatom walls. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 21, 182–198 (1961)
Munk, W. H. and G. Riley: Absorption of nutrients by aquatic plants. J. mar. Res. 11, 215–240 (1952)
Nelson, D. H. and J. J. Goering: Near-surface silica dissolution in the upwelling region off northwest Africa. Deep-Sea Res. 24, 65–74 (1977)
O'Conner, T. L. and S. A. Greenberg: The kinetics for the solution of silica in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem., Ithaca 63, 1195–1198 (1958)
Osterberg, C., A. G. Carey and H. Curl: Acceleration of sinking rates of radionuclides in the ocean. Nature, Lond. 200, 1276–1277 (1963)
Smayda, T. J.: Some measurements of the sinking rate of fecal pellets. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 621–625 (1969)
Smayda, T. J.: The suspension and shinking of phytoplankton in the sea. Oceanogr. mar. biol. Ann. Rev. 8, 353–414 (1970)
Turner, J. T.: Sinking rates of fecal pellets from the marine copepod Pontella meadii. Mar. Biol. 40, 249–260 (1977)
Van Lier, J. A., P. L. De Bruyn and J. T. G. Overbeek: The solubility of quartz. J. Phys. Chem., Ithaca 64, 1657 (1960)
Wiebe, P. H., S. H. Boyd and C. Winget: Particulate matter sinking to the deep-sea floor at 2 000 m in the Tongue of the ocean, Bahama, with a description of a new sedimentation trap. J. mar. Res. 34, 341–354 (1976)
Wollast, R.: The silica problem. In: The sea, Vol. 5, pp 349–392. Ed. by E. D. Gordberg. New York: John Wiley and Sons 1974
Yamaji, I.: Illustrations of the marine plankton of Japan, 369 pp. Tokyo: Hoikusha 1977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Anraku, Hiroshima
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamatani, A. Dissolution rates of silica from diatoms decomposing at various temperatures. Marine Biology 68, 91–96 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393146
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393146