Abstract
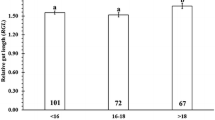
Adult horseshoe crabs Limulus polyphemus (L.) feed on a wide variety of infaunal and epifaunal invertebrates during their spring spawning migration in Delaware Bay, New Jersey, USA. Comparison of the gut contents with estimates of available prey showed that the most abundant potential prey item, the bivalve Gemma gemma, was avoided. The thinner shelled but comparatively scarce clam Mulinia lateralis was a preferred prey item. In the laboratory, crabs fed on G. gemma when it was the only available item but not when M. lateralis or soft-shell clams, Mya arenaria, were offered in conjunction. Large M. lateralis (>10mm) were preferred to small M. lateralis; there was no discrimination between M. lateralis and M. arenaria of the same size. Male and female horseshoe crabs had similar gut contents and laboratory feeding preferences, despite the fact that females are larger than males. Crabs spawning later in the summer contained more food than did crabs collected at the peak of spawning activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Barber, S. D.: Chemoreception and proprioreception in Limulus. J. exp. Zool. 131, 51–69 (1956)
Botton, M. L.: Predation by adult horseshoe crabs, Limulus polyphemus (L.) and its effect on benthic intertidal community structure of breeding beaches in Delaware Bay, New Jersey. Unpublished Ph. D. thesis, Rutgers University 1982
Botton, M. L.: The importance of predation by horseshoe crabs, Limulus polyphemus, to an intertidal sand flat community. J. mar. Res. 42, 139–161 (1984)
Botton, M. L. and H. H. Haskin: Distribution and feeding of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, on the continental shelf off New Jersey. Fish. Bull., U.S. (In press)
Carriker, M. R.: Observations on the penetration of tightly closing bivalves by Busycon and other predators. Ecology 32, 73–83 (1951)
Carriker, M. R.: The role of physical and biological factors in the culture of Crassostrea and Mercenaria in a salt-water pond. Ecol. Monogr. 29, 219–266 (1959)
Carter, J. A. and D. H. Steele: Attraction to and selection of prey by immature lobsters (Homarus americanus). Can. J. Zool. 60, 326–336 (1982)
Cohen, E. (Ed.): Biomedical applications of the horseshoe crab (Limulidae), 688 pp. New York: Liss 1979
Darnell, R. M.: Food habits of fishes and larger invertebrates of Lake Ponchartrain, Louisiana, an estuarine community. Publ. Univ. Texas, Inst. mar. Sci. 5, 353–416 (1958)
Elner, R. W. and D. G. Raffaelli: Interactions between two marine snails, Littorina rudis Maton and Littorina nigrolineata Gray, a predator, Carcinus maenas (L.), and a parasite, Microphallus similis Jagerskiold. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 43, 151–160 (1980)
Hamilton, P. V.: Predation on Littorina irrorata (Mollusca: Gastropoda) by Callinectes sapidus (Crustacea: Portunidae). Bull. mar. Sci. 26, 403–409 (1976)
Haskin, H. H.: The selection of food by the common oyster drill, Urosalpinx cinerea, Say. Proc. natl Shellfish. Assoc. 1950, 62–68 (1950)
Hughes, R. N.: Optimal foraging theory in the marine context. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. ann. Rev. 18, 423–481 (1980)
Ivlev, V.S.: Experimental ecology of the feeding of fishes, 302 pp. New Haven: Yale University Press 1961
Krantz, G. and J. Chamberlin. Blue crab predation on cultchless oyster spat. Proc. natl. Shellfish. Assoc. 68, 38–41 (1978)
Landers, W. S.: Notes on the predation of the hard clam, Venus mercenaria, by the mud crab, Neopanope texana. Ecology 35, 442 (1954)
Lockhead, J. A.: Arthropoda. Xiphosura polyphemus. In: Selected invertebrate types, pp 360–381. Ed. by F. A. Brown. New York: Wiley 1950
Lockwood, S.: The horse food crab. Am. Nat. 4, 257–273 (1870)
MacKenzie, C. L.: Predation on hard clam (Mercenaria mercenaria) populations. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 106, 530–537 (1977)
McDermott, J. J.: The predation of oysters and barnacles by crabs of the family Xanthidae. Proc. P. Acad. Sci. 34, 199–211 (1960)
Rudloe, A.: Limulus polyphemus: A review of the ecologically significant literature. In: Biomedical applications of the horseshoe crab (Limulidae), pp 27–35. Ed. by E. Cohen. New York: Liss 1979
Rudloe, A.: Aspects of the biology of juvenile horseshoe crabs, Limulus polyphemus. Bull. mar. Sci. 31, 125–133 (1981)
Schneider, D. C.: Equalization of prey numbers by migratory shorebirds. Nature, Lond. 271, 353–354 (1978)
Sekiguchi, K. and K. Nakamura: Ecology of the extant horseshoe crabs. In: Biomedical applications of the horseshoe crab (Limulidae), pp 37–45. Ed. by E. Cohen. New York: Liss 1979
Shuster, C. N., Jr.: Observations on the natural history of the American horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. Third report on investigations of methods of improving the shellfish resources of Massachusetts. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Contribution no. 564, 18–23 (1950)
Shuster, C. N., Jr.: Distribution of the American horseshoe “crab”, Limulus polyphemus (L.). In: Biomedical applications of the horseshoe crab (Limulidae), pp 3–26. Ed. by E. Cohen. New York: Liss 1979
Shuster, C. N., Jr.: A pictorial review of the natural history and ecology of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, with reference to other Limulidae. In: Physiology and biology of horseshoe crabs, pp 1–51. Ed. by J. Bonaventura and C. Bonaventura. New York: Liss 1982
Smith, O. R. and E. Chin: The effects of predation on soft clams, Mya arenaria. Natl Shellfish. Assoc. Convention Addr., 37–44 (1951)
Smith, O. R., Baptist, J. P. and E. Chin: Experimental farming of the soft-shell clam, Mya arenaria, in Massachusetts, 1949–1953. Comm. Fish. Rev. 17, 1–16 (1955)
Strauss, R.: Reliability estimates for Ivlev's electivity index, the forage ratio, and a proposed linear index of food selection. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 108, 344–352 (1979)
Tagatz, M. E.: Biology of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, in the St. Johns River, Florida. Fish. Bull, U.S. 67, 17–33 (1968)
Whetstone, J. and A. Eversole: Predation on hard clams, Mercenaria mercenaria, by mud crabs, Panopeus herbstii. Proc. natl Shellfish. Assoc. 68, 42–48 (1978)
Woodin, S. A.: Disturbance and community structure in a shallow water sand flat. Ecology 62, 1052–1066 (1981)
Wyse, G. A.: Receptor organization and function in Limulus chelae. Z. vergl. Physiol. 73, 249–273 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. K. Pierce, College Park
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Botton, M.L. Diet and food preferences of the adult horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus in Delaware Bay, New Jersey, USA. Mar. Biol. 81, 199–207 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393118
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393118