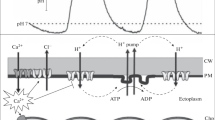
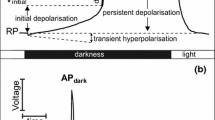
Abstract
The electrophysiological membrane parameters of the unicellular green alga Eremosphaera viridis were determined using an improved computer-supported single-microelectrode technique. These cells developed an average membrane potential of-150 mV in the light and a specific resistance of 1 Ω m2 with an external potassium concentration of 1.1 mM and pH 5.5. In the dark, many cells showed a less polarized potential of 30–40 mV and a smaller membrane resistance. At potassium concentrations in the external medium higher than 1 mM, the membrane potential strongly depends on the external potassium content apart from a small electrogenic component. At concentrations lower than 1 mM K+, a dependence of the membrane potential upon external potassium concentrations could not be verified. Inserting the internal ion activities in the Goldmann equation shows that, in this range, the proton conductance seems to be predominant over the potassium conductance. Transient changes in the membrane potential and in the membrane resistance were observed after switching off the light, after addition of 3-(3′,4′-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea or N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, after a sudden decrease in temperature, and after current pulses. These changes resemble the action potentials (AP) found in other plant cells (Chara, Acetabularia). On average, the AP has a delay period of 5.1 s and a duration of 43.8 s showing a sudden decrease and a slower regeneration. The voltage peak during an AP followed exactly the Nernst potential of potassium over a range of external potassium concentrations from 5 μM to 0.2 M. This is true for depolarization or hyperpolarization, depending on the external K+-concentration. Tetraethylammonium-hydrogensulphate, a rather specific inhibitor of K+ channels in nervous cells, suppressed the AP. The correlation of the appearance of the AP with a short-term opening of potassium channels in the membrane of Eremosphaera is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP:
-
action potential
- DCCD:
-
N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
- Em :
-
membrane potential (mV)
- DCMU:
-
3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
- TEA:
-
tetraethylammonium-hydrogensulphate
References
Beilby, M.J., Coster, H.G.L. (1979) The action potential in Chara corallina. II. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 6, 323–335
Beilby, M.J., Walker, N.A. (1981) Chloride transport in Chara. I. Kinetics and current-voltage curves for a probable proton symport. J. Exp. Bot. 32, 43–54
Bentrup, F.W. (1979) Reception and transduction of electrical and mechanical stimuli. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, N. S., vol. 7: Physiology of movements, pp. 42–70, Haupt, W., Feinleib, M.E., eds. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Christlieb, T.H., Weber, A. (1980) Die Bedeutung der Zelloberfläche für die Sorption von Blei durch eine coccale Grünalge. Environ. Technol. Lett. 1, 311–318
Felle, H., Bentrup, F.W. (1976) Effect of light upon membrane potential, conductance, and ion fluxes in Riccia fluitans. J. Membr. Biol. 27, 153–170
Felle, H. (1981) A study of the current-voltage relationships of electrogenic active and passive membrane elements in Riccia fluitans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 646, 151–160
Findlay, G.P. (1982) Electrogenic and diffusive components of the membrane of Hydrodiction africanum. J. Membr. Biol. 68, 179–190
Geisweid, H.-J. (1982) Elektrische Eigenschaften der einzelligen Grünalge Eremosphaera viridis und ihre Beeinflussung durch das Schwermetall Cadmium. Ph. D. thesis, University of Würzburg
Geisweid, H.-J., Simonis, W., Urbach, W. (1982) Electrophysiological membrane properties of the unicellular green alga Eremosphaera viridis. Plant Physiol. 69, Suppl. 67 (Abstr.)
Gilly, W.M.F., Armstrong, C.M. (1982) Divalent cations and the activation kinetics of potassium channels in squid giant axons: J. Gen. Physiol. 79, 965–996
Gradmann, D. (1970) Einfluß von Licht, Temperatur und Außenmedium auf das elektrische Verhalten von Acetabularia crenulata. Planta 93, 323–353
Gradmann, D. (1976) “Metabolic” action potentials in Acetabularia. J. Membr. Biol. 29, 23–45
Gradmann, D., Mummert, H. (1980) Plant action potentials. In: Plant membrane transport: current conceptual issues, pp. 333–344, Spanswick, R.M., Lucas, W.J., Dainty, J., eds. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam New York
Hille, B. (1978) Ionic channels in excitable membranes. Biophys. J. 22, 283–294
Keifer, D.W., Lucas, W.J. (1982) Potassium channels in Chara corallina. Control and interaction with the electronic H+ pump. Plant Physiol. 69, 781–788
Kies, L. (1967) Oogamie bei Eremosphaera viridis de Bary. Flora (Jena), Abt. B 157, 1–12
Kishimoto, U. (1966) Action potential of Nitella internodes. Plant Cell Physiol. 7, 559–572
Köhler, K. (1982) Untersuchungen zum elektrogenen Membrantransport bei einer photoautotrophen Suspensionskultur von Chenopodium rubrum. Ph. D. thesis, University of Tübingen
Ohkawa, T.A., Köhler, K., Bentrup, F.W. (1981) Electrical membrane potential and resistance in photoautotrophic suspension cells of Chenopodium rubrum L. Planta 151, 88–94
Portis, A.R., Heldt, H.W. (1976) Light dependent changes of Mg2+ concentration in the stroma in relation to the Mg2+ depending of CO2 fixation in intact chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 449, 434–446
Prins, H.B.A., Harper, J., Higinbotham, N. (1980) Membrane potentials of Vallisneria leaf cells and their relation to photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 65, 1–5
Raven, J.A., Smith, F.A. (1978) Effect of temperature and external pH on the cytoplasmic pH of Chara corallina. J. Exp. Bot. 29, 853–866
Robinson, D.G., Sachs, H., Mayer, F. (1976) Cytokinesis in the green alga Eremosphaera viridis: plasmalemma formation from “open membranes”. Planta 129, 75–82
Schefczik, K., Simonis, W., Schiebe, M. (1983) Continuous registration of membrane resistances of plant cells using a single electrode technique. Plant. Physiol. 72, 368–375
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. (1977) Control of membrane potential and excitability of Chara cells with ATP and Mg2+. J. Membr. Biol. 37, 167–192
Slayman, C.W., Long, W.S., Wu, C.Y.-H. (1973) The relationship between ATP and an electrogenic pump in the plasma membrane of Neurospora crassa. J. Membr. Biol. 14, 305–338
Slayman, C.L., Long, W.S., Gradmann, D. (1976) “Action potentials” in Neurospora crassa, a mycelial fungus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 426, 732–744
Smith, R.L., Bold, H.C. (1966) Phycological studies. VI. Investigations of the algal genera Eremosphaera and Oocystis. University of Texas, Publ. No. 6612
Smith, P.T., Walker, N.A. (1976) Chloride transport in Chara corallina and the electrochemical potential difference for hydrogen ions. J. Exp. Bot. 27, 451–459
Spanswick, R.M. (1972) Evidence for an electrogenic ion pump in Nitella. I. The effects of pH, potassium, sodium, light and temperature on membrane potential and resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 288, 73–89
Spanswick, R.M. (1981) Electrogenic ion pumps. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 32, 267–289
Tazawa, M., Shimmen, T. (1980) Action potential in Characeae: some characteristics revealed by internal perfusion studies. In: Plant membrane transport: current conceptual issues, pp. 349–362, Spanswick, R.M., Lucas, W.J., Dainty, J., eds. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam New York
Ulbricht, W. (1977) Ionic channels and gating currents in nerve block of sodium and potassium channels. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 6, 7–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köhler, K., Geisweid, H.J., Simonis, W. et al. Changes in membrane potential and resistance caused by transient increase of potassium conductance in the unicellular green alga Eremosphaera viridis . Planta 159, 165–171 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392988
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392988