Abstract
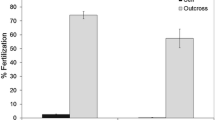
Electrophoretic analysis of planulae obtained from controlled breeding experiments with the coral Goniastrea favulus during spawning events in 1986 and 1987 on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia, shows that offspring are produced equally frequently by outcrossing or self-fertilization, leading to a genetically determined rate of selfing of around 50%. Field rates of selfing may be greater than this as a consequence of the limited dispersal of gametes within this species. However, the level of heterozygote depression found in one population is well below that which would be predicted for such levels of selfing. In one enzyme system, glucosephosphate isomerase, the maternal phenotype continues to be expressed in the planula larva for between 11 and 17 d after fertilization. This effect is postulated to result from a residual of maternal enzyme and RNA derived from a relatively large egg.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Ayala, F. J., Hedgecock, D., Zumwalt, G. S., Valentine, J. W. (1973). Genetic variation in Tridacna maxima, an ecological analog of some unsuccessful evolutionary lineages. Evolution 27: 177–199
Ayre, D. J., Resing, J. M. (1986). Sexual and asexual production of planulae in reef corals. Mar. Biol. 90: 187–190
Babcock, R. C. (1984). Reproduction and distribution of two species of Goniastrea (Scleractinia) from the Great Barrier Reef Province. Coral Reefs 2: 187–195
Baker, H. G. (1955). Self-compatibility and establishment after “long distance” dispersal. Evolution 9: 347–348
Brown, A. H. D. (1979). Enzyme polymorphisms in plant populations. Theor. Popul. Biol. 15: 1–42
Bucklin, A., Hedgecock, D., Hand, C. (1984). Genetic evidence of self-fertilization in the sea anemone Epiactis prolifera. Mar. Biol. 84: 175–182
Fadlallah, Y. H. (1983). Sexual reproduction, development and larval biology in scleractinian corals. Coral Reefs 2: 129–150
Fairburn, D. J., Roff, D. A. (1980). Testing genetic models of isozyme variability without breeding data: can we depend on the χ2? Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 37: 1149–1159
Heyward, A. J., Babcock, R. C. (1986). Self- and cross-fertilization in scleractinian corals. Mar. Biol. 90: 191–195
Hill, W. G. (1975). Linkage disequilibrium among multiple neutral alleles produced by mutation in finite populations. Theor. Popul. Biol. 8: 117–126
Kojis, B. L., Quinn, N. L. (1981). Aspects of sexual reproduction and larval development in the shallow water hermatypic coral Goniastrea australensis (Edwards and Haime, 1857). Bull. mar. Sci. 31: 558–573
Price, S. C., Jain, S. K. (1981). Are inbreeders better colonizers? Oecologia 49: 283–286
Schemski, D. W., Lande, R. (1985). The evolution of self-fertilization and inbreeding depression in plants. II Empirical observations. Evolution 39: 41–52
Shaw, C. R., Prasad, R. (1970). Starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes a compilation of recipes. Biochem. Genet. 4: 297320
Shields, W. M. (1982) Inbreeding and the paradox of sex: a resolution. Evolutionary Theory 5: 245–279
Stoddart, J. A. (1983). Asexual production of planulae in the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Mar. Biol. 76: 279–284
Swofford, D. L., Selander, R. B. (1981). BIOSYS-1: a FORTRAN program for the comprehensive analysis of electrophoretic data in population genetics and systematics. J. Hered. 72: 281–283
Wallace, C. C. (1985). Reproduction, recruitment and fragmentation in nine sympatric species of the coral genus Acropora. Mar. Biol. 88: 217–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoddart, J.A., Babcock, R.C. & Heyward, A.J. Self-fertilization and maternal enzymes in the planulae of the coral Goniastrea favulus . Mar. Biol. 99, 489–494 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392556
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392556