Abstract
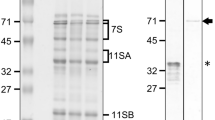
Antibodies raised against purified glutelins and prolamines were employed as probes to study the cellular routes by which these proteins are deposited into protein bodies of rice (Oryza sativa L.) endosperm. Three morphologically distinct protein bodies, large spherical, small spherical, and irregularly-shaped, were observed, in agreement with existing reports. Immunocytochemical studies showed the presence of glutelins in the irregularly-shaped protein bodies while the prolamines were found in both the large and small spherical protein bodies. Both the large and small spherical protein bodies, distinguishable by electron density and gold-labeling patterns, appear to be formed by direct deposition of the newly formed proteins into the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In contrast, glutelin protein bodies are formed via the Golgi apparatus. Small electron-lucent vesicles are often found at one side of the Golgi. Electron-dense vesicles, whose contents are labeled by glutelin antibody-gold particles, are commonly observed at the distal side of the Golgi apparatus and fuse to form the irregularly shaped protein bodies in endosperm cells. These observations indicate that the transport of rice glutelins from their site of synthesis, the ER, to the site of deposition, the protein bodies, is mediated by the Golgi apparatus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- Da:
-
dalton
- DAF:
-
days after flowering
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- GL:
-
irregularly shaped
- L:
-
large spherical
- S:
-
small spherical (protein bodies)
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PTA:
-
phosphotungstic acid
References
Baumgartner, B., Tokuyasu, K., Chrispeels, M.J. (1980) Immunocytochemical localization of reserve protein in the endoplasmic reticulum of developing bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) cotyledons. Planta 150, 419–425
Bechtel, D.R., Juliano, B.O. (1980) Formation of protein bodies in the starchy endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.): a reinvestigation. Ann. Bot. 45, 503–509
Bechtel, D.B., Pomeranz, Y. (1978) Ultrastructure of mature ungerminated rice (Oryza sativa) caryopsis. The starch endosperm. Am. J. Bot. 65, 684–691
Briarty, L.G., Hughes, C.E., Evers, A.D. (1979) The developing endosperm of wheat — A sterological analysis. Ann. Bot. 44, 641–658
Bendayan, M., Zollinger, M. (1983) Ultrastructural localization of antigenic sites on osmium-fixed tissues applying the protein A-gold technique. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, 101–109
Craig, S., Goodchild, D.J. (1984) Periodate acid treatment of sections permits on-grid immunogold localization of seed vicillin in ER and Golgi. Protoplasma 122, 35–44
Doman, D.C., Trelease, R.N. (1985) Protein A-gold immunocytochemistry of isocitrate lysase in cotton seeds. Protoplasma 124, 157–167
Farquhar, M.G., Palade, G.E. (1981) The Golgi apparatus (complex) — (1954–1981) — from artifact to center stage. J. Cell Biol. 91, 77S-103S
Greenwood, J.S., Chrispeels, M.J. (1985a) Immunocytochemical localization of phaseolin and phytohemagglutinin in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex of developing bean cotyledons. Planta 164, 295–302
Greenwood, J.S., Chrispeels, M.J. (1985b) Correct targeting of the bean storage protein protein phaseolin in the seeds of transformed tobacco. Plant Physiol. 79, 65–71
Harris, N., Juliano, B.O. (1977) Ultrastructure of endosperm protein bodies in developing rice grains differing in protein content. Ann. Bot. 41, 1–5
Ivanova, D.J. (1974) Cytological investigation of protein deposit formation in the endosperm of rice. Sov. Plant Physiol. (Engl. transln. of Fiziol. Rast.) 21, 795–799
Khoo, V., Wolf, M.J. (1970) Origin and development of protein granules in maize endosperm. Am. J. Bot. 57, 1042–1050
Krishnan, B.H., Okita, T.W. (1986) Structural relationships among rice glutelin polypeptides. Plant Physiol 81, 748–753
Larkins, B.A., Hurkman, W.J. (1978) Synthesis and deposition of zein in protein bodies of maize endosperm. Plant Physiol. 62, 256–263
Lucas, W.J., Franceschi, V.R. (1982) Organization of the sieveelement walls of leaf minor veins. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 81, 209–221
Luthe, D.S. (1983) Storage protein accumulation in developing rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds. Plant Sci. Lett. 32, 147–158
Oparka, N., Harris, N. (1982) Rice protein body formation: all types are initiated by dilation of the endoplasmic reticulum. Planta 154, 184–188
Parker, M.L. (1982) Protein accumulation in developing endosperm of a high-protein line of Triticum dicoccoides. Plant Cell Environ. 5, 37–43
Parker, M.L., Hawes, C.R. (1982) The Golgi apparatus in developing endosperm of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Planta 154, 277–283
Pesacreta, T.C., Lucas, W.J. (1984) Plasma membrane coat and a coated vesicle-associated reticulum of membranes: Their structure and possible interrelationship in Chara corallina. J. Cell Biol. 98, 1537–1545
Spurr, A.R. (1969) A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–43
Tanaka, K., Sugimoto T., Ogawa, M., Kasai, Z. (1980) Isolation and characterisation of two types of protein bodies in the rice endosperm. Agric. Biol. Chem. 44, 1633–1639
Villareal, R.M., Juliano, B.O. (1978) Properties of glutelin from mature and developing rice grain. Phytochemistry 17, 177–182
Walburg, G., Larkins, B.A. (1986) Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding 12S globulin mRNAs. Plant Molec. Biol. 6, 161–169
Wen, T.-N., Luthe, D.S. (1985) Biochemical characterization of rice glutelin. Plant Physiol. 78, 172–177
Wu, H-K., Chen, Y-T. (1978) Protein bodies in developing rice grain. Proc. Natl. Sci. Council (Taiwan) 2, 281–192
Yamagata, H., Sugimoto, T., Tanaka, K., Kasai, Z. (1982) Biosynthesis of storage proteins in developing rice seeds. Plant Physiol. 70, 1094–1100
Yamagata, H., Tanaka, K. (1986) The site of synthesis and accumulation of rice storage proteins. Plant Cell Physiol. 27, 135–145
Zhao, W-M., Gatehouse, J.A., Boulter, D. (1983) The purification and partial amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from the glutelin fraction of rice grains: homology to pea legumin. FEBS Lett. 162, 96–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, H.B., Franceschi, V.R. & Okita, T.W. Immunochemical studies on the role of the Golgi complex in protein-body formation in rice seeds. Planta 169, 471–480 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392095
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392095