Abstract
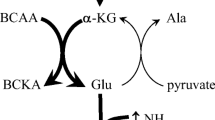
Adenine nucleotide (AN) degradation has been shown to occur during intense exercise in man and in the horse, at or close to the point of fatigue. The aim of the study was to compare plasma ammonia concentration ([NH3]) as a result of intense exercise with plasma [lactate]. Plasma glutamine concentration ([Gln]) was also measured pre- and post-exercise. On separate occasions, nine healthy subjects (two females) exercised on a motorised treadmill for periods of between 30 s and 210 s, at 5.6 m · s −1 (0% incline). On one occasion, running at the same speed, two subjects ran at +4% incline whilst one other subject ran at + 7% incline. Blood samples were taken and plasma was analysed for [lactate], [NH3] and [Gln]. Subjects showed varying degrees of AN degradation as indicated by plasma [NH3]. A comparison of plasma [NH3] with that of plasma [lactate] indicated a marked increase in AN degradation, corresponding to a [lactate] of around 14 mmol · l−1 in plasma. The data further support the hypothesis that there is a critical intramuscular pH below which there is a stimulus to AN degradation during intense exercise, possibly as a result of a substantial reduction in the kinetics of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) rephosphorylation provided by phosphocreatine, resulting in an increase in [ADP].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babij P, Matthews SM, Rennie MJ (1983) Changes in blood ammonia, lactate and amino acids in relation to workload during bicycle ergometer exercise in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 50:405–411
Balsom PD, Ekblom B, Soderlund K, Sjodin B, Hultman E (1993) Creatine supplementation and dynamic high-intensity intermittent exercise. Scand J Mod Sci Sports 3:143–149
Banister EW, Allen ME, Mekjavic IB, Singh AK, Legge B, Mutch BJC (1983) The time course of ammonia and lactate accumulation in blood during bicycle exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 51:195–202
Broberg S, Sahlin K (1989) Adenine nucleotide degradation in human skeletal muscle during prolonged exercise. J Appl Physiol 67:116–122
Buono MJ, Clancy TR, Cook JR (1984) Blood lactate and ammonium ion accumulation during graded exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 57:135–139
Dudley GA, Staron RS, Murray TF, Hagerman FC, Luginbuhl A (1983) Muscle fibre composition and blood ammonia levels after intense exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 54:582–586
Eriksson LS, Broberg S, Bjorkman O, Wahren J (1985) Ammonia metabolism during exercise in man. Clin Physiol 5:325–336
Faller J, Fox IH (1982) Ethanol-induced hyperuricemia N Engl J Med 307:1598–1602
Fonseca-Wollheim F (1990) Pre-analytical increase of ammonia in blood specimens from healthy subjects. Clin Chem 36:1483–1487
Greenhaff PL, Harris RC, Snow DH, Sewell DA, Dunnett M (1991) The influence of metabolic acidosis upon exercise metabolism in the thoroughbred horse. Eur J Appl Physiol 63:129–134
Harris RC, Hultman E (1985) Adenine nucleotide depletion in human muscle in response to intermittent stimulation in situ. J Physiol (Lond) 365:73P
Harris RC, Marlin DJ, Snow DH (1987) Metabolic response to maximal exercise of 800 m and 2000 m in the thoroughbred horse. J Appl Physiol 63:12–19
Harris RC, Marlin DJ, Snow DH, Harkness RA (1991) Muscle ATP loss and lactate accumulation at different work intensities in the exercising thoroughbred horse. Eur J Appl Physiol 62:235–244
Itoh H, Ohkuwa T (1990) Peak blood ammonia and lactate after submaximal, maximal and supramaximal exercise in sprinters and long distance runners. Eur J Appl Physiol 60:271–276
Itoh H, Ohkuwa T (1991) Ammonia and lactate in the blood after short-term sprint exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 62:22–25
Katz A, Sahlin K, Henriksson J (1986) Muscle ammonia metabolism during isometric contraction in humans. Am J Physiol 250:C834-C840
Meyer RA, Terjung RL (1979) Differences in ammonia and adenylate metabolism in contracting fast and slow muscle. Am J Physiol 237: C111-C118
Meyer RA, Terjung RL (1980) AMP deamination and IMP reamination in working skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 239:C32-C38
Sahlin K, Katz A (1988) Purine nucleotide metabolism. In: Poortmans JR (ed) Principles of exercise biochemistry. Karger, Basel, pp 120–139
Sahlin K, Palmskog G, Hultman E (1978) Adenine nucleotide and IMP contents of the quadriceps muscle in man after exercise. Pflügers Arch 374:193–198
Sewell DA, Harris RC (1992) Adenine nucleotide degradation in the thoroughbred horse with increasing exercise duration. Eur J Appl Physiol 65:271–277
Sewell DA, Harris RC, Hanak J, Jahn P (1992) Muscle adenine nucleotide degradation in the thoroughbred horse as a consequence of racing. Comp Biochem Physiol [B] 101:375–381
Snow DH, Harris RC, Gash SP (1985) Metabolic response of equine muscle to intermittent maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 58:1689–1697
Wilkerson JE, Batterton DL, Horvath SM (1977) Exercise induced changes in blood ammonia levels in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 37:255–263
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sewell, D.A., Gleeson, M. & Blannin, A.K. Hyperammonaemia in relation to high-intensity exercise duration in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 69, 350–354 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392042
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392042