Summary
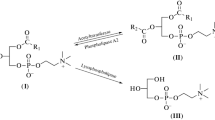
3′–5′ Exonucleases from various sources were found to toxicogenate 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide (“activated” cyclophosphamide) by splitting the oxazaphosphorinane ring and releasing an alkylating moiety and acrolein. Neither cyclophosphamide (CP) nor the deactivated metabolites of CP, 4-keto-CP and carboxyphosphamide nor 4-(S-ethanol)-sulfido-CP were attacked by 3′–5′ exonucleases. DNA polymerases with proofreading activity, such as DNA polymerase I from E. coli or DNA polymerase δ from rabbit bone marrow, exhibited a tenfold higher specific activity with “activated” CP than “plain” 3′–5′ phosphodiesterases such as snake venom phosphodiesterase or 3′,5′ cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase from bovine heart tissue.
High levels of toxicogenating activity were estimated in peripheric human lymphocytes and tissues of lymphatic origin, suggesting that enzymatic toxicogenation plays a key role with respect to the cytotoxic specificity of “activated” CP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcon RA (1968) Fluorometric determination of acrolein and related compounds with m-aminophenol. Anal Chem 40:1704–1708
brock N, Hohorst HJ (1962) Über die Aktivierung von Cyclophosphamid im Warmblüterorganismus. Naturwissenschaften 49:610–611
Brock N, Hohorst HJ (1977) The problem of specificity and selectivity of alkylating cytostatics: studies on N-2-chloroethyl-amidooxazaphosphorinanes. Z Krebsforsch 88:185–215
Brutlag D, Kornberg A (1972) Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. A proofreading function for the 3′–5′ exonuclease activity in deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. J Biol Chem 247:241–248
Byrnes JJ, Downey KM, Black VL, So AG (1976) A new mammalian DNA polymerase with 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity: DNA polymearse δ. Biochemistry 5:2817–2823
Byrnes JJ, Downey KM, Que BG, Lee MYWT, Black VL, So AG (1977) Selective inhibition of the 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity associated with DNA polymerase: a mechanism of mutagenesis. Biochemistry 16:3740–3746
Draeger U, Peter C, Hohorst HJ (1976) Deactivation of cyclophosphamide (NSC-26271) metabolites by sulfhydryl compounds. Cancer Treat Rep 60:355–359
Hill DL, Kirk CM, Struck FP (1970) Isolation and identification of 4-ketocyclophosphamide, a possible active form of the antitumor agent cyclophoshamide. J Am Chem Soc 92:3207–3208
Hohorst HJ, Draeger U, Peter G, Voelcker G (1976) The problem of oncostatic specificity of cyclophosphamide (NSC-26271): studies on reactions that control the alkylating and cytotoxic activity. Cancer Treat Rep 60:309–315
Lee MYWT, Tan CK, So AG, Downey KM (1980) Purification of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase δ from calf thymus: partial characterization of physical properties. Biochemistry 19:2096–2101
Lee MYWT, Tan CK, So AG, Downey KM (1981) Structural and functional properties of calf thymus DNA polymerase δ. Prog Nucleic Acid Ras Mol Biol 26:83–96
Peter G, Wagner T, Hohorst HJ (1976) Studies on 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide (NSC 181815): a simple preparation method and its application for the synthesis of a new class of activated sulfur-containing cyclophosphamide (NSC-26271) derivatives. Cancer Treat Rep 60:429–435
Peter G, Hohorst HJ (1979) Synthesis and preliminary antitumor evaluation of 4-(SR)-sulfido-cyclophosphamide. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 3:181–188
Struck RF, Kirk MC, Mellet LB, Eidaveer S, Hill DL (1971) Urinary metabolites of the antitumor agent cyclophosphamide. Mol Pharmacol 7:519–528
Voelcker G, Bielicki L, Hohorst HJ (1981) Evidence for enzymatic toxification of activated cyclophosphamide (4-hydroxycyclophosphamide). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 99:A 58–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Bonn-Bad Godesberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bielicki, L., Voelcker, G. & Hohorst, H.J. Enzymatic toxicogenation of “Activated” cyclophosphamide by 3′–5′ exonucleases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 105, 27–29 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391828
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391828