Summary
The effect of CO2 on the 32P-labelling of polyphosphates and acid-soluble organic phosphates is studied in synchronously grown cultures of the green alga Ankistrodesmus braunii, using trichloroacetic acid treatment and acid hydrolysis for the fractionation of the phosphorus compounds.
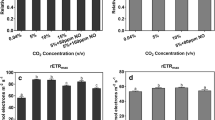
Three per cent CO2 in nitrogen causes an inhibition of the labelling of polyphosphates but a marked increase of 32P in organic phosphates, whereas oxygen (CO2-free air) produces the reverse effect. Polyphosphates and ATP are the fractions most stimulated by O2, while stable organic phosphates show the strongest inhibition. Labelling of nucleic acids is relatively indifferent to both oxygen and CO2. Three per cent CO2 in air causes the same distribution of 32P-labelling as 3 per cent CO2 in N2.
32P-labelling is strongly dependent on the pH of the medium. In the absence of CO2, polyphosphate labelling is highest in the acidic range, whereas organic phosphates and ATP show optimum labelling and the highest percentage of the total 32P in the alkaline pH range. The effect of CO2 is strongest between pH 5 and 6, that of oxygen between pH 8 and 9. Apparently the pH of the medium exerts a considerable influence upon the phosphate metabolism inside the cells.
Increasing concentration of CO2 lead to the same change of 32P-labelling in nitrogen as in air and to saturation at about 1 per cent CO2 under the conditions used. The curves are in good agreement with those of O2-evolution at increasing concentrations of CO2, but they show completely different rates.
Young cells respond to CO2 and O2 differently from cells in the photosynthetically most active stage. In young cells both gasses are less effective.
The effect of CO2 is explained by a strong increase in noncyclic photophosphorylation which can proceed only slowly in N2. ATP-consumption connected with high rates of CO2-fixation may be the reason for the low rates of 32P-labelling in the polyphosphate fraction when CO2 is present. The influence of external pH on 32P-labelling is partly due to the pH-dependence of phosphate uptake, but the different response of several fractions to the pH of the medium suggests that the pH of the cytoplasm and possibly even the pH of the interior of the chloroplasts is affected by the external pH. The effect of O2 in the absence of CO2 or at low CO2-concentrations is explained by the well-known inhibition of photosynthesis by oxygen. Increasing concentrations of CO2 reverse this inhibition and correspondingly change the distribution of 32P between the phosphate fractions. The change in sensitivity to CO2 and O2 with the cell age is consistent with the change in the rates of maximum photosynthetic CO2-fixation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Coombs, J., Whittingham, C.P.: The mechanism of inhibition of photosynthesis by high partial pressures of oxygen in Chlorella. Proc. roy. Soc. B 164, 511–520 (1966a).
——: The effect of high partial pressures of oxygen on photosynthesis in Chlorella I. The effect on end products of photosynthesis. Phytochem. 5, 643–651 (1966b).
Dilley, R.A., Rothstein, A.: Chloroplast membrane characteristics. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 135, 427–443 (1967).
Dodd, W.A., Bidwell, G.S.: The effect of pH on the products of photosynthesis in 14CO2 by chloroplast preparations from Acetabularia mediterranea. Plant Physiol. 47, 779–783 (1971).
Ellyard, P.W., Gibbs, M.: Inhibition of photosynthesis by oxygen in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 44, 1115–1121 (1969).
Essl, A.: Diss. Würzburg 1969.
Gimmler, H.: Diss. Würzburg 1967.
—, Neimanis, S., Eilmann, I., Urbach, W.: Photophosphorylation and photosynthetic 14CO2-fixation in vivo. II. Comparison of cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation with photosynthetic 14CO2-fixation during the synchronous life cycle of Ankistrodesmus braunii. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 64, 358–366 (1971).
Graham, D., Whittingham, C.P.: The path of carbon during photosynthesis in Chlorella pyrenoidosa at high and low carbon dioxide concentrations. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 58, 418–427 (1968).
Hager, A.: Lichtbedingte pH-Erniedrigung in einem Chloroplasten-Kompartiment als Ursache der enzymatischen Violaxanthin-Zeaxanthin-Umwandlung; Beziechungen zur Photophosphorylierung. Planta (Berl.) 89, 224–243 (1969).
Hase, E., Miyachi, S., Mihara, S.: A preliminary note on the phosphorus compounds in chloroplasts and volutin granules isolated from Chlorella cells. Studies on Microalgae and Photosynthetic Bacteria, 619–626, Tokyo 1963.
Heber, U.: Conformational changes of chloroplasts induced by illumination of leaves in vivo. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 180, 302–319 (1969).
—, French, C.S.: Effects of oxygen on the electron transport chain of photosynthesis. Planta (Berl.) 79, 99–112 (1968).
—, Santarius, K.A.: Direct and indirect transfer of ATP and ADP across the chloroplast envelope. Z. Naturforsch. 25b, 718–728 (1970).
Heldt, H.W., Rapley, L.: Unspecific permeation and specific uptake of substances in spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Letters 7, 139–142 (1970).
Hess, J.L., Tolbert, N.E.: Glycolate pathway in algae. Plant Physiol. 42, 371–379 (1967).
Jackson, W.A., Volk, R.J.: Photorespiration. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 21, 385–432 (1970).
Jeschke, W.D., Simonis, W.: Über die Wirkung von CO2 auf die lichtabhängige Cl--Aufnahme bei Elodea densa: Regulation zwischen nichtcyclischer und cyclischer Photophosphorylierung. Planta (Berl.) 88, 157–171 (1969).
Kaden, J.: Diss. Würzburg 1965.
Kanai, R., Aoki, S., Miyachi, S.: Quantitative separation of inorganic polyphosphates in Chlorella cells. Plant and Cell Physiol. 6, 467–473 (1965).
Kandler, O., Tanner, W.: Die Photoassimilation von Glucose als Indikator für die Lichtphosphorylierung in vivo. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 79, (48)-(57) (1966).
Latzko, E., Garnier, R. v., Gibbs, M.: Effect of photosynthesis, photosynthetic inhibitors and oxygen on the activity of ribulose-5-phosphate kinase. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 39, 1140–1144 (1970).
Ouellet, C., Benson, A.A.: The path of carbon in photosynthesis. XIII. pH-Effects in C14O2-fixation by Scenedesmus. J. exp. Bot. 3, 237–245 (1952).
Plaut, Z., Gibbs, M.: Glycolate formation in intact spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 45, 470–474 (1970).
Rensen, J.J.S. van: Action of some herbicides in photosynthesis of Scenedesmus as studied by their effects on oxygen evolution and cyclic photophosphorylation. Meded. Landbouwhogeschool Wageningen 71, Nr. 9 (1971).
Senger, H.: Charakterisierung einer Synchronkultur von Scenedesmus obliquus, ihrer potentiellen Photosyntheseleistung und des Photosynthesequotienten während des Entwicklungscyclus. Planta (Berl.) 90, 243–266 (1970).
Seuberling, H.B.: Diss. Wüzburg, 1969.
Simonis, W.: Problems of photosynthetic phosphorylation in vivo by unicellular algae (Ankistrodesmus). In: Thomas, J.B., Goedheer, J.C., Currents in photosynthesis, p. 217–223. Rotterdam: A. D. Donker 1966.
—, Kating, H.: Untersuchungen zur lichtabhängigen Phosphorylierung III. Die CO2-Abhängigkeit der 32P-Einlagerung in Ankistrodesmus. Z. Naturforsch. 11b, 704–708 (1956).
Stålfelt, M.G.: Das Kohlendioxyd, Handbuch Pflanzenphysiologie, Hrsg. v. W. Ruhland, Bd. V, 2, S. 81–99. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960.
Ullrich, W.R.: Zur Wirkung von Sauerstoff auf die 32P-Markierung von Polyphosphaten und organischen Phosphaten bei Ankistrodesmus braunii im Licht. Planta (Berl.) 90, 272–285 (1970a).
—: Die Wirkung von O2 und CO2 auf die 32P-Markierung der Polyphosphate von Ankistrodesmus braunii bei der Photosynthese. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 83, 435–438 (1970b).
—: Nitratabhängige nichtcyclische Photophosphorylierung bei Ankistrodesmus braunii in Abwesenheit von CO2 und O2. Planta (Berl.) 100, 18–30 (1971).
—, Simonis, W.: Die Bildung von Polyphosphaten bei Ankistrodesmus braunii durch Photophosphorylierung im Rotlicht von 683 und 712 nm unter Stickstoffatmosphäre. Planta (Berl.) 84, 358–367 (1969).
Ullrich-Eberius, C.I., Simonis, W.: Der Einfluß von Natrium- und Kaliumionen auf die Phosphataufnahme bei Ankistrodesmus braunii. Planta (Berl.) 93, 214–226 (1970).
Urbach, W., Gimmler, H.: Photophosphorylierung und photosynthetische 14CO2-Fixierung in vivo. I. Vergleich von cyclischer und nichtcyclischer Photophosphorylierung mit der photosynthetischen 14CO2-Fixierung. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 62, 276–286 (1970).
—, Simonis, W.: Further evidence for the existence of cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation in vivo by means of desaspidin and DCMU. Z. Naturforsch. 22b, 537–540 (1967).
Warburg, O., Krippahl, G.: Glykolsäurebildung in Chlorella. Z. Naturforsch. 15b, 197–199 (1960).
Whittingham, C.P., Bermingham, M., Hiller, R.G.: The photometabolism of glucose in Chlorella. Z. Naturforsch. 18b, 701–706 (1963).
Wintermans, J.F.G.M.: On the formation of polyphosphates in Chlorella in relation to conditions for photosynthesis. Proc. kon. ned. Akad. Wet. C57, 574–583 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. W. Schumacher zum 70. Geburtstag gewidmet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullrich, W.R. Der Einfluß von CO2 und pH auf die 32P-Markierung von Polyphosphaten und organischen Phosphaten bei Ankistrodesmus braunii im Licht. Planta 102, 37–54 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391448
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391448