Abstract
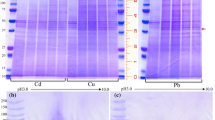
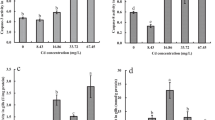
Sea scallops Placopecten magellanicus, which had been trawl-collected in late November, 1982 off the Rhode Island, USA coast, were exposed to 20 μg of Cd or Cu per liter for a period of seven weeks in a flowing seawater system. Metal analyses of kidneys from both groups indicated uptake of both metals, although the tissue concentrations of Cd declined markedly in the Cu-treated scallops. The ultrastructural appearance of tubule cells of kidneys from Cd-exposed scallops was indistinguishable from controls. In contrast, tubule cells from scallops exposed to Cu showed marked cellular degeneration with loss of concretions. These ultrastructural changes were associated with significant reductions in renal isocitrate dehydrogenase activity in the Cu-treated scallops. Elemental analyses conducted on the kidney concretions and on the cytosolic metal-binding proteins of Cd-exposed scallops showed a 6-to 7-fold increase in Cd content of both these metalsequestering compartments, with concomitant changes in Zn, Mn, and Cu content. Loss of the concretions from Cu-treated scallops precluded analysis of this compartment, but Cu sequestration within cytosolic metal-binding proteins was associated with marked reductions of Zn and Cd from these proteins, suggesting disruption of this cellular mechanism for control of divalent metal cations. These findings support the hypothesis that toxic metal perturbation of normal homeostatic mechanisms that control divalent metal cation bioavailability is important factor in mediating cell injury from these agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bryan, G. W.: The occurrence and seasonal variation of trace metals in the scallops Pecten maximus (L.) and Chalmys opercularis (L.). J. mar. biol. Ass. UK 53 145–166 (1973)
Carmichael, N. G. and B. A. Fowler: Cadmium accumulation and toxicity in the kidney of the bay scallop Argopecten irradians. Mar. Biol. 65, 35–43 (1981)
Carmichael, N. G., K. S. Squibb, D. W. Engel and B. A. Fowler: Metals in the molluscan kidney: uptake and subcellular distribution of 109Cd, 54Mn and 65Zn by the clam, Mercenaria mercenaria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65A, 203–206 (1980)
Carmichael, N. G., K. S. Squibb and B. A. Fowler: Metals in the molluscan kidney: a comparison of two closely related bivalve species (Argopecten) using X-ray microanalysis and atomic absorption spectroscopy. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 36, 1149–1155 (1979)
Coombs, T. L.: Cadmium in aquatic organisms. In: The chemistry, biochemistry, and biology of cadmium, pp 93–139. Ed. by M. Webb. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press 1979
Coombs, T. L. and S. G. George: Mechanisms of immobilization and detoxication of metals in marine organisms. In: Physiology and behaviour of marine organisms, pp 179–187. Ed. by D. L. McLusky and A. J. Berry. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1978
Doyle, L. J., N. J. Blake, C. C. Woo and P. Yevich: Recent biogenic phosphorite: concretions in mollusc kidneys. Science, Wash. DC 199, 1431–1433 (1978)
Engel, D. W. and B. A. Fowler: Factors influencing the accumulation and toxicity of cadmium to marine organisms. Envir. Health Perspect. 28, 81–88 (1979a)
Engel, D. W. and B. A. Fowler: Copper and cadmium-induced changes in the metabolism and structure of molluscan gill tissue. In: Marine pollution: functional responses, pp 239–256. Ed. by W. B. Vernberg, A. Calabrese, F. P. Thurberg and F. J. Vernberg. New York: Academic Press 1979b
Fowler, B. A.: Intracellular compartmentation of metals in aquatic organisms: relationships to mechanisms of cell injury. Envir. Health Perspect. 71, 121–128 (1987)
Fowler, B. A., J. Abel, C.-G. Elinder, J.-J. Hapke, J. H. R. Kägi, J. Kleiminger, Y. Kojima, A. J. M. Schoot Uiterkamp, E. K. Silbergeld, S. Silver, K. H. Summer and R. J. P. Williams: Structure, mechanism and toxicity. In: Changing metal cycles and human health, pp 391–404. Ed. by J. Niragu. Dahlem Workshop Reports. Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag 1984
Fowler, B. A., N. G. Carmichael and K. S. Squibb: Factors affecting trace-metal uptake and toxicity to estuarine organisms. II. Cellular mechanisms. In: Biological monitoring of marine pollutants, pp 145–163. Ed. by F. J. Vernberg, A. Calabrese, F. P. Thurberg and W. B. Vernberg. New York: Academic Press 1981
Fowler, B. A., D. W. Engel and M. Brouwer: Purification and characterization studies of cadmium-binding proteins from the American oyster Crassostrea virginica. Envir. Health Perspect. 65, 63–70 (1986)
Fowler, B. A. and M. M. Megginson: Isolation and partial characterization of a high molecular weight Cd/Zn binding protein from the kidney of the scallop Placopecten magellanicus: preliminary studies. Envir. Health Perspect 65, 199–204 (1986)
Fowler, B. A., D. A. Wolfe and W. F. Hettler: Mercury and iron uptake by cytosomes in mantle epithelial cells of quahog clams (Mercenaria mercenaria) exposed to mercury. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 32, 1767–1775 (1975)
George, S. G. and B. J. S. Pirie: The occurrence of cadmium in subcellular particles in the kidney of the marine mussel, Mytilus edulis, exposed to cadmium. Biochim. biophys. Acta 580, 234–244 (1979)
George, S. G., B. J. S. Pirie and T. L. Coombs: Isolation and elemental analysis of metal-rich granules from the kidney of the scallop, Pecten maximus (L.). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 42, 143–156 (1980)
Gould, E., R. A. Grieg, D. Rusanowsky and B. C. Marks: Metalexposed sea scallops, Placopecten magellanicus (Gmelin): a comparison of the effects and uptake of cadmium and copper. In: Marine pollution and physiology: recent advances, pp 157–186. Ed. by F. J. Vernberg, F. P. Thurberg, A. Calabrese and W. Vernberg. Columbia, SC: University of South Carolina Press 1985
Grieg, R. A., T. K. Sawyer, E. J. Lewis and M. E. Galasso: A study of metal concentrations in relation to gill color and pathology in the rock crab. Arch. environ. Contam. Toxicol. 11, 539–549 (1982)
Kägi, J. H. R. and M. Nordberg (eds.): Metallothionein 378 pp. Basel: Birkhauser 1979
Kägi, J. H. R., M. Vasak, K. Lerch, D. E. O. Gilg, P. Hunziker, W. R. Bernhard and M. Good: Structure of mammalian metallothionein. Envir. Health Perspect. 54, 93–103 (1984)
Liss, R. G.: Uptake and depuration of metals by sea scallops (Placopecten magellanicus) exposed to drilling mud. M. S. thesis. Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1979
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr and R. J. Randall: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265–275 (1951)
Miller, W. L., N. J. Blake and R. H. Byrne: Uptake of Mn54 by the beach clam, Donax variabilus (Say 1822) from a resin buffered seawater system. Mar. Envir. Res. 17, 163–166 (1985a)
Miller, W. L., N. J. Blake and R. H. Byrne: Uptake of Zn65 and Mn54 into body tissues and renal concretions by the southern quahog, Mercenaria campechiensis (Gmelin): effects of elevated phosphate and metal concentrations. Mar. envir. Res. 17, 167–171 (1985b)
Petering, D. H. and B. A. Fowler: Roles of metallothionein and related proteins in metal metabolism and toxicity: problems and perspectives. Envir. Health Perspect. 65, 217–224 (1986)
Ridlington, J. W. and B. A. Fowler: Isolation and partial characterization of cadmium-binding protein from the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Chem. Biol. Interactions 25, 127–138 (1979)
Thurberg, F. P., A. Calabrese, E. Gould, R. A. Greig, M. A. Dawson and R. K. Tucker: Response of the lobster, Homarus americanus, to sublethal levels of cadmium and mercury. In: Physiological responses of marine biota to pollutants, pp 185–197. Ed. by F. J. Vernberg, A. Calabrese, F. P. Thurberg and W. B. Vernberg. New York: Academic Press 1977
Wood, J. M. A. M. Chakrabarty, P. J. Craig, U. Forstner, B. A. Fowler, U. Herms, I. S. Krull, D. Mackay, G. J. Olson, D. H. Russell, W. Salomons and S. Silver: Speciation in systems under stress. In: The importance of chemical speciation in environmental processes, pp 425–441. Ed. by M. Bernhard, F. E. Brinckman and P. J. Sadler. Dahlem Workshop Report, No. 33. Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag 1986
Yevich, C. A. and P. P. Yevich: Histopathological Effects of cadmium and copper on the sea scallop Placopecten magellanicus. In: Marine pollution and physiology: recent advances, pp 187–198. Ed. by F. J. Vernberg, F. P. Thurberg, A. Calabrese and W. B. Vernberg. Columbia, SC: University of South Carolina Press 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Lawrence, Tampa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fowler, B.A., Gould, E. Ultrastructural and biochemical studies of intracellular metal-binding patterns in kidney tubule cells of the scallop Placopecten magellanicus following prolonged exposure to cadmium or copper. Mar. Biol. 97, 207–216 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391304
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391304