Abstract
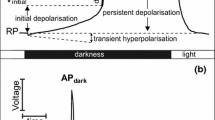
A depolarisation of the membrane potential difference (about-170 mV) of Chara corallina is observed in response to changes in cell turgor pressure using the pressure probe technique. The depolarisation occurs in phase with the pressure pulse (0.2 s duration) and is independent of the direction of the applied pressure gradient. This latter finding is in contradiction to results predicted on the basis of electro-kinetic phenomena. Pressure induced electrical leakages were ruled out by measuring the depolarisation in response to pressure in individual segments of the internode which were electrically isolated from one another. The changes in potential were recorded by external electrodes and an internal electrode which was positioned close to the micropipette of the pressure probe inserted through one of the electrically isolated nodes. The depolarisation in response to increasing positive or negative pressure gradients in the intact node region and in the intact middle segments was comparable to that monitored in the node region containing the pressure probe. Action potentials were initiated when the pressure gradients exceeded at least 2 bar. The action potentials were elicited at random in one of the two compartments adjacent to the node regions, but were never found to be initiated in the node regions themselves. The pressure-induced action potentials are explained in terms of an electro-mechanical compression (or expansion) of a local membrane area and discussed in their relevance to the propagation of pressure signals in response to water and salt stress in higher plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
potential difference
References
Barry, P.H., Hope, A.B.: Electro-osmosis in Chara and Nitella cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 193, 124–128 (1969a)
Barry, P.H., Hope, A.B.: Electroosmosis in membranes: Effects of unstirred layers and transport numbers. Biophys. J. 9, 729–757 (1969b)
Bentrup, F.W.: 3. Reception and transduction of electrical and mechanical stimuli. In: Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, Plant Movements. Haupt, W., Feinleib, M.E., eds., Vol. 2, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978
Fettiplace, R., Andrews, D.M., Haydon, D.A.: The thickness, composition and structure of some lipid bilayers and natural membranes. J. Membrane Biol. 5, 277–296 (1971)
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B.: Electrical properties of plant cells: Methods and findings. In: Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, New Series. Lüttge, U., Pitman, M.G., eds., Vol. II, Part A, pp. 53–92. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Gutknecht, J.: Salt transport in Valonia: Inhibition of potassium uptake by small hydrostatic pressures. Science 160, 68–70 (1968)
Hüsken, D., Steudle, E., Zimmermann, U.: Pressure probe technique for measuring water relations of cells in higher plants. Plant Physiol. (1978) in press
MacRobbie, E.A.C.: Functions of ion transport in plant cells and tissues. Int. Rev. Biochem. Plant Biochem. II, Northcote, D.H., ed., Vol. 13, pp. 211–247. Baltimore: University Park Press 1977
Mummert, H., Gradmann, D.: Voltage dependent potassium fluxes and the significance of action potentials in Acetabularia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 443, 443–450 (1976)
Pickard, B.G.: Action potentials in higher plants, Bot. Rev. 39, 172–201 (1973)
Spanswick, R.M.: Electrical coupling between cells of higher plants: A direct demonstration of intercellular communication. Planta 102, 215–227 (1972)
Williams, St. E., Spanswick, R.M.: Propagation of the neuroid action potential of the carnivorous plant Drosera. J. Comp. Physiol. 108, 211–223 (1976)
Zimmermann, U.: Cell turgor pressure regulation and turgor pressure mediated transport processes. In: Integration of Activity in the Higher Plant. Proc. of the 31th Symp. of the Soc. of Exp. Biol. Jennings, D., ed., pp. 117–154. Cambridge: University Press 1977
Zimmermann, U.: The physics of turgor regulation in plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 29 (1978) in press
Zimmermann, U., Räde, H., Steudle, E.: Kontinuierliche Druckmessung in Pflanzenzellen. Naturwissenschaften 56, 634 (1969)
Zimmermann, U., Steudle, E.: Action of indoleacetic acid on membrane structure and transport. In: Regulation of Cell Membrane Activities in Plants. Marré, E., Ciferri, O., eds., pp. 231–241. Amsterdam: Elsevier-North-Holland 1977
Zimmermann, U., Steudle, E.: Physical aspects of water relations of plant cells. Adv. Bot. Res. (1978) in press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmermann, U., Beckers, F. Generation of action potentials in Chara corallina by turgor pressure changes. Planta 138, 173–179 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391175
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391175