Summary
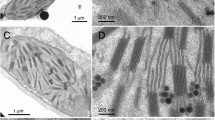
The permeability of the plastid envelope during the development of Avena sativa plastids was investigated by light scattering and uptake of various labelled compounds (malate, succinate, glutamate, α-ketoglutarate, citrate, glycine, sucrose). The results presented show that a primary event during greening is a change in permeability, thereby allowing an increased transport of metabolites across the membranes of very early etio-chloroplast stages. The results are discussed in view of an adaption of the plastid envelope permeability to the changing requirements of externally synthesized precursors and intermediates during development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HEPES:
-
N-2-Hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethane-sulfonic acid
- MES:
-
2(N-Morpholino)ethane-sulfonic acid
References
Bisalputra, T., Bailey, A.: The fine structure of the chloroplast envelope of a red alga, Bangia fusco-purpurea. Protoplasma (Wien) 76, 443–454 (1973)
Cobb, A.H., Wellburn, A.R.: Changes in plastid envelope polypeptides during chloroplast development. Planta (Berl.) 121, 273–282 (1974)
Cockburn, B.J., Wellburn, A.R.: Changes in the envelope permeability of developing chloroplasts. J. exp. Bot. 25, 36–49 (1974)
Drumm, H.E., Margulies, M.M.: In vitro protein synthesis by plastids of Phaseolus vulgaris. IV. Amino acid incorporation by etioplasts and effect of illumination of leaves on incorporation by plastids. Plant Physiol. 45, 435–442 (1970)
Gimmler, H., Schäfer, G., Kraminer, H., Heber, U.: Amino acid permeability of the chloroplast envelope as measured by light scattering, volumetry and amino acid uptake. Planta (Berl.) 120, 47–61 (1974)
Heber, U.: Metabolite exchange between chloroplasts and cytoplasm. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25, 393–421 (1974)
Heldt, H.W., Rapley, L.: Specific transport of inorganic phosphate, 3-phosphoglycerate and dihydroxyacetonephosphate, and of dicarboxylates across the inner membrane of spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Letters 10, 143–148 (1970)
Heldt, H.W., Sauer, F.: The inner membrane of the chloroplast envelope as the site of specific metabolite transport. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 234, 83–91 (1971)
Klingenberg, M., Pfaff, E.: Means of terminating reactions. In: Methods in enzymology. Vol. X. pp. 680–684. Eds.: Colowick, S.P., Kaplan, N.I. New York: Academic Press 1967
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Wellburn, A.R., Wellburn, F.A.M.: A new method for the isolation of etioplasts with intact envelopes. J. exp. Bot. 22, 972–979 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hampp, R., Schmidt, H.W. Changes in envelope permeability during chloroplast development. Planta 129, 69–73 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390916
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390916