Summary
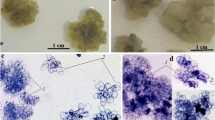
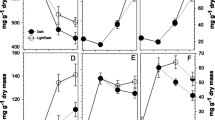
Callus from hypocotyls of white spruce (Picea glauca [Moench] Voss) was grown on agar under defined conditions with high levels of calcium nitrate. Transfer of callus to liquid suspension cultures and maintenance of suspensions either under a regime of constant temperature and light or under alternating conditions similar to those of a late spring day, affected the content of free sugars, tannins, and aldehydes. Under the alternating conditions the levels of these substances increased greatly compared to those under the constant environment. By contrast, vascularization of cell clumps, which was comparable to the differentiation of hypocotyls in seedlings, was obtained only under constant conditions. Cells at the centre of the clumps developed secondary wall thickenings and bordered pits, and were surrounded by cambial-like initials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson, J. V., Patterson, J. A.: Accelerated chromatographic analysis of amino acids commonly found in physiological fluids on a spherical resin of specific design. Analyt. Biochem. 13, 265–280 (1965)
Brown, C. L., Sax, K.: The influence of pressure on the differentiation of secondary tissues. Amer. J. Bot. 49, 583–691 (1962)
Chafe, S. C., Durzan, D. J.: Tannin inclusions in cell suspension cultures of white spruce. Planta (Berl.) 113, 251–262 (1973)
Constabel, F.: Tannins in tissue cultures of Juniperus communis L. Planta med. (Stuttg.) 11, 417–421 (1963)
Constabel, F.: Phenolics in tissue cultures derived from Juniperus communis L. In: Intern. Conf. on Plant Tissue Culture, p. 183–210, White, P. R., Grove, A., eds. Berkeley, Calif.: McCutchan Press 1965
Dickinson, R. G., Jacobson, N. W.: A new sensitive and specific test for the detection of aldehydes: Formation of 6-mercapto-3-substituted-S-triazole(4,3-b)-S-tetrazines. Chem. Commun. 1970, 1719
Durzan, D. J., Steward, F. C.: Cell and tissue culture of white spruce and jack pine. Bimo. Res. Notes 24, 30 (1968)
Durzan, D. J., Steward, F. C.: Morphogenesis in cell cultures of gymnosperms: some growth patterns. Intern. Union Forest Res. Organizations, Sect. 22, Invited paper, Varparanta, Finland, 20, pp., Abstr. Comm. Inst. For. Fenn. 74, No. 6, 16–17 (1970)
Haccius, B.: Haben Gewebekultur-Embryonen einen Suspensor? Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 78, 11–21 (1965)
Jacquiot, C.: 1947. Effet inhibiteur des tannins sur le developpement des cultures in vitro du cambium de certains arbres forestiers. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 225, 434–436 (1947)
Johansen, D. A.: Plant embryology. Waltham, Mass.: Chronica Bot. 1950
Jorgensen, E., Balsillie, D.: Formation of heartwood phenols in callus tissue of red pine (Pinus resinosa). Canad. J. Bot. 47, 1015–1016 (1969)
Konar, R. N., Oberoi, Y. P.: In vitro development of embryoids on the cotyledons of Biota orientalis. Phytomorphology 15, 137–140 (1965)
Mopper, K., Degens, E. T.: A new chromatographic sugar autoanalyzer with a sensitivity of 10-10 moles. Analyt. Biochem. 45, 147–153 (1972)
Romberger, J. A.: Meristems, growth, and development in woody plants. U.S.D.A. Forest Serv. Tech. Bull. No. 1293 (1963)
Smith, I.: Chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques. In: Chromatography, vol. 1, p. 308–354. New York: Interscience 1960
Steward, F. C., Shantz, E. M.: The chemical induction of growth in plant tissue cultures. I. Methods and tissue culture and the analysis of growth. In: The chemistry and mode of action of plant growth substances, p. 165–186, Wain, R. L., Wightman, F., eds. New York: Acad. Press 1958
Wetmore, R. H., Steeves, T. A.: Morphological introduction to growth and development. In: Plant physiology, an advanced treatise, vol. VI A, p. 3–166, F. C. Steward, ed. New York: Acad. Press 1971
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durzan, D.J., Chafe, S.C. & Lopushanski, S.M. Effects of environmental changes on sugars, tannins, and organized growth in cell suspension cultures of white spruce. Planta 113, 241–249 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390511
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390511