Summary
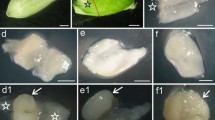
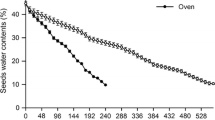
The mature seed of celery (Apium graveolens, L.) contains a small axile linear embryo surrounded by endosperm which occpies the bulk of the seed. The endosperm is living and consists of mostly large angular thick-walled cells containing aleurone grains (often with globoids) and lipid droplets. — Using de-embryonated seeds, it has been shown that the endosperm was induced to break down by gibberellin. The aleurone grains became swollen and lost their contents and the bulk of each cell wall was hydrolyzed. However, a thin resistant layer of wall remained around each protoplast. The wall hydrolysis caused the endosperm to break down into individual cells which could be plasmolyzed and therefore appeared to be still living. All cells of the endosperm responded to gibberellin in a similar way although the cells near the radicle appeared to degrade more rapidly than those elsewhere. There was no change in the absence of the hormone. The response was apparently specific to gibberellin and did not occur in the presence of ethylene, kinetin, abscisic acid and indole acetic acid. The results were the same in light and in darkness. — It has been thought that endosperm breakdown during germination of seed such as celery involved release of hydrolases from the expanding embryo. The results of this study indicate that endosperm breakdown might be caused by hydrolases arising in the endosperm itself in response to gibberellin released from the embryo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GA:
-
gibberellic acid
- PAS:
-
periodic acid-Schiff reagent
References
Abeles, F.B.: Role of RNA and protein synthesis in abscission. Plant Physiol. 43, 1577–1586 (1968)
Ashford, A.E., Jacobsen, J.V.: Cytochemical localization of phosphatase in barley aleurone cells: The pathway of gibberellic acid-induced enzyme release. Planta (Berl.) 120, 81–105 (1974)
Beevers, H.: Metabolic production of sucrose from fat. Nature (Lond.) 191, 433–436 (1961)
Beevers, L., Loveys, B., Pearson, J.A., Wareing, P.F.: Phytochrome and hormonal control of expansion and greening of etiolated wheat leaves. Planta (Berl.) 90, 286–294 (1970)
Black, M.: Light-controlled germination of seeds. Symp. Soc. exp. Biol. 23, 193–218 (1969)
Bornman, C.H.: Some ultrastructural aspects of abscission in Coleus and Gossypium. S. Afr. J. Sci. 63, 325–331 (1967)
Briggs, D.E.: Biochemistry of barley germination. Action of gibberellic acid on barley endosperm. J. Inst. Brew. (Lond.) 69, 13–19 (1963)
Chen, S.S.C., Thimann, K.V.: Studies on the germination of light-inhibited seeds of Phacelia tanacetifolia. Israel J. Bot. 13, 57–73 (1964)
Cooke, R.J., Saunders, P.F., Kendrick, R.E.: Red light induced production of gibberellin-like substances in homogenates of etiolated wheat leaves and in suspensions of intact etioplasts. Planta (Berl.) 124, 319–328 (1975)
Eb, van der, A.A., Nieuwdorp, P.J.: Electron microscopic structure of the aleurone cells of barley during germination. Acta bot. neerl. 15, 690–699 (1967)
Evans, A., Smith, H.: Localization of phytochrome in etioplasts and its regulation in vitro of gibberellin levels. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. in press
Frost-Christensen, H.: Embryo development in ripe seeds of Eranthis hiemalis and its relation to gibberellic acid. Physiol. Plantarum (Kbh.) 30, 200–205 (1974)
Fulcher, R.G., O'Brien, T.P., Lee, J.W.: Studies on the aleurone layer. 1. Conventional and fluorescence microscopy of the cell wall with emphasis on phenol-carbohydrate complexes in wheat. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 25, 23–34 (1972)
Hayward, H.E.: Umbelliferae, Apium graveolens. In: The structure of economic plants. New York: MacMillan 1938
Horton, R.F., Osborne, D.J.: Senescence, abscission and cellulase activity in Phaseolus vulgaris. Nature (Lond.) 214, 1086–1089 (1967)
Ikuma, H., Thiman, K.V.: Action of gibberellic acid on lettuce seed germination. Plant Physiol. 35, 557–566 (1960)
Ikuma, H., Thiman, K.V.: The role of the seed-coats in germination of photosensitive lettuce seeds. Plant Cell Physiol. 4, 169–185 (1963)
Jacobsen, J.V., Knox, R.B., Pyliotis, N.A.: The structure and composition of aleurone grains in the barley aleurone layer. Planta (Berl.) 101, 189–209 (1971)
Jensen, W.A.: Botanical histochemistry. San Francisco: Freeman 1962
Jones, R.L.: The fine structure of barley aleurone cells. Planta (Berl.) 85, 359–375 (1969a)
Jones, R.L.: The effect of ultracentrifugation on fine structure and α-amylase production in barley aleurone cells. Plant Physiol. 44, 1428–1438 (1969b)
Jones, R.L.: The structure of the lettuce endosperm. Planta (Berl.) 121, 133–146 (1974)
Junttila, O.: The mechanism of low temperature dormancy in mature seeds of Syringa species. Physiol. Plantarum (Kbh.) 29, 256–263 (1973)
Köhler, D.: Veränderungen des Gibberellingehaltes von Salatsamen nach Belichtung. Planta (Berl.) 70, 42–45 (1966)
Kondo, M.: Über die in der Landwirtschaft Japans gebrauchten Samen. Ber. Ohara Inst. Landw. Forsch. 1, 420–424 (1919)
MacLeod, A.M., Palmer, G.H.: The embryo of barley in relation to modification of the endosperm. J. Inst. Brew. (Lond.) 72, 580–589 (1966)
Mares, D.J., Stone, B.A.: Studies on wheat endosperm. 1. Chemical composition and ultrastructure of the cell walls. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 26, 793–812 (1973)
Martin, A.C.: The comparative internal morphology of seeds. Amer. Midland Naturalist 36, 573–660 (1946)
McNeil, M., Albersheim, P., Taiz, L., Jones, R.: On the structure of the walls of barley aleurone cells. Plant Physiol., Suppl. 53, 15 (1974)
McNeil, M., Albersheim, P., Taiz, L., Jones, R.: The structure of plant cell walls VII. Barley aleurone cells. Plant Physiol. 55, 64–68 (1975)
Morinaga, T.: Effect of alternating temperature upon the germination of seeds. Amer. J. Bot. 13, 141–158 (1926)
Morre, D.J.: Cell wall dissolution and enzyme secretion during leaf abscission. Plant Physiol. 43, 1545–1559 (1968)
Nabors, M.W., Lang, A.: The growth physics and water relations of red-light-induced germination in lettuce seeds. I. Embryos germinating in osmoticum. Planta (Berl.) 101, 1–25 (1971a)
Nabors, M.W., Lang, A.: The growth physics and water relations of red-light-induced germination in lettuce seeds. II. Embryos germinating in water. Planta (Berl.) 101, 26–42 (1971b)
Netolitzky, F.: Anatomie der Angiospermen — Samen. Handbuch der Pflanzenanatomie. Bd. X. Berlin: Borntraeger 1926
Paleg, L.: In: Regulateurs naturels de la croissance végétale. Ed.: J.P. Nitsch. pp. 303–317. Paris: CNRS 1963
Paleg, L., Hyde, B.: Physiological effects of gibberellic acid. VII. Electron microscopy of barley aleurone cells. Plant Physiol. 39, 673–680 (1964)
Palevitch, D., Thomas, T.H., Austin, R.B.: Dormancy-release of celery seed by a growth retardant, N-dimethylaminosuccinamic acid (Alar). Planta (Berl.) 100, 370–372 (1971)
Radley, M.: Site of production of gibberellin-like substances in germinating barley embryos. Planta (Berl.) 75, 164–171 (1967)
Radley, M.: The effect of the endosperm on the formation of gibberellin by barley embryos. Planta (Berl.) 86, 218–223 (1969)
Reeve, R.M.: A specific hydroxylamine-ferric chloride reaction for histochemical localisations of pectin. Stain Technol. 34, 209–211 (1959)
Reid, D.M., Clements, J.B., Carr, D.J.: Red light induction of gibberellin synthesis in leaves. Nature 217, 580–582 (1968)
Spurr, A.R.: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–43 (1969)
Stokes, P.: A physiological study of embryo development in Heracleum sphondylium L. III. The effect of temperature on metabolism. Ann. Bot. 17, 157–173 (1953a)
Stokes, P.: The stimulation of growth by low temperature in embryos of Heracleum sphondylium L. J. exp. Bot. 4, 222–234 (1953b)
Taiz, L., Jones, R.L.: Gibberellic acid β-1,3-glucanase and the cell walls of barley aleurone layers. Planta (Berl.) 92, 73–84 (1970)
Taylor, G.A.: Some factors affecting germination of celery seed. Plant Physiol. 24, 93–102 (1949)
Thomas, T.H., Palevitch, D., Austin, R.B.: Stimulation of celery seed germination with plant growth regulators. Proc. 11th Brit. Weed Control Conf. 760–765 (1972)
Varner, J.E.: Gibberellic acid controlled synthesis of α-amylase in barley endosperm. Plant Physiol. 39, 413–415 (1964)
Yomo, H., Iinuma, H.: Enzymes of the aleurone layer of barley endosperm. Proc. Amer. Soc. Brew. Chem. 97, 97–102 (1964)
Yomo, H., Iinuma, H.: Production of gibberellin-like substance in the embryo of barley during germination. Planta (Berl.) 71, 113–118 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Most of this work was performed in the Department of Vegetable Crops at the Volcani Center, Bet Dagan, while J.V. Jacobsen was a Research Fellow there.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobsen, J.V., Pressman, E. & Pyliotis, N.A. Gibberellin-induced separation of cells in isolated endosperm of celery seed. Planta 129, 113–122 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390017
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390017