Summary
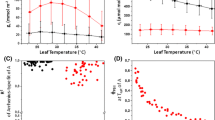
Evolution of CO2 into CO2-free air was measured in the light and in the dark over a range of temperatures from 15 to 50°. Photosynthetic rates were measured in air and O2-free air over the same range of temperatures. Respiration in the light had a different sensitivity to temperature compared with respiration in the dark. At the lower temperatures the rate of respiration in the light was higher than respiration in the dark, whereas at temperatures above 40° the reverse was observed. For any one species the maximum rates of photosynthesis and photorespiration occur at about the same temperature. The maximum rate for dark respiration generally is found at a temperature about 10° higher. Zea mays and Atriplex nummularia showed no enhancement of photosynthesis in O2-free air nor any evolution of CO2 in CO2-free air at any of the temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson, A. A., and M. Calvin: The path of carbon in photosynthesis. VII. Respiration and photosynthesis. J. exp. Bot. 1, 63–68 (1950).
Björkman, O.: The effect of oxygen concentration on photosynthesis in higher plants. Physiol. Plantarum (Copenh.) 19, 618–633 (1966).
Bravdo, B.: Decrease in net photosynthesis caused by respiration. Plant Physiol. 43, 479–483 (1968).
Brown, A. H., and D. Weis: Relation between respiration and photosynthesis in the green algae Ankistrodesmus braunii. Plant Physiol. 34, 224–234 (1959).
Decker, J. P.: A rapid, post-illumination deceleration of respiration in green leaves. Plant Physiol. 30, 82–84 (1955).
—, and J. D. Wien: Carbon dioxide surges in green leaves. J. Solar Energy Sci. Eng. 2, 39–41 (1958).
Downes, R. W., and J. D. Hesketh: Enhanced photosynthesis at low oxygen concentration: differential response of temperate and tropical grasses. Planta (Berl.) 78, 79–84 (1968).
Downton, J., and E. B. Tregunna: Carbon dioxide compensation — its relation to photosynthetic carboxylation reactions, systematics of the Gramineae, and leaf anatomy. Canad. J. Bot. 46, 207–215 (1968).
El-Sharkawy, M., and J. D. Hesketh: Effects of temperature and water deficit on leaf photosynthetic rates of different species. Crop. Sci. 4, 514–518 (1964).
——: Photosynthesis among species in relation to characteristics of leaf anatomy and CO2-diffusion resistances. Crop Sci. 5, 517–521 (1965).
—, R. S. Loomis, and W. A. Williams: Apparent reassimilation of respiratory carbon dioxide by different plant species. Physiol. Plantarum (Copenh.) 20, 171–186 (1967).
Everson, G., and M. D. Slack: Distribution of carbonic anhydrase in relation to the C4 pathway of photosynthesis. Phytochem. 7, 581–584 (1968).
Forrester, M. L., G. Krotkov, and C. D. Nelson: Effect of oxygen on photosynthesis, photorespiration and respiration in detached leaves. I. Soybean. Plant Physiol. 41, 422–427 (1966).
———: Effect of oxygen on photosynthesis, photorespiration and respiration in detached leaves. II. Corn and other monocotyledons. Plant Physiol. 41, 428–431 (1966).
Gaastra, P.: Photosynthesis of crop plants as influenced by light, carbon dioxide, temperature, and stomatal diffusion resistance. Meded. Landbouwhogesch. Wageningen 59, No 13 (1959).
Graham, D., and D. A. Walker: Some effects of light on the interconversion of metabolites in green leaves. Biochem. J. 82, 554–560 (1962).
Hatch, M. D., and C. R. Slack: Photosynthesis by sugar-cane leaves. A new carboxylation reaction and the pathway of sugar formation. Biochem. J. 101, 103–111 (1966).
Hatch, M. D., C. R. Slack, and H. S. Johnson: Further studies on a new pathway of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation in sugar-cane and its occurrence in other plant species. Biochem. J. 102, 417–422 (1967).
Hesketh, J.: Enhancement of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in the absence of oxygen, as dependent upon species and temperature. Planta (Berl.) 76, 371–374 (1967).
—: Effects of light and temperature during plant growth on subsequent leaf CO2 assimilation rates under standard conditions. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 21, 235–241 (1968).
—, and R. Musgrave: Photosynthesis under field conditions. IV. Light studies with individual corn leaves. Crop. Sci. 2, 311–315 (1962).
Hoch, G., O. H. Owens, and B. Kok: Photosynthesis and respiration. Arch. Biochem. 101, 171–180 (1963).
Hofstra, G.: An approach to the study of the physiological control of translocation in higher plants. Doct. dissert., Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, B. C. (1967).
Holmgren, P., and P. G. Jarvis: Carbon dioxide efflux from leaves in light and darkness. Physiol. Plantarum (Copenh.) 20, 1045–1051 (1967).
Johnson, H. S., and M. D. Hatch: Distribution of the C4-dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis and its occurrence in dicotyledenous plants. Phytochem. 7, 375–380 (1968).
Kortschak, H. P., C. E. Hartt, and G. O. Burr: Carbon dioxide fixation in sugarcane leaves. Plant Physiol. 40, 209–213 (1965).
Krotkov, G.: Effect of light on respiration. In: Photosynthesis mechanisms in green plants. Washington, D.C.: Nat. Acad. Sci.-Nat. Res. Counc. Publ. 1145, p. 452–454, 1963.
Marsh, H. V., J. M. Galmiche, and M. Gibbs: Effect of light on the tricarboxylic acid cycle in Scenedesmus. Plant Physiol. 40, 1013–1022 (1963).
Murata, Y., and J. Iyama: Studies on the photosynthesis of forage crops. II. Influence of air temperature upon the photosynthesis of some forage and grain crops. Proc. Crop. Sci. Soc. Japan 31, 315–321 (1963).
Ozbun, J. L., R. J. Volk, and W. A. Jackson: Effect of light and darkness on gaseous exchange of bean leaves. Plant Physiol. 39, 523–527 (1964).
Tregunna, E. B. Flavin mononucleotide control of glycolic acid oxidase and photorespiration in corn leaves. Science 151, 1239–1241 (1966).
—, and J. Downton: Carbon dioxide compensation in members of the Amaranthaceae and some related families. Can J. Bot. 45, 2385–2387 (1967).
—, G. Krotkov, and C. D. Nelson: Evolution of carbon dioxide by tobacco leaves during the dark period following illumination with light of different intensities. Canad. J. Bot. 39, 1045–1056 (1961).
———: Further evidence on the effects of light on respiration during photosynthesis. Canad. J. Bot. 42, 989–997 (1964).
———: Effect of oxygen on the rate of photorespiration in detached tobacco leaves. Physiol. Plantarum (Copenh.) 20, 723–733 (1966).
Weis, D., and A. H. Brown: Kinetic relationships between photosynthesis and respiration in the algal flagellate Ochromonas malhamensis. Plant Physiol. 34, 235–239 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofstra, G., Hesketh, J.D. Effects of temperature on the gas exchange of leaves in the light and dark. Planta 85, 228–237 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389400
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389400