Summary
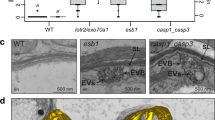
The effect of ethylene on abscission of flower pedicels of tobacco plants has been investigated. For the first 2 h of exposure to C2H4, the pedicels bend rather than break in response to applied force, but after 2.5 h exposure they break at the abscission zone under an applied force of 40 g. The break strength of the abscission zone decreases exponentially with time to 5 g at 5 h after beginning of the C2H4 treatment. An examination of the tissue at the fine structural level 2 h after exposure to C2H4 reveals the accumulation of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in the abscission cells. Rough ER becomes increasingly abundant by 3–5 h exposure of the tissue to C2H4. There is approximately a 30 fold increase in RER by 5 h of exposure, as compared to untreated tissue.
Loss in the integrity of the membranes of microbodies occurs by 5 h exposure of the tissue to C2H4. As cell wall degradation proceeds, fibrous material, vesicular structures, and electron dense bodies—the latter often appearing striated—develop in the disintegrating wall. Little change is seen in the structure of nuclei, mitochondria, chloroplasts and in the crystalloid cores of microbodies during the first 5 h of exposure of the tissue to C2H4. However, disorganization of cytoplasmic components does occur in cells where cell wall breakdown is at an advanced stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles, F. B.: Role of RNA and protein synthesis in abscission. Plant Physiol. 43, 1577–1586 (1968).
—: Abscission: Role of cellulase. Plant Physiol. 44, 447–452 (1969).
Abeles, F. B., Holm, R. E.: Enhancement of RNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and abscission by ethylene. Plant Physiol. 41, 1337–1342 (1966).
Addicott, F. T.: Plant hormones in the control of abscission. Biol. Rev. 45, 485–524 (1970).
Bornman, C. H.: Some ultrastructural aspects of abscission in Coleus and Gossypium. S. Afr. J. Sci. 63, 325–331 (1967).
Breidenbach, R. W., Kahn, A., Beevers, H.: Characterization of glyoxysomes from castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 43, 705–713 (1968).
Chrispeels, M. J., Varner, J. E.: Gibberellic acid-enhanced synthesis and release of α-amylase and ribonuclease by isolated barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 42, 398–406 (1967).
Dela Fuente, R. K., Leopold, A. C.: Senescence processes in leaf abscission. Plant Physiol. 43, 1496–1502 (1968).
Elson, C., Hartmann, H. A., Shug, A. L., Shrago, E.: Antimycin A: stimulation of cell division and protein synthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Science 168, 385–386 (1970).
Filner, P., Varner, J. E.: A simple and unequivocal test for de novo synthesis of enzymes: density labeling of barley α-amylase with H2O18. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 58, 1520–1526 (1967).
Frederick, S. E., Newcomb, E. H.: Cytochemical localization of catalase in leaf microbodies (peroxisomes). J. Cell Biol. 43, 343–353 (1969).
Gahagan, H. E., Holm, R. E., Abeles, F. B.: Effect of ethylene on peroxidase activity. Physiol. Plantarum (Cph.) 21, 1270–1279 (1968).
Gerhardt, B. P., Beevers, H.: Developmental studies on glyoxysomes in Ricinus endosperm. J. Cell Biol. 44, 94–102 (1970).
Halperin, W.: Ultrastructural localization of acid phosphatase in cultured cells of Daucus carota. Planta (Berl.) 88, 91–102 (1969).
Herrero, F. A., Hall, W. C.: General effects of ethylene on enzyme systems in the cotton leaf. Physiol. Plantarum (Cph.) 13, 736–750 (1960).
Horton, R. F., Osborne, D. J.: Senescence, abscission, and cellulase activity in Phaseolus vulgaris. Nature (Lond.) 214, 1086–1089 (1967).
Jackson, M. B., Osborne, D. J.: Ethylene, the natural regulator of leaf abscission. Nature (Lond.) 225, 1019–1022 (1970).
Jacobsen, J. F., Varner, J. E.: Gibberellic acid-induced synthesis of protease by isolated aleurone layers of barley. Plant Physiol. 42, 1596–1600 (1967).
Jensen, T. E., Valdovinos, J. G.: Fine structure of abscission zones. I. Abscission zones of the pedicels of tobacco and tomato flowers at anthesis. Planta (Berl.) 77, 298–318 (1967).
——: Fine structure of abscission zones. III. Cytoplasmic changes in abscising pedicels of tobacco and tomato flowers. Planta (Berl.) 83, 303–313 (1968).
Jones, R. L.: Gibberellic acid and the fine structure of barley aleurone cells. I. Changes during the lag-phase of α-amylase synthesis. Planta (Berl.) 87, 119–133 (1969a)
—: Gibberellic acid and the fine structure of barley aleurone cells. II. Changes during the synthesis and secretion of α-amylase. Planta (Berl.) 88, 73–86 (1969b).
Lewis, L. N., Varner, J. E.: Synthesis of cellulase during abscission of Phaseolus vulgaris leaf explants. Plant Physiol. 46, 194–199 (1970).
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Morré, D. J.: Cell wall dissolution and enzyme secretion during leaf abscission. Plant Physiol. 43, 1545–1559 (1968).
Mueller, D. M. J.: Crystal-containing bodies associated with peristome ontogeny in a moss. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 30, 615–618 (1970).
Novikoff, A. B., Goldfischer, S.: Visualization of peroxisomes (microbodies) and mitochondria with diaminobenzidine. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 17, 675–680 (1969).
Osborne, D. J.: Hormonal mechanisms regulating senescence and abscission. In: The biochemistry and physiology of plant growth substances (F. Wightman and G. Setterfield, eds.). Ottawa: Runge Press 1968.
Osborne, D. J. Ridge, I.: Ethylene, enzymes, and cell extension. In: Proceedings of the Seventh Intern. Conf. on Plant Growth Substances (D. J. Carr, ed.). New York: Plenum Press (in press).
Paleg, L.: Physiological effects of gibberellic acid. II. On starch hydrolyzing enzymes of barley endosperm. Plant Physiol. 35, 902–906 (1960).
Ridge, I., Osborne, D. J.: Regulation of peroxidase activity by ethylene in Pisum sativum: Requirements for protein and RNA synthesis. J. exp. Bot. 21, 720–734 (1970).
Stahman, M. A., Clare, B. G. Woodbury, W.: Increased disease resistance and enzyme activity induced by ethylene and ethylene production by Black Rot infected sweet potato tissue. Plant Physiol. 41, 1505–1512 (1966).
Tolbert, N. E., Oeser, A., Yamazaki, R. K., Hageman, R. H., Kisaki, T.: A survey of plants for leaf peroxisomes. Plant Physiol. 44, 135–147 (1969).
Valdovinos, J. G., Jensen, T. E.: Fine structure of abscission zones. II. Cell wall changes in abscising pedicels of tobacco and tomato flowers. Planta (Berl.) 83, 295–302 (1968).
—— Sicko, L. M.: Ethylene induced rough endoplasmic reticula in abscission cells. Plant Physiol. 47, 162–163 (1971).
Varner, J. E.: Gibberellic acid controlled synthesis of α-amylase in barley endosperm. Plant Physiol. 39, 413–415 (1964).
— Chandra, G. Ram: Hormonal control of enzyme synthesis in barley endosperm. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 52, 100–106 (1964).
Vigil, E. L.: Intracellular localization of catalase (peroxidatic) activity in plant microbodies. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 17, 425–428 (1969).
—: Cytochemical and developmental changes in microbodies (glyoxysomes) and related organelles of castor bean endosperm. J. Cell Biol. 46, 435–454 (1970).
Webster, B. D.: Anatomical aspects of abscission. Plant Physiol. 43, 1512–1544 (1968).
Yager, R. E.: Possible role of pectic enzymes in abscission. Plant Physiol. 35, 157–162 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valdovinos, J.G., Jensen, T.E. & Sicko, L.M. Fine structure of abscission zones. Planta 102, 324–333 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386617
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386617