Summary
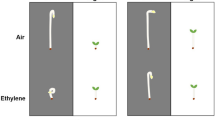
Removing endogenous ethylene by hypobaric treatment, or displacing it with carbon dioxide inhibits hook development in etiolated pea seedlings. When seedlings are returned to a normal atmosphere, hook formation occurs in darkness. Addition of ethylene accelerates this process. When ethylene induces hook formation, cell division in the hook tissue is rather inhibited by the gas. These data suggest that endogenous ethylene causes formation of the hook by inducing expansion of certain cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apelbaum, A., Burg, S.P.: Effects of ethylene and 2,4-D on cell expansion in Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol. (1972a) (in press).
Apelbaum, A., Burg, S.P.: Effect of ethylene on cell division and DNA synthesis in Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol. (1972b) (in press).
Beyer, E.M., Jr., Morgan, P.W.: Effect of ethylene on the uptake, distribution, and metabolism of indoleacetic acid-1-14C and-2-14C and naphthaleneacetic acid-1-14C. Plant Physiol. 46, 157–162 (1970).
Burg, S.P., Apelbaum, A., Eisinger, W., Kang, B.G.: Physiology and mode of action of ethylene. HortSci. 6, 359–364 (1971).
Burg, S.P., Apelbaum, A., Kang, B.G.: Control of cell division, expansion and differentiation by ethylene. In: Modern aspects of hormonal regulation in plant growth and development, Y. Vardar and H. Kaldewey, eds. Berlin: Verlag Chemie (in press).
Burg, S.P., Burg, E.A.: Role of ethylene in fruit ripening. Plant Physiol. 37, 179–189 (1962).
Burg, S.P., Burg, E.A.: Fruit storage at subatmospheric pressures. Science 153, 314–315 (1966a).
Burg, S.P., Burg, E.A.: The interaction between auxin and ethylene and its role in plant growth. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 55, 262–269 (1966b).
Burg, S.P., Burg, E.A.: Inhibition of polar auxin transport by ethylene. Plant Physiol. 42, 1224–1228 (1967a).
Burg, S.P., Burg, E.A.: Molecular requirements for the biological activity of ethylene. Plant Physiol. 42, 144–152 (1967b).
Burg, S.P., Burg, E.A.: Auxin stimulated ethylene formation: Its relationship to auxin inhibited growth, root geotropism and other plant processes. In: Biochemistry and physiology of plant growth substances, F. Wightman and G. Setterfield, eds., p. 1275–1294. Ottawa: Runge Press 1968.
Burg, S.P., Burg, E.A.: Interaction of ethylene, oxygen and carbon dioxide in the control of fruit ripening. Qual. Plant. Mater. Veg. 14, 185–200 (1969).
Crocker, W., Zimmerman, P.W.: Ethylene induced epinasty and the relationship of gravity to it. Contr. Boyce Thompson Inst. 4, 177–218 (1932).
Goeschl, J.D., Pratt, H.K.: Regulatory roles of ethylene in the etiolated growth habit of Pisum sativum. In: Biochemistry and physiology of plant growth substances, F. Wightman and G. Setterfield, eds., p. 1229–1242. Ottawa: Runge Press 1968.
Goeschl, J.D., Pratt, H.K., Bonner, B.A.: An effect of light on the production of ethylene and the growth of the plumular portion of etiolated pea seedlings. Plant Physiol. 42, 1077–1080 (1967).
Kang, B.G., Burg, S.P.: Involvement of ethylene in phytochrome-mediated carotenoid synthesis. Plant Physiol. (1972) (in press).
Kang, B.G., Ray, P.M.: Ethylene and carbon dioxide as mediators in the response of the bean hypocotyl hook to light and auxins. Planta (Berl.) 87, 206–216 (1969).
Kang, B.G., Yocum, C.S., Burg, S.P., Ray, P.M.: Ethylene and carbon dioxide; mediation of hypocotyl hook opening response. Science 156, 958–959 (1967).
Ku, H.S., Suge, H., Rappaport, L., Pratt, H.K.: Stimulation of rice coleoptile growth by ethylene. Planta (Berl.) 90, 333–339 (1970).
Laan, P.A. van der: Der Einfluß von Aethylen auf die Wuchsstoffbildung bei Avena und Vicia. Rec. Trav. bot. neerl. 31, 691–742 (1934).
Lyon, C.J.: Ethylene inhibition of auxin transport by gravity in leaves. Plant Physiol. 45, 644–646 (1970).
Marinos, N.G.: Some responses of Avena coleoptiles to ethylene. J. exp. Bot. 11, 227–235 (1960).
Maxie, E.C., Crane, J.C.: Effect of ethylene on growth and maturation of the fig, Ficus carcia L., fruit. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 92, 255–267 (1968).
Miller, P.M., Sweet, H.C., Miller, J.H.: Growth regulation by ethylene in fern gametophytes. I. Effects on protonemal and rhizoidal growth and interaction with auxin. Amer. J. Bot. 57, 212–217 (1970).
Morgan, P.W., Gausman, H.W.: Effects of ethylene on auxin transport. Plant Physiol. 41, 45–52 (1966).
Morgan, P.W., Powell, R.D.: Involvement of ethylene in responses of etiolated bean hypocotyl hook to coumarin. Plant Physiol. 45, 553–557 (1970).
Rubinstein, B.: The role of various regions of the bean hypocotyl on red light-induced hook opening. Plant Physiol. 48, 183–186 (1971a).
Rubinstein, B.: Auxin and red light in the control of hypocotyl hook opening in beans. Plant Physiol. 48, 187–192 (1971b).
Valdovinos, J.G., Ernest, L.C., Henrry, E.W.: Effect of ethylene and gibberellic acid on auxin synthesis. Plant Physiol. 42, 1803–1806 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, B.G., Burg, S.P. Ethylene as a natural agent inducing plumular hook formation in pea seedlings. Planta 104, 275–281 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386311
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386311