Abstract
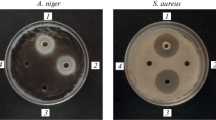
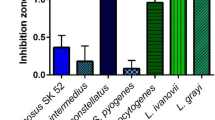
A bacterial strain, SCE2, identified as Bacillus polymyxa, produced an anti-microbial substance active against yeasts, fungi and different genera of Gram-positive and-negative bacteria, in liquid medium and in plate assays. This substance appeared to be an antibiotic different from the polymyxin group, mainly because of its action against the majority of Gram-positive bacteria tested and its lack of activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a species usually killed by polymyxins. Preliminary characterization showed resistance to heat (65°C, 2 h), to proteases, trypsin, lysozyme, deoxyribonuclease I, ribonuclease A, phospholipase C, ethanol, acetone, chloroform, ether and to strong alkali treatment (2 M NaOH). The molecular weight was less than 3500. The B. polymyxa strain harboured a plasmid that did not correlate with antibiotic production; after curing experiments, a derivative strain, SCE2(46), was isolated that lacked the plasmid pES1, but showed the same inhibitory spectrum as the wild-type strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, E.P. & Florey, H.W. 1949 Antibiotics from bacteria in the genus Bacillus. In Antibiotics, pp. 471–492 and 1533–1541. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Anthony, B.F., Giuliano, D.M. & Oh, W. 1972 Nursery outbreak of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. American Journal of Diseases of Children 124, 41–44.
Bastos, M.C.F., Bonaldo, M.C. & Penido, E.G.C. 1980 Constitutive erythromycin resistance plasmid in Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of General Microbiology 121, 513–516.
Evans, R.M. 1965 The Chemistry of the Antibiotics in Medicine. Oxford: Pergamon.
Giambiagi-Marval, M., Mafra, M.A., Penido, E.G.C. & Bastos, M.C.F. 1990 Distinct groups of plasmids correlated with bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of General Microbiology 136, 1591–1599.
Gordon, R.E., Haynes, W.C. & Pang, H.N. 1973 The Genus Bacillus. Agriculture Handbook 427. Washington DC: Agriculture Research Service, US Department of Agriculture.
Gross, D.C. & Vidaver, A.K. 1978 Bac-like substances produced by Rhizobium japonicum and other slow-growing rhizobia. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 36, 936–943.
Joseph, M.V., Desai, J.D. & Desai, A.J. 1983 Production of antimicrobial and bacteriocin-like substances by Rhizobium trifolii. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 45, 532–535.
Konisky, J. 1978 The bacteriocins. In The Bacteria, ed. Gunsalus, I.C. pp. 71–136. London: Academic Press.
Kurusu, K., Ohba, K., Arai, T. & Fukushima, K. 1987 New peptide antibiotics LI-FO3, FO4, FO5, FO7, and FO8, produced by Bacillus polymyxa. Journal Antibiotics XL, 1506–1514.
Line, M.A. & Loutit, M.W. 1971 Non-symbiotic nitrogen fixing organisms from some New Zealand tussock-grassland soils. Journal of General Microbiology 66, 309–318.
Majumdar, S.K. & Bose, S.K. 1958 Mycobacillin, a new anti-fungal antibiotic produced by B. subtilis. Nature 181, 134–135.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. & Sambrook, J. 1982 Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Nakajima, N., Chihara, S. & Koyama, Y. 1972 A new antibiotic, gatavalin. I. Isolation and characterization. Journal of Antibiotics 25, 243–247.
Newton, B.A. 1956 The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriological Reviews 20, 14–27.
Newton, C.G.P. 1949 Antibiotics from a strain of Bacillus subtilis: bacilipin A and B and bacilysin. British Journal of Experimental Pathology 30, 306–319.
Reeves, P. 1965 The bacteriocins. Bacteriological Reviews 29, 24–45.
Schaeffer, P. 1969 Sporulation and the production of antibiotics, exoenzymes, and exotoxins. Bacteriological Reviews 33, 48–71.
Seldin, L. 1992 Primary characterization of the bacteriophage BA-4 from a nitrogen-fixing Bacillus azotofixans strain. Microbios 71, 167–177.
Seldin, L. & Penido, E.G.C. 1986 Identification of Bacillus azotofixans using API tests. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek; Journal of Microbiology and Serology 52, 403–409.
Seldin, L. & Penido, E.G.C. 1990 Production of a bacteriophage, a phage tail-like bacteriocin and an antibiotic by Bacillus azotofixans. Anais Academia Brasileira de Ciências 62, 85–94.
Seldin, L., VanElsas, J.D. & Penido, E.G.C. 1983 Bacillus nitrogen fixers from Brazilian soils. Plant and Soil 70, 243–255.
Seldin, L., VanElsas, J.D. & Penido, E.G.C. 1984 Bacillus azotofixans sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing species from Brazilian soils and grass roots. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 34, 451–456.
Sharon, N., Pinsky, A., Turner-Graff, R., Babad, J. & Cercos, A.P. 1954 Classification of the antifungal antibiotics from Bacillus subtilis. Nature 174, 1190–1191.
Sneath, P.H.A. 1986 Endospore-forming Gram-positive rods and cocci. In Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, eds Sneath, P.H.A., Mair, N.S. & Shape, E. pp. 1104–1139. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
Steensma, H.Y. & Robertson, L.A. 1978 Lysogeny in Bacillus. FEMS Microbiology Letters 3, 313–317.
Steensma, H.Y., Robertson, L.A. & VanElsas, J.D. 1978 The occurrence and taxonomic value of PBS X-like defective phages in the genus Bacillus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek; Journal of Microbiology and Serology 44, 353–366.
Tagg, J.R., Dajani, A.S. & Wannamaker, L.W. 1976 Bacteriocins of Gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriological Reviews 40, 722–756.
VanElsas, J.D. & Penido, E.G.C. 1981 Characterization of phages of Bacillus subtilis isolated from Brazilian soils. Revista Brasileira de Microbiologia 12, 48–54.
Vogler, K. & Studer, R.O. 1966 The chemistry of the polymyxin antibiotics. Experientia 22, 345–416.
Warren, R.L. 1980 Exfoliative toxin plasmids of bacteriophage group 2 Staphylococcus aureus: sequence homology. Infection and Immunity 30, 601–606.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosado, A.S., Seldin, L. Production of a potentially novel anti-microbial substance by Bacillus polymyxa . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 9, 521–528 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386287
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386287