Summary
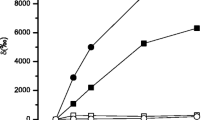
Ion uptake was studied using 32P, 35S, 22Na and 42K as tracers in synchronized cells of Ankistrodesmus, which were slightly starved with respect to the ions to be investigated. In the light and in the dark, phosphate uptake is maximal between pH 5.5 and 6.5. Whereas Na+ in comparison to K+ enhances phosphate uptake in the light (8 to 9-fold) and in the dark, Ca++ exerts only a slightly stimulatory effect. The stimulation of phosphate binding by Na+ occurs rapidly, even after less than 5 sec of incubation, and also in the presence of an equimolar concentration of K+.
The pH-dependence of Na+-uptake in the light and in the dark is comparable to a dissociation curve: Na+-uptake increases with decreasing extracellular H+-concentration and is inversely proportional to phosphate uptake in the absence of Na+. The light:dark ratio of Na+-uptake at pH 8 amounts to 7:1. Mere adsorption of Na+ is similarly dependent on the pH. K+ strongly competes with Na+-uptake, even at pH 8. K+-uptake proceeds in a quite different manner from Na+-uptake and has an optimum at pH 7.
Sulfate is taken up linearly in a biphasic process as a function of time; the pH-optimum lies between pH 7.5 and 8. K+ but not Na+ slightly enhances sulfate uptake.
The Na+-enhancement of phosphate uptake can be related neither to a sodium-potassium exchange pump nor to a photosynthesis-dependent ion-exchange reaction.
The results suggest that the uptake of phosphate, Na+ and K+, and the influence of alkali cations on phosphate uptake, but not sulfate uptake, are strongly dependent on fixed charges of the plasmalemma or even of the cell wall. These fixed charges may even prevent an active ion uptake.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Baumeister, W., Conrad, D.: Über Beziehungen zwischen der Natriumversorgung und dem Phosphathaushalt bei Scenedesmus obliquus (Turp.) Kuetz. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 79, 15–26 (1966).
Briggs, G. E., Hope, A. B., Robertson, R. N.: Electrolytes and plant cells. James, W. O., ed. Oxford: Blackwell 1961.
Brinckmann, E., Lüttge, U.: Vorübergehende pH-Änderungen im umgebenden Medium intakter grüner Zellen bei Beleuchtungswechsel. Z. Naturforsch. 27b, 277–284 (1972).
Coster, H. G. L., Hope, A. B.: Ionic relations of cells of Chara australis. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 21, 243–254 (1968).
Domanski-Kaden, J., Simonis, W.: Veränderungen der Phosphatfraktionen, besonders des Polyphosphats, bei synchronisierten Kulturen von Ankistrodesmus braunii. Arch. Mikrobiol. (Im Druck).
Eisenman, G.: On the elementary atomic origin of equilibrium ionic specificity. In: Membrane transport and metabolism, p. 163–179, Kleinzeller, A., Kotyk, A. eds. London-New York: Academic Press 1961.
Epstein, E., Hagen, C. E.: A kinetic study of the absorption of alkali cations by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 27, 457–474 (1952).
Hyde, A. H.: Nature of the calcium effect in phosphate uptake by barley roots. Plant and Soil 24, 328–331 (1966).
Jeschke, W. D.: Lichtabhängige Veränderungen des Membranpotentials bei Blattzellen von Elodea densa. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 62, 158–172 (1970).
Jeschke, W. D.: Wirkung von K+ auf die Fluxe und den Transport von Na+ in Gerstenwurzeln, K+-stimulierter Na+-Efflux in der Wurzelrinde. Planta (Berl.) 106, 73–90 (1972).
Leggett, J. E., Galloway, R. A., Gauch, H. G.: Calcium activation of orthophosphate absorption by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 40, 897–902 (1965).
Marschner, H.: Wechselwirkungen zwischen Ca++ und Alkaliionen bei der Aufnahme durch Pflanzenzellen. In: Membranes, transport, vol. III, p. 89–95, Broda, E., Locker, A., Springer-Lederer, H., eds. Wien: Med. Akademie 1971.
Mengel, K.: Stofftransport durch Zellgrenzflächen. In: Die Zelle, Struktur und Funktion, S. 343–372, Metzner, H. Hrsg. Stuttgart: Wiss. Verl. Ges. 1971.
Northcote, D. H., Goulding, K. J., Horne, R. W.: The chemical composition and structure of the cell wall of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biochem. J. 70, 391–397 (1958).
Passow, H.: Passive ion permeability of the erythrocyte membrane. Progr. Biophys. molec. Biol., 19, 2, 425–467 (1969).
Pirson, A., Ruppel, H. G.: Über die Induktion einer Teilungshemmung in synchronen Kulturen von Chlorella. Arch. Mikrobiol. 42, 299–309 (1962).
Rains, D. W., Epstein, E.: Sodium absorption by barley roots: role of the dual mechanism of alkali cation transport. Plant Physiol. 42, 314–318 (1967).
Shieh, Y. J., Barber, J.: Intracellular sodium and potassium concentrations and net cation movements in Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 233, 594–603 (1971).
Siegenthaler, P. A., Belsky, M. M., Goldstein, S., Menna, M.: Phosphate uptake in an obligately marine fungus. II. Role of culture conditions, energy sources, and inhibitors. J. Bact. 93, 1281–1288 (1967).
Simonis, W., Urbach. W.: Über eine Wirkung von Natriumionen auf die Phosphataufnahme und die lichtabhängige Phosphorylierung von Ankistrodesmus braunii. Arch. Mikrobiol. 46, 265–286 (1963).
Steveninck, R. F. M. van, Mittelheuser, C. J., Steveninck, M. E. van: The effect of Tris-buffer on ion uptake and on the ultrastructure of chloroplasts, mitochondria and cellular membranes. In: Liverpool-workshop on ion transport. Anderson, W. P. ed., 1972.
Teorell, T.: Zur qualitativen Behandlung der Membranpermeabilität. (Eine erweiterte Theorie.) Z. Elektrochem. 55, 460–469 (1951).
Ullrich, W. R.: Der Einfluß von CO2 und pH auf die 32P-Markierung von Polyphosphaten und organischen Phosphaten bei Ankistrodesmus braunii im Licht. Planta (Berl.) 102, 37–54 (1972a).
Ullrich, W. R.: Untersuchungen über die Raten der Polyphosphatsynthese durch die Photophosphorylierung bei Ankistrodesmus braunii. Arch. Mikrobiol. (Im Druck) (1972b).
Ullrich-Eberius, C. I., Simonis, W.: Der Einfluß von Natrium- und Kalium-Ionen auf die Photophosphorylierung bei Ankistrodesmus braunii. Planta (Berl.) 92, 358–373 (1970a).
Ullrich-Eberius, C. I., Simonis, W.: Der Einfluß von Natrium- und Kaliumionen auf die Phosphataufnahme bei Ankistrodesmus braunii. Planta (Berl.) 93, 214–226 (1970b).
Vallée, M., Jeanjean, R.: Le système de transport de SO4 = chez Chlorella pyrenoidosa et sa régulation. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 150, 599–617 (1968).
Varma, A. K., Nicholas, D. J. D.: Studies on the incorporation of labelled sulphate into cells and cell-free extracts of Nitrosomonas europaea. Arch. Mikrobiol. 73, 293–307 (1970).
Weigl, J.: Die Permeation von Ionen als Bewegung durch eine elektrostatische Barriere. Z. Naturforsch. 25b, 1149–1154 (1970).
White, R. C., Barber, G. A.: An acidic polysaccharide from the cell wall of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 264, 117–128 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullrich-Eberius, C.I. Die pH-Abhängigkeit der Aufnahme von H2PO -4 , SO =4 , Na+ und K+ und ihre gegenseitige Beeinflussung bei Ankistrodesmus braunii . Planta 109, 161–176 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386124
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386124