Abstract
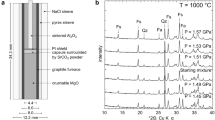
The mineral paragonite, NaAl2[AlSi3O10 (OH)]2, has been synthesized on its own composition starting from a variety of different materials. Indexed powder data and refined cell parameters are given for both the 1M and 2M1 polymorphs obtained. The upper stability limit of paragonite is marked by its breakdown to albite + corundum + vapour. The univariant equilibria pertaining to this reaction have been established by reversing the reaction at six different pressures, the equilibrium curve running through the following \(P_{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}} {\text{O}}} - T - \) intervals: 1 kb: 530°–550° C 2 kb: 555°–575° C 3 kb: 580°–600° C 5kb: 625°–640° C 6 kb: 620°–650° C 7 kb: 650°–670° C.
Comparison with the upper stability limit of muscovite (Velde, 1966) shows that paragonite has a notably lower thermal stability thus explaining the field observation that paragonite is absent in many higher grade metamorphic rocks in which muscovite is still stable.
The enthalpy and entropy of the paragonite breakdown reaction have been estimated. Since intermediate albites of varying structural states are in equilibrium with paragonite, corundum and H2O along the univariant equilibrium curve, two sets of data pertaining to the entropy of paragonite (S 0298 ) as well as the enthalpy (Δ H 0f,298 ) and Gibbs free energy (Δ G 0f,298 ) of its formation were computed, assuming (1) high albite and (2) low albite as the equilibrium phase. The values are: (1) (2) S 0298 67.8±3.9 cal deg−1 gfw−1 63.7±3.9 cal deg−1 gfw−1 ΔH 0f,298 −1417.9±2.7 kcal gfw−1 −1420.2±2.6 kcal gfw−1 ΔG 0f,298 −1327.4±4.0 kcal gfw−1 −1328.5±4.0 kcal gfw−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyd, F. R., England, J. L.: Apparatus for phase equilibrium measurements at pressures up to 50 kb and temperatures up to 1750° C. J. Geophys. Res. 65, 741–748 (1960).
Burnham, Charles W.: Lattice constant refinement. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yearbook 61, 132–135 (1962).
Burnham, C. Wayne, Holloway, J. R., Nicholas, D. F.: Thermodynamic properties of water to 1000° C and 10,000 bars. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Papers 132, 96 p. (1969).
Chatterjee, N. D.: Phasenpetrologie der alpidisch metamorphosierten Gesteine in den italienischen Westalpen nebst Untersuchungen zur Stabilität des Paragonits. Habil.-Schrift, University of Bochum, 162 p. (1968).
Eugster, H. P., Yoder, H. S.: Paragonite. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yearbook 53, 111–114 (1954).
—: Paragonite. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Yearbook 54, 124–126 (1955).
Evans, B. W.: Application of a reaction-rate method to the breakdown equilibria of muscovite and muscovite plus quartz. Am. J. Sci. 263, 647–667 (1965).
Frey, M.: A mixed-layer paragonite/phengite of low-grade metamorphic origin. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 24, 63–65 (1969).
Gruner, J. W.: Conditions for the formation of paragonite. Am. Mineralogist 27, 131–134 (1942).
Harder, H.: Untersuchungen an Paragoniten und an natriumhaltigen Muskoviten. Heidel-berger Beitr. Mineral. Petrogr. 5, 227–271 (1956).
Robie, R. A., Waldbaum, D. R.: Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 °K (25.0° C) and one atmosphere (1.013 bars) pressure and at higher temperatures. U.S. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1259, 256 p. (1968).
Ross, M.: X-ray diffraction effects by non-ideal crystals of biotite, muscovite, montmorillonite, mixed-layer clays, graphite and periclase. Z. Krist. 126, 80–97 (1968).
Sand, L. B., Roy, R., Osborn, E. F.: Stability relations of some minerals in the Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O system. Econ. Geol. 52, 169–179 (1957).
Schairer, J. F., Bowen, N. L.: The system K2O-Al2O3-SiO2. Am. J. Sci. 253, 681–746 (1955).
Schaller, W. T., Stevens, R. E.: The validity of paragonite as a mineral species. Am. Mineralogist 26, 541–545 (1941).
Stirland, D. J., Thomas, A. G., Moore, N. C.: Observations on thermal transformations in alumina. Trans. Brit. Ceram. Soc. 57, 69–84 (1958).
Turner, F. J.: Metamorphic petrology. 403 p. New York: McGraw-Hill 1968.
Tuttle, O. F.: Two pressure vessels for silicate-water studies. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 60, 1727–1729 (1949).
Velde, B.: Upper stability limit of muscovite. Am. Mineralogist 51, 924–929 (1966).
Weisbrod, A.: Détermination rapide des variations réactionelles d'entropie et d'enthalpie à partir des courbes éxperimentales d'equilibre; tracé rapide des courbes théoriques d'equilibre. Bull. Soc. Franc. Minéral. Crist. 91, 444–452 (1968).
Zen, E-an: Free energy of formation of pyrophyllite from hydrothermal data: values, discrepancies and implications. Am. Mineralogist 54, 1592–1606 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Adapted from a part of the author's “Habilitationsschrift” accepted by the Ruhr University, Bochum (Chatterjee, 1968).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, N.D. Synthesis and upper stability of paragonite. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 27, 244–257 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385781
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385781