Abstract
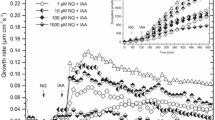
Using both 1-mm segments of corn (Zea mays L.) coleoptiles and a preparation of membranes isolated from the same source, we have compared the effectiveness of several inhibitors of geotropism and polar transport in stimulating uptake of auxin (indole-3-acetic acid, IAA) into the tissue and in competing with N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA) for a membrane-bound site. Low concentrations of 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid (TIBA), NPA, 2-chloro-9-hydroxyfluorene-9-carboxylic acid (morphactin), and fluorescein, eosin, and mercurochrome all stimulated net uptake of [3H]IAA by corn coleoptile tissues while higher concentrations reduced the uptake of both [3H]IAA and another lipophilic weak acid, [14C]benzoic acid. Since low concentrations of fluorescein and its derivatives competed for the same membrane-bound site in vitro as did morphactin and NPA, the basis for both the specific stimulation of auxin accumulation and the inhibition of polar auxin transport by all these compounds may be their ability to interfere with the carrier-mediated efflux of auxin anions from cells. At higher concentrations, the decrease in accumulation of weak acids was nonspecific and thus may be the result of acidification of the cytoplasm and a general decrease in the driving force for uptake of the weak acids. Triiodobenzoic acid was an exception. Low concentration of TIBA (0.1–1 μM) were much less effective than NPA in competing for the NPA receptor in vitro, but little different from NPA in ability to stimulate auxin uptake. One possibility is that TIBA, a substance which is polarly transported, may compete with auxin for the polar transport site while NPA, morphactin, and the fluorescein derivatives may render this site inactive.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C1-NPA:
-
2,3,4,5-tetrachloro-N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid
- IAA:
-
indole-3-acetic acid
- α-NAA:
-
α-naphthaleneacetic acid
- β-NAA:
-
β-naphthalenacetic acid
- NPA:
-
N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid
- TIBA:
-
2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid
References
Edwards, K., Goldsmith, M.H.M. (1980) pH dependent accumulation of indoleacetic acid by corn coleoptile sections, a system capable of polar transport of auxin. Planta 147, 457–466
Goldsmith, M.H.M. (1977) The polar transport of auxin. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 28, 439–478
Hertel, R. (1974) Auxin transport and in vitro auxin binding. In: Membrane transport in plants, pp. 457–461, Zimmermann, M., Dainty, J., eds. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Katekar, G.E., Geissler, A.E. (1975) Auxin transport inhibitors: Fluorescein and related compounds. Plant Physiol. 56, 645–646
Lembi, C.A., Morrè, D.J., Thomson, K.-S., Hertel, R. (1971) N-1-Naphthylphthalamic acid binding activity of a plasma membrane-rich fraction from maize coleoptiles. Planta 99, 37–45
Rubery, P.H. (1977) The specificity of carrier-mediated auxin transport by suspension-cultured crown gall cells. Planta 135, 275–283
Rubery, P.H., Sheldrake, A.R. (1974) Carrier-mediated auxin transport. Planta 118, 101–121
Snedecor, G.N., Cochran, W.G. (1967) Statistical Methods, 6th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Sussman, M.R., Gardner, G. (1980) Solubilization of the receptor for N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid. Plant Physiol. 66, 1074–1078
Sussman, M.R., Goldsmith, M.H.M. (1981) The mechanism of auxin uptake and action of N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid in corn coleoptile cells. Planta 151, 15–25
Thomson, K.-S. (1972) The binding of 1-N-napthylphthalamic acid (NPA), an inhibitor of auxin transport, to particulate fractions of corn coleoptiles. In: Hormonal regulation in plant growth and development, pp. 83–88, Kaldewey, H., Vardar, Y., eds. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim.
Thomson, K.-S., Hertel, R., Muller, S., Tavares, J.E. (1973) 1-N-Naphthylphthalamic acid and 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid: In-vivo binding to particulate cell fractions and action on auxin transport in corn coleoptiles. Planta 109, 337–352
Thomson, K.-S., Leopold, A.C. (1974) In vitro binding of morphactins and N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid in corn coleoptiles and their effects on auxin transport. Planta 115, 259–270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sussman, M.R., Goldsmith, M.H.M. The action of specific inhibitors of auxin transport on uptake of auxin and binding of N-1-naphthylphthalamic acid to a membrane site in maize coleoptiles. Planta 152, 13–18 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384978
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384978