Abstract
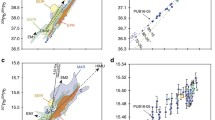
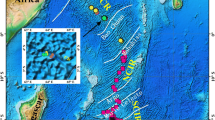
Lead isotopic analyses of a suite of basaltic rocks from the Juan de Fuca-Gorda Ridge and nearby seamounts confirm an isotopically heterogeneous mantle known since 1966. The process of mixing during partial melting of a heterogeneous mantle necessarily produces linear data arrays that can be interpreted as secondary isochrons. Moreover, the position of the entire lead isotope array, with respect to the geochron, requires that U/Pb and Th/Pb values are progressively increased over the age of the earth. Partial melting theory also dictates analogous behavior for the other incompatible trace elements. This process explains not only the LIL element character of MOR basalts, but also duplicates the spread of radiogenic lead data collected from alkali-rich oceanic basalts. This dynamic, open-system model of lead isotopic and chemical evolution of the mantle is believed to be the direct result of tectonic flow and convective overturn within the mantle and is compatible with geophysical models of a dynamic earth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, R.L., Hein, S.M.: Computer simulation of Pb and Sr isotope evolution of the earth's crust and upper mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 37, 1–18 (1973)
Barnes, I.L., Murphy, T.J., Gramlich, J.W., Shields, W.R.: Lead separation by anodic deposition and isotope ratio mass spectrometry of microgram and smaller samples. Anal. Chem. 45, 1881–1884 (1973)
Barr, S.M.: Geology of the northern end of Juan de Fuca ridge and adjacent continental slope. Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, Univ. of British Columbia, 287 p. (1972)
Bertrand, W.G.: A geological reconnaissance of the Dellwood Seamount area, northeast Pacific Ocean, and its relationship to plate tectonics. Unpublished M.Sc. thesis, Univ. of British Columbia, 151 p. (1972)
Budinger, T.F.: Cobb Seamount. Deep-Sea Res. 14, 191–201 (1967)
Catanzaro, E.J.: Absolute isotopic abundance ratios of three common lead reference samples. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 3, 343–346 (1967)
Catanzaro, E.J., Murphy, T.J., Shields, W.R., Garner, E.L.: Absolute isotopic abundance ratios of common, equal-atom, and radiogenic lead isotopic standards. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Std. 72A, 261–267 (1968)
Church, S.E.: Trace element abundances in ocean sediments and altered basalts — Their implications for andesite genesis (abst). Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 53, 546 (1972)
Church, S.E.: Limits of sediment involvement in the genesis of orogenic volcanic rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 39, 17–32 (1973)
Church, S.E., Bansal, B.M., Wiesmann, H.: The distribution of K, Ti, Zr, U and Hf in Apollo 14 and 15 materials. In: The Apollo 15 Lunar Samples, J.W. Chamberlain, C. Watkins, eds., p. 210–213. Houston: Lunar Science Inst. 1973
Church, S.E., Tilton, G.R.: Lead and strontium studies in the Cascade Mountains: Bearing on andesite genesis. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 84, 431–453 (1973)
Compston, W., Oversby, V.M.: Lead isotopic analysis using a double-spike. J. Geophys. Res. 74, 4338–4348 (1969)
Dymond, J.R., Watkins, N.D., Nayudu, Y.R.: Age of Cobb seamount. J. Geophys. Res. 73, 3977–3979 (1968)
Gast, P.W.: Isotopic geochemistry of volcanic rocks. In: Basalts: The Poldervaart treatise on rocks of basaltic composition 1, H.H. Hess, ed., p. 325–358. New York: John Wiley & Sons—Interscience 1967
Gast, P.W.: Trace element fractionation and the origin of tholeiitic and alkaline magma types. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 32, 1057–1086 (1968)
Gast, P.W., Tilton G.R., Hedge, C.E.: Isotopic composition of lead and strontium from Ascension and Gough Islands. Science 145, 1181–1185 (1964)
Gordon, R.B.: Observation of crystal plasticity under high pressure with application to the earth's mantle. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 1248–1254 (1971)
Green, D.H.: Composition of basaltic magmas as indicators of conditions of origin: application to oceanic volcanism. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London, Ser. A 268, 707–725 (1971)
Green, D.H., Ringwood, A.E.: The genesis of basaltic magmas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 15, 103–190 (1967)
Haines, E.L., Zartman, R.E.: Uranium concentration and distribution in six peridotite inclusions of probable mantle origin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 20, 45–53 (1973)
Hart, S.R.: K, Rb, Cs contents and K/Rb, K/Cs ratios of fresh and altered submarine basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 6, 293–303 (1969)
Hedge, C.E., Peterman, Z.E.: The strontium isotopic composition of basalts from the Gorda and Juan de Fuca Rises, northeastern Pacific Ocean. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 27, 114–120 (1970)
Hubbard, N.J., Gast, P.W., Rhodes, J.M., Bansal, B.M., Weismann, H., Church, S.E.: Nonmare basalts: Part II. In: Proceedings of the Third Lunar Science Conference 2, D. Heymann, ed., p. 1161–1174. Cambridge: M.I.T. Press 1973
Isacks, B., Oliver, J., Sykes, L.R.: Seismology and the new global tectonics. J. Geophys. Res. 73, 5855–5900 (1968)
Jaffey, A.H., Flynn, K.F., Glendenin, L.E., Bentley, W.C., Essling, A.M.: Precision measurement of the half-lives and specific activities of U235 and U238. Phys. Rev. C4, 1889–1906 (1971)
Kay, R.W., Gast, P.W.: The rare earth content and origin of alkali-rich basalts. J. Geol. 81, 653–682 (1973)
Kay, R., Hubbard, N.J., Gast, P.W.: Chemical characteristics and origin of oceanic ridge volcanic rocks. J. Geophys. Res. 75, 1585–1614 (1970)
Kulm, L.D., Huene, R. von, Duncan, J.R., Ingle, J.C., Kling, S.A., Musich, L.F., Piper, D.J.W., Pratt, R.M., Schrader, H., Weser, O., Wise, S.W., Jr.: Site 177. In: Initial reports of the deep sea drilling project, XVIII, p. 233–285. Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office 1973
LeRoux, L.J., Glendenin, L.E.: Half-life of Th232. Proc. Nat'l. Mtg. on Nucl. Energy, Pretoria, South Africa, 78 (1963)
MacLeod, N.S., Pratt, R.M.: Petrology of volcanic rocks recovered on Leg 18. In: Initial reports of the deep sea drilling project, XVIII, p. 935–945. Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office 1973
Mattinson, J.M.: Preparation of hydrochloric and nitric acids at ultralow lead levels. Anal. Chem. 44, 1715–1716 (1972)
McManus, D.A.: Major bathymetric features near the coast of Oregon, Washington and Vancouver Island. Northwest Sci. 38, 65–82 (1964)
Melson W.G.: Preliminary results of a geophysical study of portions of the Juan de Fuca ridge and Blanco fracture zone, 1–33. U.S. Dept. of Commerce ESSA Technical Memorandum C & GSTM 6. Springfield, Va.: Natl. Technical Information Service 1969
Oxburgh, E.R., Turcotte, D.L.: Mid-ocean ridges and geotherm distribution during mantle convection. J. Geophys. Res. 73, 2643–2662 (1968)
Patterson, C.C.: Characteristics of lead isotope evolution on a continental scale in the earth. In: Isotopic and cosmic chemistry, 19, p. 244–268. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1964
Patterson, C.C., Tatsumoto, M.: The significance of lead isotopes in detrital feldspar with respect to chemical differentiation within the earth's mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 28, 1–22 (1964)
Peterman, Z.E., Hedge, C.E.: Related strontium isotopic and chemical variations in oceanic basalts. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull 82, 493–500 (1971)
Rennick, W.L.: A model of lead isotope evolution in the earth's crust and upper mantle. Unpublished M.A. thesis, Univ. of California, Santa Barbara, 93 p. (1973)
Ringwood, A.E.: Mineralogy of the deep mantle: Current status and future developments. In: The nature of the solid earth, E.C. Robertson, ed., p. 67–92. New York: McGraw-Hill 1972
Shaw, D.M.: Trace element fractionation during anatexis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 34, 237–243 (1970)
Shields, W.R., ed.: Analytical mass spectrometry section: Summary of activities July 1969 to June 1970. U.S. Dept. of Commerce N.B.S. Technical Note 546, 120 p. Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office 1970
Sinha, A.K., Tilton, G.R.: Isotopic evolution of common lead. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 37, 1823–1849 (1973)
Stocker, R.L., Ashby, F.M.: On the rheology of the upper mantle. Rev. Geophys. 11, 391–426 (1973)
Sun, S.S.: Lead isotope studies of young volcanic rocks from oceanic, islands, mid-ocean ridges and island arcs. Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, Columbia University, 139 p. (1973)
Tatsumoto, M.: Genetic relations of oceanic basalts as indicated by lead isotopes. Science 153, 1094–1101 (1966a)
Tatsumoto, M.: Isotopic composition of lead in volcanic rocks from Hawaii, Iwo Jima, and Japan. J. Geophys. Res. 71, 1721–1733 (1966b)
Tatsumoto, M., Hedge, C.E., Engel, A.E.J.: Potassium, rubidium, strontium, thorium, uranium and the ratio of strontium-87 to strontium-86 in oceanic tholeiitic basalts. Science 150, 886–888 (1965)
Tatsumoto, M., Knight, R.J., Allegre, C.J.: Time differences in the formation of meteorites as determined from the ratio of lead-207 to lead-206. Science 180, 1279–1283 (1973)
Tilton, G.R.: Isotopic lead ages of chondritic meteorites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 19, 321–329 (1973)
Tilton, G.R., Steiger, R.H.: Mineral ages and isotopic composition of primary lead at Manitouwadge, Ontario. J. Geophy. Res. 74, 2118–2132 (1969)
Wasserburg, G.J.: Geochronology and isotopic data bearing on development of the continental crust. In: Advances in earth science, p 431–459. Cambridge: MIT Press 1966
Whittaker, E.J.W., Muntus, R.: Ionic radii for use in geochemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 34, 945–956 (1970)
Zartman, R.E., Tera, F.: Lead concentration and isotopic compositions in five peridotite inclusions of probable mantle origin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 20, 54–66 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Analytical work done while the author held a National Research Council Associateship at the Johnson Space Center, Houston, Texas.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Church, S.E., Tatsumoto, M. Lead isotope relations in oceanic Ridge basalts from the Juan de Fuca-Gorda Ridge area N.E. Pacific Ocean. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 53, 253–279 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382443
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382443