Summary
To investigate whether volume reduction of the hippocampal formation of schizophrenics, as described previously, is paralleled by loss of neurons and fibre systems, tissue volumes and cell numbers of all parts of the hippocampal formation in post mortem brains of 13 schizophrencis and 11 agematched controls belonging to the Vogt collection were determined.
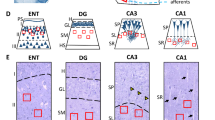
Volumes of the whole hippocampal formation (P < 0.01), the whole pyramidal band (P < 0.001) and the hippocampal segments CA1/CA2 (P < 0.01), CA3 (P < 0.05), CA4 (P < 0.01) were decreased, whereas no significant volume reduction of the alveus and fimbria hippocampi and presubiculum/subiculum could be found. The perforant path showed a trend towards volume reduction (P < 0.1).
The absolute number of pyramidal cells (tissue volume × cell density) was diminished in CA1/CA2 (P < 0.05), CA3 (P < 0.05) and CA4 (P < 0.05), but was not significantly changed in the prosubiculum/subiculum, the presubiculum/parasubiculum and the granular cell layer of the dentate fascia.
Pyramidal cell loss in CA1/CA2, CA3, CA4 was more distinct in the paranoid patients than in catatonics. The findings are discussed with respect to current hypotheses of limbic dysfunction in schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asarnow +RF, MacCrimmon DJ (1982) Attention/information processing, neuropsychological functioning, and thought disorder during the acute and partial recovery phases of schizophrenia: a longitudinal study. Psychiatry Res 7:309–319
Babb ThL, Lieb JP, Brown JW, Pretorius J, Crandall PH (1984) Distribution of pyramidal cell density and hyperexcitability in the epileptic human hippocampal formation. Epilepsia 25:721–728
Ball MJ (1977) Neuronal loss, neurofibrillary tangles and granulovascuolar degeneration and dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 37:111–118
Ball MJ, Hachinski V, Fox A, Kirshen AJ, Merskey H, Fisman M, Blume W, Kral VA, Fox H (1985) A new definition of Alzheimer's disease: a hippocampal dementia. Lancet 1:14–18
Baribeau-Braun J, Picton TW, Gosselin JY (1983) Schizophrenia: a neurophysiological evaluation of abnormal information processing. Science 219:874–876
Bogerts B (1977) Quantitativ-morphometrische Untersuchungen am Corpus geniculatum laterale und Colliculus superior der Ratte nach vollständigem Lichtentzug. J Hirnforsch 18:303–319
Bogerts B (1984) Zur Neuropathologie der Schizophrenien. Fortschr Neurol Psychiat 52:428–437
Bogerts B, Häntsch J, Herzer M (1983) A morphometric study of the dopamine containing cell groups in the mesencephalon of normals, Parkinson patients and schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 18:951–960
Braak H (1972) Zur Pigmentarchitektonik der Großhirnrinde des Menschen II. Subiculum. Z Zellforsch 131:235–254
Braak H (1974) On the structure of human archicortex I. The Cornu Ammonis. Cell Tiss Res 152:349–383
Brown R, Colter N, Corselles JAN, Crow TJ, Frith CD, Jagoe R, Johnstone EC, Marsh L (1986) Postmortem evidence of structural brain changes in schizophrenia. Differences in brain weight, temporal horn area and parahippocampal gyrus compared with affective disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43:36–42
Chronister RB, White LE (1975) Fiber architecture of the hippocampal formation: anatomy, projections, and structural significance. In: Issacson RL, Pribram KH (eds) The hippocampus. Vol 1. structure and development. Plenum Press, New York and London, p 21
Davison K, Bagley CR (1969) Schizophrenia - like psychosis associated with organic disorders of the central nervous system. A review of the literature. In: Hertington RN (ed) Current problems in Neuropsychiatry. Br J Psychiatry Special Publication No. 4, Ashford, 1969, pp 113–187
Devaney KO, Johnson HA (1984) Changes in cell density within the human hippocampal formation as a function of age. Gerontology 30:100–108
Foy RF, Chiaia NL, Teyler TJ (1984) Reversal of hippocampal sexual dimorphism by gonadal steroid manipulation. Brain Res 321:311–314
Franks RD, Adler LE, Waldo MC, Alpert J, Freedman R (1983) Neurophysiological studies of sensory gating in mania: comparison with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 18:989–1005
Halgren E, Wilson CL, Squires NK, Engel J, Walter RD, Crandall PH (1983) Dynamics of the hippocampal contribution to memory: stimulation and recording studies in humans. In: Seifert W (ed) Neurobiology of the Hippocampus. Academic Press, London, pp 2–19
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL (1984) Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 225:1168–1170
Jellinger K, Grisold W (1980) Zur Morphologie der sogenannten hirnatrophischen Prozesse. In: Frydl V (ed) Das ärztliche Gespräch, 34 “Neuropathologisches Symposium” (1980, Haar) Herausgegeben von der Medizinischen Abteilung der Troponwerke Köln
Juraska JM (1984) Sex differences in developmental plasticity in the visual cortex and hippocampal dentate gyrus. In: De Vries GJ, De Bruin JPC, Uylings HBM, Corner MA (eds) Progress in brain research, vol 61, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam, pp 205–214
Lange H, Thörner G, Hopf A, Schröder KF (1976): Morphometric studies of the ncuropathological changes in choreatic diseases. J Neurol Sci 28:401–425
Lesch A, Bogerts B (1984) The diencephalon in schizophrenia: evidence for reduced thickness of the periventricular grey matter. Eur Arch Psychiatr Neurol Sci 234:212–219
Lorente de No R (1934) Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex II. Continuation of the study of the ammonic system. J Psycholog Neurol 46:113–177
Malamud N (1967) Psychiatric disorder with intracranial tumors of the limbic system. Arch Neurol 17:113–123
Mouritzen Dam A (1979) The density of neurons in the human hippocampus. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 5:249–264
Mouritzen Dam A (1980) Epilepsy and neuron loss in the hippocampus. Epilepsia 21:617–629
Pandya DH, Seltzer B (1982) Association areas of the cerebral cortex. Trends Neurosci 5:386–390
Papez JW (1937) A proposed mechanism of emotion. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 38:725–743
Pribram KH, Mc Guiness (1975): Summary In: Isaacson RL, Pribram KH (eds) The Hippocampus, vol 2, Neurophysiology and behaviour. Plenum Press, New York and London pp. 429–441
Probst A, Basler V, Bron B, Ulrich J (1983) Neuritic plaques in senile dementia of Alzheimer type: a Golgi analysis in the hippocampal region. Brain Res 268:249–254
Roberts DR (1963) Schizophrenia and the brain. J Neuropsychiat 5:71–79
Rose J (1938) Zur normalen und pathologischen Architektur der Ammonsformation. J Psychol Neurol 49:137–186
Scheibel AB, Kovelman JA (1984) A neurohistological correlate of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 19:1601–1621
Scheibel ME, Crandall PH, Scheibel AB (1974) Complex in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 15:55–80
Schmajuk NA (1984) Psychological theories of hippocampal function. Physiol Psychol 12:166–183
Schwartz BD, Winstead DK, Adinoff B (1983) Temporal integration deficit in visual information processing by chronic schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 18:1311–1320
Siegel C, Waldo M, Mizner G, Adler LE, Freedman R (1984) Deficits in sensory gating in schizophrenic patients and their relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:607–612
Stevens JR (1973) An anatomy of schizophrenia? Arch Gen Psychiatry 29:177–189
Stevens JR (1982) Neuropathology of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:1131–1139
Swaab DF, Hofman MA (1984) Sexual differentiation of the human brain. De Vries GJ, De Bruin JPC, Uylings HBM, Corner MA (eds) Progress in brain research, vol 61. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 361–373
Swanson LW (1983) The hippocampus and the concept of the limbic system. In: Seifert W (ed) Neurobiology of the hippocampus. Academic Press, London pp 2–19
Torrey EF, Peterson MR (1974) Schizophrenia and the limbic system. Lancet 2:942–946
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Rheinische Landesklinik, Psychiatrische Klinik der Universität Düsseldorf, Bergische Landstrasse 2, D-4000 Düsseldorf 12 Federal Republic of Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falkai, P., Bogerts, B. Cell loss in the hippocampus of schizophrenics. Eur Arch Psychiatr Neurol Sci 236, 154–161 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380943
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380943