Summary
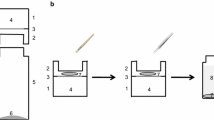
The evaporation of water through a plastic membrane coated with plant was (30–70 μg cm2) from grape berries or fractions thereof was determined. The hydrocarbon, alcohol and aldehyde fractions caused the highest reduction of evaporation. Their effect was identical to the complete wax or to mineral paraffin wax. The main constituent of the grape cuticle wax, the triterpene oleanolic acid, had no effect on evaporation in the artificial system. Free docosanoic acid did not suppress evaporation whereas the mixture of free fatty acids (the main constituents are the C24 and C26 acids) from grape wax reduced evaporation slightly. The results from this artificial system suggest that the alcohol, hydrocarbon and aldehyde fractions are the active components of the grape cuticle which prevent water loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, G. T., and V. K. La Mer: The evaporation resistance of monolayers of long-chain acids and alcohols and their mixtures. In: Retardation of evaporation by monolayers (ed. by V. K. La Mer). New York: Academic Press 1962).
Chambers, T. C., and J. V., Possingham: Studies of the fine structure of the wax layer of sultana grapes. Aust. J. Biol. Sci., 16, 818–825 (1963).
Langmuir, L., and V. D., Schaefer: Rates of evaporation of water through compressed monolayers on water. J. Franklin Inst. 235, 119–162 (1943).
Mansfield, W. W.: Influence of monolayers on the natural rate of evaporation of water. Nature (Lond.) 175, 247–249 (1955).
Martin, J. T.: Determination of the components of plant cuticles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 11, 635–640 (1960).
Martin, R. J. L., and G. L. Stott: The physical factors involved in the drying of Sultana grapes. Aust. J. agric. Res. 8, 444–459 (1957)
Orgell, W. H.: The isolation of plant cuticle with pectic enzymes. Plant Physiol. 30, 78–80 (1955).
Radler, F.: Reduction of loss of moisture by the cuticle wax components of grapes. Nature (Lond.) 207, 1002–1003 (1965).
—, and D. H. S. Horn: The composition of grape cuticle wax. Aust. J. Chem. 18, 1059–1069 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grncarevic, M., Radler, F. The effect of wax components on cuticular transpiration-model experiments. Planta 75, 23–27 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380835
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380835