Summary
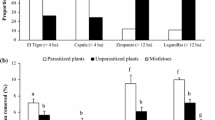
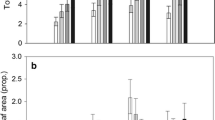
The effect of defoliation by herbivores, checkerspot caterpillars (Euphydryas phaeton) and sawfly larvae (Macrophya nigra and Tenthredo grandis), on the reproductive output of turtlehead (Chelone spp.) was examined. Defoliation prior to development of flower buds reduced the number of reproductive stalks, flower buds, flowers and seed capsules. Severe herbivory, after flower buds appeared, decreased the final number of seed capsules and seeds per capsule. The availability of the host plants to the herbivores was a function of prior defoliation and environmental conditions. Sawfly larvae, by defoliating the plants in midsummer, forced prediapause checkerspot caterpillars to wander in search of food plants. Decimation of these perenials by postdiapause checkerspot caterpillars in a dry spring retarded growth of turtlehead and, consequently, most of the plants were not available for egg-laying by sawflies and checkerspots.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentley S, Whittaker LB, Malloch AJC (1980) Field experiments on the effects of grazing by a chrysomelid beetle (Gastrophysa viridula) on seed production and quality in Rumex obtusifolius and Rumex crispus. J Ecol 68:671–674
Boscher J (1979) Modified reproduction strategy of leek Allium porrum in response to a phytophagous insect, Acrolepiopsis assestella. Oikos 33:451–456
Brussard PF, Vawter AT (1975) Population structure, gene flow and natural selection in populations of Euphydryas phaeton. Heredity 34:407–415
Clark EC (1956) The Great Basin tent caterpillar in relation to bitterbush in California. Calif Fish Game 42:131–142
Cox CS, McEvoy PB (1983) Effect of summer moisture stress on the capacity of tansy ragwort (Senecio jacobaea) to compensate for defoliation by cinnabar moth (Tyria jacobaeae). J Appl Ecol 20:225–234
Dempster JP (1982) The ecology of the cinnabar moth, Tyria jacobaeae L. (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Adv Ecol Res 12:1–36
Haukioja E, Niemela P (1979) Birch leaves as a resource for herbivores: seasonal occurrence of increased resistance in foliage after mechanical damage of adjacent leaves. Oecologia 39:151–159
Hawkes RB, Johnson GR (1978) Longitarsus jacobaeae aids moth in the biological control of tansy ragwort, pp. 193–196. In: TE Freeman (ed) Proc IV Internatl Symp Biol Control Weeds. Univ Florida, Gainesville
Hendrix SD (1979) Compensatory reproduction in a biennial herb following defoliation. Oecologia 42:107–118
Hendrix SD, Trapp EJ (1981) Plant-herbivore interactions: insect induced changes in host plant sex expression and fecundity. Oecologia 49:119–122
Inouye DW (1982) The consequences of herbivory: a mixed blessing for Jurinea mollis (Asteraceae). Oikos 39:269–272
Islam Z, Crawley MJ (1983) Compensation and regrowth in ragwort (Senecio jacobaea) attacked by cinnabar moth (Tyria jacobaeae). J Ecol 71:829–843
Kittock DL, Williams JH (1967) Effect of leaf removal at four stages of growth on yield of castor beans. Agron J 59:489–490
Knight WE, Hollowell EA (1962) Response of crimson clover to different defoliation intensities. Crop Sci 2:124–127
Laude HM, Kadish A, Love RM (1957) Differential effect of herbage removal on range species. J Range Mgt 10:116–120
Lee TD, Bazzaz FA (1980) Effects of defoliation and competition on growth and reproduction in the annual plant Abutilon theophrasti. J Ecol 68:813–821
Lincoln DE, Newton TS, Ehrlich PR, Williams KS (1982) Coevolution of the checkerspot butterfly Euphydryas chalcedona and its larval food plant Diplacus aurantiacus: larval response to protein and leaf resin. Oecologia 52:216–223
Maun MA, Cavers PB (1971) Seed production and dormancy in Rumex crispus. I. The effects of removal of cauline leaves at anthesis. Can J Bot 49:1123–1130
Meijden E van der (1976) Changes in the distribution pattern of Tyria jacobaeae during the larval period. Neth J Zool 26:136–161
Myers JH (1981) Interactions between western tent caterpillars and wild rose: a test of some general plant herbivore hypotheses. J Anim Ecol 50:11–25
Myers JH, Post BJ (1981) Plant nitrogen and insect population fluctuations: a test with the cinnabar moth-tansy ragwort system. Oecologia 48:151–156
Pauli AW, Laude HH (1959) Protein and carbohydrate relationships in winter wheat as influenced by mechanical injury. Agron J 51:55–57
Rausher MD, Feeny P (1980) Herbivory, plant density, and plant reproductive success: the effect of Battus philenor on Aristolochia reticulata. Ecology 61:905–917
Rausher MD, MacKay DA, Singer MC (1981) Pre- and post-alighting host discrimination by Euphdyras editha butterflies: the behavioural mechanisms causing clumped distributions of egg clusters. Anim Beh 29:1220–1228
Rockwood LL (1973) The effect of defoliation on seed production of six Costa Rica tree species. Ecology 54:1363–1369
Stamp NE (1982) Aggregation behavior in Baltimore checkerspot caterpillars, Euphydryas phaeton (Nymphalidae). J Lepid Soc 36:31–41
Tsubaki Y, Shiotsu Y (1982) Group feeding as a strategy for exploiting food resources in the burnet moth Pryeria sinica. Oecologia 55:12–20
Walpole PR, Morgan DG (1974) The influence of leaf removal upon the development of the grain of winter wheat. Ann Bot, New Series 38:779–782
White RR (1974) Food plant defoliation and larval starvation of Euphydryas editha. Oecologia 14:307–315
Whittaker JB (1982) The effect of grazing by a chrysomelid beetle, Gastrophysa viridula, on growth and survival of Rumex crispus on a shingle bank. J Ecol 70:291–296
Williams KS, Lincoln DE, Ehrlich PR (1983) The coevolution of Euphydryas chalcedona butterflies and their larval host plants I. Larval feeding behavior and host plant chemistry. Oecologia 56:323–329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stamp, N.E. Effect of defoliation by checkerspot caterpillars (Euphydryas phaeton) and sawfly larvae (Macrophya nigra and Tenthredo grandis) on their host plants (Chelone spp.). Oecologia 63, 275–280 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379889
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379889