Summary
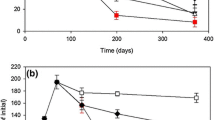
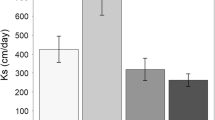
The effects of hydroperiod on decomposition rates of senescent Acer rubrum leaves were tested in microcosms in a controlled laboratory environment. Microcosm treatments included continuously flooded, continuously unflooded, and fluctuating hydroperiods. All flooding treatments promoted decomposition but variations in hydroperiod had no significant effects. A leaching experiment indicated the higher decay rates under flooded conditions were primarily due to high leaching losses from soaking. Unlike nutrient dynamics in the field, where net accumulation occurs, nitrogen and phosphorus in the litter in the microcosms exhibited net losses. The major external inputs which provide a source of nitrogen and phosphorus for immobilization in the field were lacking in the microcosms. Calcium, magnesium, and potassium exhibited net losses except for calcium in the unflooded microcosms. The microcosm results demonstrated the importance of external inputs to litter nutrient relations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JM (1973) The breakdown and decomposition of sweet chestnut and beech leaf litter in two deciduous woodland soils. I. Breakdown, leaching and decomposition. Oecologia 12:251–274
Anderson JM, MacFadyen A (1976) The role of terrestrial and aquatic organisms in decomposition processes. Blackwell Scientific Pub., London
Bell DT, Johnson FL, Gilmore AR (1978) Dynamics of litter fall, decomposition, and incorporation in the streamside forest ecosystem. Oikos 30:76–82
Brinson MM (1977) Decomposition and nutrient exchange of litter in an alluvial swamp forest. Ecology 58:601–609
Brinson MM, Lugo AE, Brown S (1981) Primary productivity, decomposition and consumer activity in freshwater wetlands. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 12:123–161
Dabel CV, Day FP (1977) Structural comparison of four plant communities in the Great Dismal Swamp, Virginia. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 104:352–360
Davis RC (1981) Structure and function of two Antarctic terrestrial moss communities. Ecological Monographs 51:125–143
Day FP (1982) Litter decomposition rates in the seasonally flooded Great Dismal Swamp. Ecology 63:670–678
Dickinson CH, Pugh GJF (1974) Biology of plant litter decomposition. Academic Press, NY
Ewel KC, Odum HT (1978) Cypress domes: nature's tertiary treatment filter. In: Odum HT, Ewel KC (ed) Cypress wetlands for water management, recycling and conservation. Fourth Annual Report to NSF-RANN and the Rockfeller Foundation. Gainesville, Florida, p 35–60
McDowell WH, Fisher SG (1976) Autumnal processing of dissolved organic matter in a small woodland stream ecosystem. Ecology 57:561–569
Merritt RW, Lawson DL (1979) Leaf litter processing in floodplain and stream communities. In: Johnson RR, McCormick JF (technical coordinators). Strategies for protection and management of floodplain wetlands and other riparian ecosystems. General Technical Report WO-12, Forest Service, USDA, Washington, DC, p 93–105
Olson JS (1963) Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44:322–331
Reice SR (1977) The role of animal associations and current velocity in sediment specific leaf litter decomposition. Oikos 29:357–365
Short RA, Canton SP, Ward JV (1980) Detrital processing and associated macroinvertebrates in a Colorado mountain stream. Ecology 61:727–732
Shure DJ, Gottschalk MR, Parsons KA (1980) Litter decomposition dynamics in a South Carolina floodplain forest. Association of Southeastern Biologists Bulletin 27(2):63
Shure DJ, Gottschalk MR, Parsons KA (1981) Decomposition and nutrient release from litter in a South Carolina floodplain forest. Ecological Society of America Bulletin 62:112
Singh JS, Gupta SR (1977) Plant decomposition and soil respiration in terrestrial ecosystems. Bot Rev 43:449–528
Swift MJ, Heal OW, Anderson JM (1979) Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Blackwell Scientific Pub., London
Williams ST, Gray TRG (1974) Decomposition of litter on the soil surface. In: Dickinson CH, Pugh GJF (eds) Biology of plant litter decomposition. Academic Press, NY, p 611–632
Willoughby LG (1974) Decomposition of litter in fresh water. In: Dickinson CH, Pugh GJF (eds) Biology of plant litter decomposition. Academic Press, NY, p 659–681
Witkamp M, Frank ML (1969) Loss of weight, 60Co and 137Cs from tree litter in three subsystems of a watershed. Environmental Science and Technology 3:1195–1198
Witkamp M, Ausmus BS (1976) Processes in decomposition and nutrient transfer in forest systems. In: Anderson JM, MacFadyen A (ed) The role of terrestrial and aquatic organisms in decomposition processes. Blackwell Scientific Publ, London, p 375–396
Yates FK (1981) Decay rates and nutrient dynamics in confined and nonconfined leaf litter in the Great Dismal Swamp. Master's Thesis. Old Dominion University. Norfolk, Virginia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Day, F.P. Effects of flooding on leaf litter decomposition in microcosms. Oecologia 56, 180–184 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379689
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379689