Summary
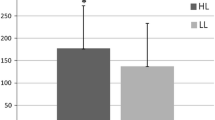
Muscle strength and muscle endurance in groups with different occupational muscular load was studied among 60 women and 69 men. The mean age of the subjects was 52.0 ± 3.4 years. Isometric grip and trunk strength were measured on dynamometers, and dynamic muscle endurance by sit-ups. A job analysis was done with the AET method including the assessment of intensity, duration and type of muscular work of each subject. According to the job analysis, the subjects were classified into groups with low or high muscular load at work. The maximal isometric hand grip strength of women with a load classified as long duration of static or dynamic load on the hands at work was 86 and 88%, respectively of the strength of those with a load of short duration. The women with high intensity in static work had a grip strength of 86% of those with low intensity. These differences in strength among women between the high and low load groups were statistically significant (P < 0.05). No other statistically significant differences in muscle strength or muscle endurance between the high and low work load groups were found, although the high work load group had systematically the lowest muscle strength and muscle endurance in almost all comparisons. Muscle strength and muscle endurance was, however, not a discriminating factor between the group classifications of static and dynamic work. The results indicated that the muscle strength and muscle endurance of middle-aged employees was systematically lower among those with high muscular load compared to those with low load at work.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen LB, Henckel P (1987) Maximal voluntary isometric strength in Danish adolescents 16–19 years of age. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:83–89
Andersson G (1981) Epidemiologic aspects on low-back pain in industry. Spine 6:53–60
Asmussen E, Heebøll-Nielsen K (1961) Isometric muscle strength of adult men and women Communications from the Testing and Observation Institute of the Danish National Association for Infantile Paralysis. Hellerup, Denmark 11:1–43
Asmussen E, Heebøll-Nielsen K, Mollbech SV (1959) Methods for evaluation of muscle strength. Communications from the Testing and Observation Institute of the Danish National Association for Infantile Paralysis, Hellerup, Denmark 5:1–13
Chaffin D (1975) Ergonomics guides. Ergonomics guide for the assessment of human static strength. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 36:505–511
Clement F (1974) Longitudinal and cross-sectional assessments of age changes in physical strength as related to sex, social class, and mental ability. J Ger 29:423–429
Färkkilä M, Aatola S, Starck J, Korhonen O, Pyykkö I (1986) Hand-grip force in lumberjacks: two-year follow-up. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 58:203–208
Heikkinen E, Arajärvi R-L, Era P, Jylhä M, Kinnunen V, Leskinen A-L, Leskinen E, Mässeli E, Pohjolainen P, Rahkila P, Suominen H, Turpeinen P, Väisänen M, Osterback L (1984) Functional capacity of men born in 1906–10, 1926–30 and 1946–50. A basic report. Scand J Soc Med [Suppl] 33:1–93
Häublein H-G (1979) Berufsbelastung und Bewegungsapparat. VEB Verlag, Volk und Gesundheit, Berlin, S 91
Ilmarinen J (ed) (1985) Work, health, and retirement age in the municipal sector (In Finnish, abstract in English). Stud Inst Occup Health, Helsinki 3:81–282
Kamon E, Goldfuss AJ (1978) In-plant evaluation of the muscle strength of workers. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 10:801–807
Karvonen M, Viitasalo J, Komi PV, Nummi J, Järvinen T (1980) Back and leg complaints in relation to muscle strength in young men. Scand J Rehab Med 12:53–59
Keyserling M, Herrin G, Chaffin D, Armstrong T, Foss M (1980) Establishing an industrial strength testing program. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 41:730–736
Kiiskinen A, Heikkinen E, Parkatti T, Pohjolainen P, Vuori I (1980) Functional aging of 40–50-year-old men in two industrial enterprises. Scand J Soc Med [Suppl] 14:12–23
Koradecka D, Markiewicz L, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I, Emeryk B (1974) Les troubles de la circulation sanguine périphérique dans l'atrophie musculaire professionelle des mains. Arch Mal Professionnelles, Méd Trav Sécurité Sociale (Paris) 35:517–523
Magora A (1974) Investigation of the relation between low back pain and occupation. 6. Medical history and symptoms. Scand J Rehab Med 6:81–88
McNeill T, Warwick D, Andersson G, Schultz A (1980) Trunk strengths in attempted flexion, extension, and lateral bending in healthy subjects and patients with low-back disorders. Spine 5:529–538
Mälkiä E (1983) Muscular performance as a determinant of physical ability in Finnish adult population (In Finnish, abstract in English) Publications of the Social Insurance Institution, Turku AL: 23, S 148
Nummi J, Järvinen T, Stambej V, Wickström G (1978) Diminished dynamic performance capacity of back and abdominal muscles in concrete reinforcement workers. Scand J Work Environ Health [Suppl 1] 4:39–46
Nygård C-H, Luopajärvi T, Cedercreutz G, Ilmarinen J (1987b) Musculoskeletal capacity of employees aged 44 to 58 years in physical, mental, and mixed work. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:555–561
Nygård C-H, Suurnakki T, Landau K, Ilmarinen J (1987a) Musculoskeletal load of municipal employees aged 44–58 years in different occupational groups Int Arch Occup Environ Health 49:251–261
Rohmert W, Landau K (1983) A new technique for job analysis. Taylor and Francis Ltd, London New York
Thorstensson A, Arvidson Å (1982) Trunk muscle strength and low back pain. Scand J Rehab Med 14:69–75
Tuxworth W, Nevill AM, White C, Jenkins C (1986) Health, fitness, physical activities, and morbidity of middle-aged male factory workers. Br J Ind Med 43:733–753
Vuori I, Sievers K (1978) Suomalaisten kuntoliikunnan harrastus (Leisure-time physical activity among Finnish women and men. In Finnish) Suomen Lääkärilehti 33:13–22
Westgaard R, Aarås A (1984) Postural muscle strain as a causal factor in the development of musculo-skeletal illnesses. Appl Ergonomics 15:162–174
Wickström G (1978a) Effects of work on degenerative back disease: A review. Scand J Work Environ Health [Suppl 1] 4:1–12
Wickström G (1978b) Symptoms and signs of degenerative back disease in concrete reinforcement workers. Scand J Work Environ Health [Suppl 1] 4:54–58
Yokomizo Y (1985) Measurement of ability of older workers. Ergonomics 28:843–854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nygård, C.H., Luopajärvi, T., Suurnäkki, T. et al. Muscle strength and muscle endurance of middle-aged women and men associated to type, duration and intensity of muscular load at work. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 60, 291–297 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378476
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378476