Summary
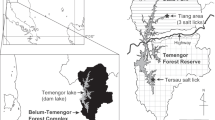
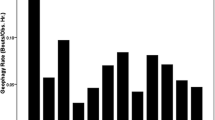
Natural mineral licks and their use by moose (Alces alces) on Isle Royale National Park, Michigan, were studied during 1982–85. The distribution of known licks suggested that they occurred in association with glacial debris, primarily in the western portions of the island. Moose utilized mineral springs extensively during the spring-summer period, and at least 5 licks were used year-round. During summer, a pronounced diel pattern of moose visitation was apparent, with peak use occurring between 0400–0800 h. Although daytime lick use declined by late June, morning and evening use continued to be relatively high throughout the study period. Peak lick use coincided with leaf-emergence in spring. Moose continued to utilize mineral licks despite the availability of ponds containing aquatic plants. Sodium appeared to be the element attracting moose to licks where they ingest copious amounts of water. Observed sodium ingestion rates (0.35 g/min) at licks indicate that licks provide a more concentrated source of sodium compared to aquatic plants (0.023 g/min). Based on the data presented, we reject the conclusions of earlier workers that aquatic plants constitute the only significant source of sodium for Isle Royale moose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho RW (1978) Ecological relationships of moose, aquatic plants, and sodium on Isle Royale National Park, Lake Superior. MS Thesis, Univ Minesota, St Paul, p 71
Aho RW, Jordan PA (1979) Production of aquatic macrophytes and its utilization by moose on Isle Royale National Park. Proc First Conf Sci Res in Natl Parks, USDI, Natl Park Serv Trans Proc Ser 5:341–348
Belovsky GE (1978) Diet optimization in a generalist herbivore: the moose. Theor Popul Biol 14:76–104
Belovsky GE (1981) A possible population response of moose to sodium availability. J Mammal 62:631–633
Belovsky GE, Jordan PA (1978) The time-energy budget of a moose. Theor Popul Biol 14:76–104
Belovsky GE, Jordan PA (1981) Sodium dynamics and adaptations of a moose population. J Mammal 62:613–621
Best DA, Lynch GM, Rongstad OJ (1977) Annual spring movements of moose to mineral licks in Swan Hills, Alberta. Proc N Am Moose Conf Workshop 13:215–228
Botking DB, Jordan PA, Dominsky AS, Lowendorf HS, Hutchinson GE (1973) Sodium dynamics in northern ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:2745–2748
Bott E, Denton DA, Goding JR, Sabine JR (1964) Sodium deficiency and corticosteroid secretion in cattle. Nature 202:461–463
Bowden RD (1981) Benthic macroinvertebrates and chemistry of three streams on Isle Royale National Park, Michigan. MS Thesis, Michigan Tech Univ, Houghton, p 112
Faaborg R (1981) The role of sodium in the growth of a boreal pond macrophyte, and the impact of macrophye herbivory by moose upon sodium flux in the watershed. MS Thesis, Univ Minnesota, St Paul, p 45
Fraser D, Hristienko H (1981) Activity of moose and white-tailed deer at mineral springs. Can J Zool 59:1991–2000
Fraser D, Arthur D, Morton JK, Thompson BK (1980a) Aquatic feeding by moose Alces alces in a Canadian lake. Holarctic Ecol 3:36–40
Fraser D, Reardon E, Dieken F, Loescher B (1980b) Sampling problems and the interpretation of chemical analysis of mineral springs used by wildlife. J Wildl Manage 44:623–631
Gordon MS (1972) Animal Physiology: principles and adaptations. Macmillan Publishing Co, Inc, New York, p 592
Hanley TA (1980) Nutritional constraints on food and habitat selection by sympatric ungulates. PhD Thesis, Univ Washington, Seattle, p 176
Huber NK (1973) Geological map of Isle Royale National Park, Keweenaw County, Michigan. Misc Geol Invest, US Geol Survey, Washington DC
Jones DIH, Miles DG, Sinclair KB (1967) Some effects of feeding sheep on low-sodium hay with and without sodium supplement. Br J Nutr 21:391–397
Jordan PA, Botkin DB, Dominski AS, Lowendorf HS, Belovsky GE (1973) Sodium as a critical nutrient of the moose of Isle Royale. Proc N Am Moose Conf Workshop 9:1–28
McCabe F, Collins JF, Walsh M (1978) “Channel” (fragipan-like) horizons in the soils of a drumlin in north-central Ireland. Proc R I Acad 78B:133–144
Murie A (1934) The moose of Isle Royale. Univ Michigan Mus Zool Misc Publ No 25
Renecker LA, Hudson RJ (1986) Seasonal energy expenditure and thermoregulatory responses of moose. Can J Zool 64:322–327
Schmidt-Neilsen K (1964) Desert mammals, physiological problems of heat and water. Oxford Univ Press, Oxford New York, p 277
Seal US, Schmitt SM, Peterson RO (1985) Carfentanil and xylazine for immobilization of moose (Alces alces) on Isle Royale. J Wildl Dis 21:48–51
Tankersley NG, Gasaway WC (1983) Mineral lick use by moose in Alaska. Can J Zool 61:2242–2249
Vander AJ, Sherman JH, Luciano DS (1980) Human physiology: the mechanisms of body function. McGraw-Hill, Inc, New York, p 724
Weeks HP Jr, Kirkpatrick CM (1976) Adaptations of white-tailed deer to naturally occurring sodium deficiencies. J Wildl Manage 40:610–625
Whittecar GR (1983) Planning the use of soils on drumlins. J Soil Water Conserv 38:396–400
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Risenhoover, K.L., Peterson, R.O. Mineral licks as a sodium source for Isle Royale moose. Oecologia 71, 121–126 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00377330
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00377330