Summary
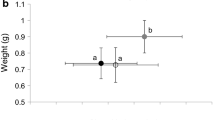
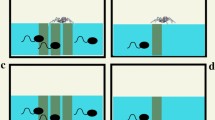
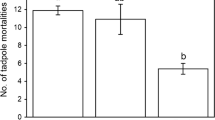
The effects of tadpole body size, tadpole sibship, and fish body size on predation of gray treefrog tadpoles, Hyla chrysoscelis, were studied in laboratory and artificial pond experiments. Tadpole body size had a significantly positive effect on the survival of tadpoles in all experiments. The relationship between tadpole biomass eaten and biomass available suggested that fish were not satiated when consuming the largest tadpoles. Large tadpoles were probably better able to evade predators. A difference in survival among full sib families of tadpoles was only present in one family, suggesting that genetic differences in predator avoidance behavior or palatability were probably secondarily important to body size per se. Fish body size had a significantly negative effect on the survival of tadpoles. Larger fish consumed a larger number and proportion of tadpoles as well as greater biomass. These results indicate that environmental factors affecting the growth rate of tadpoles cand dramatically alter their vulnerability to gape-limited predators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford RA (1986) Effects of parentage on competitive ability and vulnerability to predation in Hyla chrysoscelis tadpoles. Oecologia (Berlin) 68:199–204
Arnold SJ, Wassersug RJ (1978) Differential predation on meta-morphic anurans by garter snake (Thamnophis): Social behavior as a possible defense. Ecology 59:1014–1022
Baumann PC, Kitchell JF (1974) Diel patterns of distribution and feeding of bluegill Lepomis macrochirus in Lake Wingra, Wisconsin. Trans Amer Fish Soc 103:255–260
Berven KA (1981) Mate choice in the wood frog, Rana sylvatica. Evolution 35:707–722
Berven KA (1982) The genetic basis of altitudinal variation in the wood frog, Rana sylvatica. I. An experimental analysis of life history traits. Evolution 36:962–983
Brodie ED Jr, Formanowicz DR Jr, Brodie ED III (1978) The development of noxiousness of Bufo americanus tadpoles to aquatic insect predators. Herpetologica 34:302–306
Caldwell JP, Thorp JH, Jervey TO (1980) Predator-prey relationships among larval dragonflies, salamanders, and frogs. Oecologia (Berlin) 46:285–289
Charlesworth B (1980) Evolution in age structured populations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Cochran WG, Cox GM (1957) Experimental designs. 2nd ed. John Wiley and Sons, New York, New York, USA
Cooke AS (1974) Differential predation by newts on anuran tadpoles. British J Herpetol 5:386–390
Cronin JT, Travis J (1986) Size-limited predation on larval Rana areolata (Anura: Ranidae) by two species of backswimmer (Insecta: Hemiptera: Notonectidae). Herpetologica 42:171–174
Crump ML (1984) Ontogenetic changes in vulnerability to predator-prey in tadpoles of Hyla pseudopuma. Herpetologica 40:265–271
Emlen JM (1970) Age specificity and ecological theory. Ecology 51:588–601
Formanowicz DR Jr (1986) Anuran tadpole/aquatic insect predator-prey interactions: tadpole size and predator capture success. Herpetologica 42:367–373
Formanowicz DR Jr, Brodie EB Jr (1982) Relative palatabilities of members of a larval amphibian community. Copeia 1982:91–97
Godwin GJ, Roble SM (1983) Mating success in male treefrogs, Hyla chrysoscelis (Anura: Hylidae). Herpetologica 39:141–146
Hall DJ, Werner EE (1977) Seasonal distribution and abundance of fishes in the littoral zone of a Michigan lake. Trans Am Fish Soc 106:545–555
Heyer WR, McDiarmid RW, Weigmann DL (1975) Tadpoles, predation and pond habitats in the tropics. Biotropica 7:100–111
Howard RD (1980) Mating behavior and mating success in wood-frogs, Rana sylvatica. Anim Behav 28:705–716
Howard RD (1983) Sexual selection and variation in reproductive success in a long-lived organism. Am Nat 122:301–325
Huey RB (1980) Sprint velocity of tadpoles (Bufo boreas) through metamorphosis. Copeia 1980:537–540
Kaplan RH, Salthe SN (1979) The allometry of reproduction: an empirical view in salamanders. Am Nat 113:671–689
Keast A, Welch L (1968) Daily feeding periodicities, food uptake rates, and some dietary changes with hour of the day in some lake fishes. J Fish Res Board Can 25:1113–1114
King CE, Anderson WW (1971) Age specific selection. II. The interaction between r-and K-during population growth. Am Nat 105:137–156
Liem KF (1961) On the taxonimic status and the granular patches of the Javanese frog Rana chalconota. Herpetologica 17:69–71
Michod RE (1979) Evolution of life histories in response to agespecific mortality factors. Am Nat 113:531–550
Morin PJ (1986) Interations between intraspecific competition and predation in an amphibian predator-prey system. Ecology 67:713–720
Salthe SN (1969) Reproductive modes and the number and sizes of ova in the urodeles. Am Midl Nat 81:467–490
Schaffer WM (1974) Selection for optimal life histories: the effects of age structure. Ecology 55:291–303
Smith DC (1983) Factors controlling tadpole populations of the chorus frog (Pseudacris triseriata) on Isle Royale, Michigan. Ecology 64:501–510
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical methods. 7th ed. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, USA
Thompson DJ (1975) Towards a predator-prey model incorporating age structure: the effects of predator and prey size on the predation of Daphnia magna by Ischnura elegans. J Anim Ecol 44:907–916
Travis J (1980) Genetic variation for larval specific growth rate in the frog Hyla gratiosa. Growth 44:167–181
Travis J (1981) The control of larval growth variation in a population of Pseudacris triseriata (Anura: Hylidae). Evolution 35:423–432
Travis J (1983) Variation in growth and survival of Hyla gratiosa larvae in experimental enclosures. Copeia 1983:232–237
Travis J, Keen WH, Juiliana J (1985a) The role of relative body size in a predator-prey relationship between dragonfly naiads and larval anurans. Oikos 45:59–65
Travis J, Keen WH, Juiliana J (1985b) The effect of multiple factors on viability selection in Hyla gratiosa tadpoles. Evolution 39:1087–1099
Turnipseed G, Altig R (1975) Population density and age structure of three species of hylid tadpoles. J Herpetol 9:287–291
Verrell PA (1982) Male newts prefer large females as mates. Anim Behav 30:1254–1255
Werner EF, Gilliam JF, Hall DJ, Mittelbach GG (1983) An experimental test of the effects of predation risk on habitat use in fish. Ecology 64:1540–1548
Wilbur HM (1980) Complex life cycles. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 11:67–93
Wilbur HM, Alford RA (1985) Priority effects in experimental communities: response of Hyla to Bufo and Rana. Ecology 66:1106–1114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semlitsch, R.D., Gibbons, J.W. Fish predation in size-structured populations of treefrog tadpoles. Oecologia 75, 321–326 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376932
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376932